
Concept explainers
Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
(a) The reaction of aluminum and iron(III) oxide to form iron and aluminum oxide (known as the thermite reaction).
(b) The reaction of carbon and water at high temperature to form a mixture of gaseous CO and H2 (known as water gas and once used as a fuel).
(c) The reaction of liquid silicon tetrachloride and magnesium forming silicon and magnesium chloride. This is one step in the preparation of ultrapure silicon used in the semiconductor industry
(a)
Interpretation:
The balanced chemical equation for given reaction should be written.
Concept introduction:
The law of conservation of mass states that no atoms can be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, therefore, the number of atoms present in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms present in the products.
Answer to Problem 1PS
Aluminium and iron(III) oxide reacts together and produces liquid iron and aluminum oxide which is highly exothermic reaction. The balanced equation is given below.
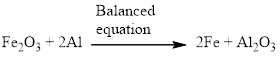
Explanation of Solution
Aluminium and iron(III) oxide reacts together and produces liquid iron and aluminum oxide which is highly exothermic reaction. The unbalanced equation is given below using correct molecular formula, the given reaction aluminium reduces the oxide of iron.

Balance the aluminum atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients.
There is one aluminium in the left side and two aluminium in the right side. Therefore according to the aluminium atom the balanced equation is given below.

Next, balance the iron atom in the equation, there are two iron atom in the left side and one iron atom in right side. For the balancing the iron atom, two molecules of iron is added to the right side. Therefore according to the iron atom the balanced equation is given below.

Now the equation is balanced, therefore the balanced equation is given below,
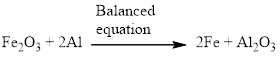
(b)
Interpretation:
The balanced chemical equation for given reaction should be written.
Concept introduction:
The law of conservation of mass states that no atoms can be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, therefore, the number of atoms present in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms present in the products.
Answer to Problem 1PS
The balanced equation is given below (b)

Explanation of Solution
Carbon monoxide reacts with water vapor which forms the carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen is called as water gas. This reaction is called as water-gas shift reaction (WGSR).
The unbalanced equation is given below using correct molecular formula, the given reaction Carbon monoxide reacts with water vapor which forms the carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and therefore the balanced equation is given below,

(c)
Interpretation:
The balanced chemical equation for given reaction should be written.
Concept introduction:
The law of conservation of mass states that no atoms can be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, therefore, the number of atoms present in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms present in the products.
Answer to Problem 1PS
Silicon tetrachloride and magnesium reacts together and produces silicon and magnesium chloride. The balanced equation is given below (c)
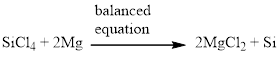
Explanation of Solution
Silicon tetrachloride and magnesium reacts together and produces silicon and magnesium chloride. The unbalanced equation is given below using correct molecular formula,
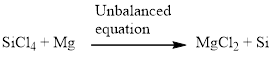
Balance the magnesium atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients.
There is one magnesium atom in the left side and one magnesium in the right side. Therefore according to the magnesium there is no change in the equation. The balanced equation is given below.
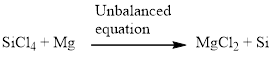
Next, balance the silicon atom in the equation, there is one silicon atom in the left side and one silicon atom in right side. Therefore according to the silicon atom the balanced equation is given below.
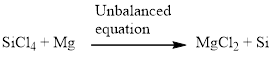
Next, balance the chlorine atom in the equation, there is four chlorine atom in the left side and two chlorine atom in the right side. Therefore 2 molecules of magnesium chloride is added to the right side of the reaction. When changing the magnesium chloride the number of magnesium is also changed therefore two molecules of magnesium is added to the left side of the reaction.
Now the equation is balanced, therefore the balanced equation is given below,
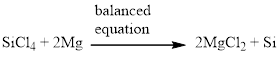
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- We discussed the solid phase resin using in peptide synthesis. Provide a mechanism, for its formation. DRAW THE MECHANISM.arrow_forwardPlease help. Every time I've asked an expert in the past, it's been wrong :(arrow_forwardPlease help everysingle time ive asked in the past, the solution has been wrongarrow_forward
- Please helparrow_forward(a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





