
Concept explainers
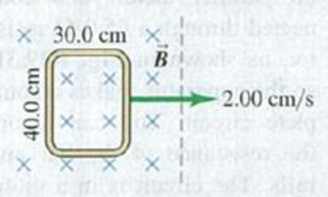
A rectangle measuring 30.0 cm by 40.0 cm is located inside a region of a spatially uniform magnetic field of 1.25 T, with the field perpendicular to the plane of the coil (Fig. E29.26). The coil is pulled out at a steady rate of 2.00 cm/s traveling perpendicular to the field lines. The region of the field ends abruptly as shown. Find the emf induced in this coil when it is (a) all inside the field; (b) partly inside the field; (c) all outside the field.
Figure E29.26
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 29 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
College Physics
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- The bar in Figure OQ23.10 moves on rails to the right with a velocity v, and a uniform, constant magnetic field is directed out of the page. Which of the following statements are correct? More than one statement may be correct. (a) The induced current in the loop is zero. (b) The induced current in the loop is clockwise. (c) The induced current in the loop is counterclockwise. (d) An external force is required to keep the bar moving at constant speed. (e) No force is required to keep the bar moving at constant speed.arrow_forwardDesign a current loop that, when rotated in a uniform magnetic field of strength 0.10 T, will produce an emf =0 sin t. where 0=110V and 0=110V .arrow_forwardA circular loop of wire with a radius of 4.0 cm is in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.060 T. The plane of the loop is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. In a time interval of 0.50 s, the magnetic field changes to the opposite direction with a magnitude of 0.040 T. What is the magnitude of the average emf induced in the loop? (a) 0.20 V (b) 0.025 V (c) 5.0 mV (d) 1.0 mV (e) 0.20 mVarrow_forward
- A rectangular conducting loop with dimensions w = 32.0 cm and h = 78.0 cm is placed a distance a = 5.00 cm from a long, straight wire carrying current I = 7.00 A in the downward direction (Fig. P32.75). a. What is the magnitude of the magnetic flux through the loop? b. If the current in the wire is increased linearly from 7.00 A to 15.0 A in 0.230 s, what is the magnitude of the induced emf in the loop? c. What is the direction of the current that is induced in the loop during this time interval?arrow_forwardFigure P23.58 is a graph of the induced emf versus time for a coil of N turns rotating with angular speed ω in a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular to the coil’s axis of rotation. What If? Copy this sketch (on a larger scale) and on the same set of axes show the graph of emf versus t (a) if the number of turns in the coil is doubled, (b) if instead the angular speed is doubled, and (c) if the angular speed is doubled while the number of turns in the coil is halved. Figure P23.58arrow_forwardTwo frictionless conducting rails separated by l = 55.0 cm are connected through a 2.00- resistor, and the circuit is completed by a bar that is free to slide on the rails (Fig. P32.71). A uniform magnetic field of 5.00 T directed out of the page permeates the region, a. What is the magnitude of the force Fp that must be applied so that the bar moves with a constant speed of 1.25 m/s to the right? b. What is the rate at which energy is dissipated through the 2.00- resistor in the circuit?arrow_forward
- A Figure P32.74 shows an N-turn rectangular coil of length a and width b entering a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude Bout directed out of the page. The velocity of the coil is constant and is upward in the figure. The total resistance of the coil is R. What are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the coil a. when only a portion of the coil has entered the region with the field, b. when the coil is completely embedded in the field, and c. as the coil begins to exit the region with the field?arrow_forwardA 500-turn coil with a 0.250m2 area is spun in Earth’s 5.00105T magnetic field, producing a 12.0-kV maximum emf. (a) As what angular velocity must the coil be spun? (b) What is unreasonable about this result? (c) Which assumption or premise is responsible?arrow_forwardReview. Figure P31.31 shows a bar of mass m = 0.200 kg that can slide without friction on a pair of rails separated by a distance = 1.20 m and located on an inclined plane that makes an angle = 25.0 with respect to the ground. The resistance of the resistor is R = 1.00 and a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.500 T is directed downward, perpendicular to the ground, over the entire region through which the bar moves. With what constant speed v does the bar slide along the rails?arrow_forward
- A flat, square coil of 20 turns that has sides of length 15.0 cm is rotating in a magnetic field of strength 0.050 T. If tlie maximum emf produced in die coil is 30.0 mV, what is the angular velocity of the coil?arrow_forwardA coil with a self-inductance of 3.0 H and a resistance of 100 2 carries a steady current of 2.0 A. (a) What is the energy stored in the magnetic field of the coil? (b) What is the energy per second dissipated in the resistance of the coil?arrow_forwardA metal bar of length 25 cm is placed perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of strength 3 T. (a) Determine the induced emf between the ends of the rod when it is not moving, (b) Determine the emf when the rod is moving perpendicular to its Length and magnetic field with a speed of 50 cm/s.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





