
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The given cyclic monosaccharide is to be converted into its acyclic form.
Concept introduction: The structural representation of sugar molecule in cyclic form is known as Haworth projection. Sugar molecule that has six-membered-ring is known as pyranose and sugar molecule that has five-membered-ring is called furanose. In Fischer projection formula, the horizontal and vertical line represents the bonds that are present above and below the plane, respectively. The verticals bonds are represented as dashed wedge and horizontal bonds as dark wedge.
Answer to Problem 28.47P
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is,
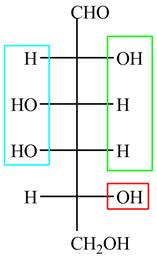
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The given cyclic monosaccharide is,
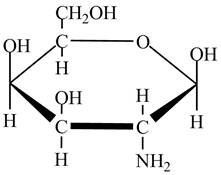
Figure 2
The steps for the conversion of Haworth projection into Fischer projection are as follow:
Step 1 In the Haworth projection, if
Step-2 The substituents which are present below the ring in the Haworth projection are drawn on the right side in the Fischer projection. Similarly, the substituents which are present above the ring in the Haworth projection are drawn on the left side in the Fischer projection.
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is,
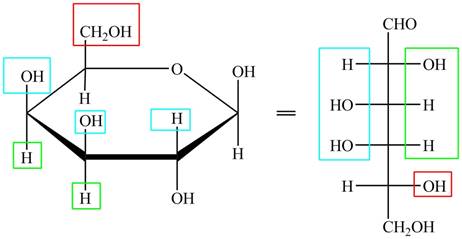
Figure 3
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The given cyclic monosaccharide is to be converted into its acyclic form.
Concept introduction: The structural representation of sugar molecule in cyclic form is known as Haworth projection. Sugar molecule that has six-membered-ring is known as pyranose and sugar molecule that has five-membered-ring is called furanose. In Fischer projection formula, the horizontal and vertical line represents the bonds that are present above and below the plane, respectively. The verticals bonds are represented as dashed wedge and horizontal bonds as dark wedge.
Answer to Problem 28.47P
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is,
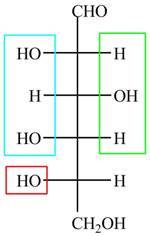
Figure 4
Explanation of Solution
The given cyclic monosaccharide is,
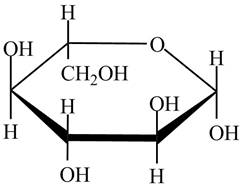
Figure 5
The steps for the conversion of Haworth projection into Fischer projection are as follow:
Step 1 In the Haworth projection, if
Step-2 The substituents which are present below the ring in the Haworth projection are drawn on the right side in the Fischer projection. Similarly, the substituents which are present above the ring in the Haworth projection are drawn on the left side in the Fischer projection.
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is,
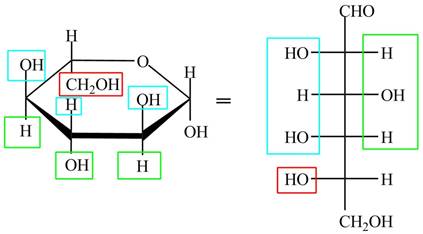
Figure 6
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is shown in Figure 4.
(c)
Interpretation: The given cyclic monosaccharide is to be converted into its acyclic form.
Concept introduction: In Fischer projection formula, the horizontal and vertical line represents the bonds that are present above and below the plane, respectively. The verticals bonds are represented as dashed wedge and horizontal bonds as dark wedge.
Answer to Problem 28.47P
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is,
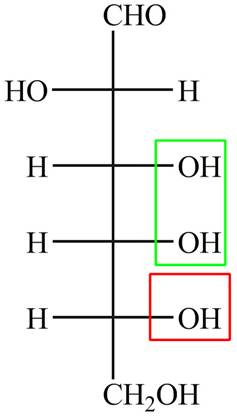
Figure 7
Explanation of Solution
The given cyclic monosaccharide is,
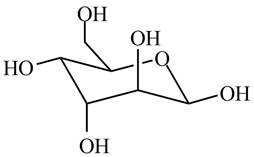
Figure 8
In the chair form, if the
The substituents on a carbon are present above the plane (i.e. either equatorial or axial position) in chair form are drawn to left side in the Fischer projection and vice versa.
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is shown below.
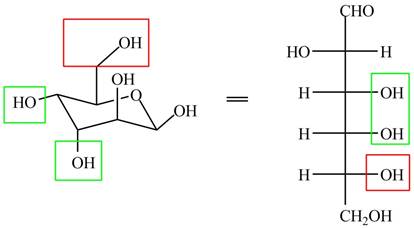
Figure 9
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is shown in Figure 7.
(d)
Interpretation: The given cyclic monosaccharide is to be converted into its acyclic form.
Concept introduction: The structural representation of sugar molecule in cyclic form is known as Haworth projection. Sugar molecule that has six-membered-ring is known as pyranose and sugar molecule that has five-membered-ring is called furanose. In Fischer projection formula, the horizontal and vertical line represents the bonds that are present above and below the plane, respectively. The verticals bonds are represented as dashed wedge and horizontal bonds as dark wedge.
Answer to Problem 28.47P
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is,
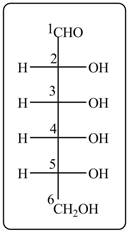
Figure 10
Explanation of Solution
The given cyclic monosaccharide is,
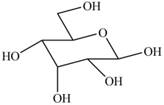
Figure 11
The steps for the conversion of Haworth projection into Fischer projection are as follow:
Step 1 In the Haworth projection, if
Step-2 The substituents which are present below the ring in the Haworth projection are drawn on the right side in the Fischer projection. Similarly, the substituents which are present above the ring in the Haworth projection are drawn on the left side in the Fischer projection.
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is,
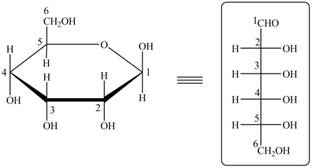
Figure 12
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is shown in Figure 10.
(e)
Interpretation: The given cyclic monosaccharide is to be converted into its acyclic form.
Concept introduction: The structural representation of sugar molecule in cyclic form is known as Haworth projection. Sugar molecule that has six-membered-ring is known as pyranose and sugar molecule that has five-membered-ring is called furanose. In Fischer projection formula, the horizontal and vertical line represents the bonds that are present above and below the plane, respectively. The verticals bonds are represented as dashed wedge and horizontal bonds as dark wedge.
Answer to Problem 28.47P
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is,
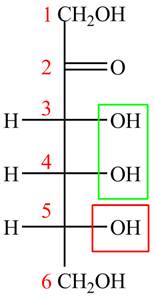
Figure 13
Explanation of Solution
The given cyclic monosaccharide is,
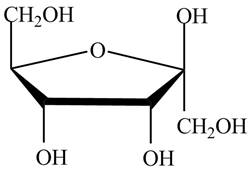
Figure 14
The steps for the conversion of Haworth projection into Fischer projection are as follow:
Step 1 In the Haworth projection, if
Step-2 The substituents which are present below the ring in the Haworth projection are drawn on the right side in the Fischer projection. Similarly, the substituents which are present above the ring in the Haworth projection are drawn on the left side in the Fischer projection.
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is,
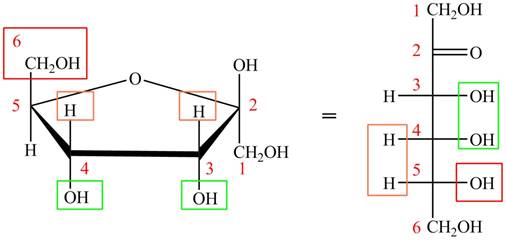
Figure 15
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is shown in Figure 13.
(f)
Interpretation: The given cyclic monosaccharide is to be converted into its acyclic form.
Concept introduction: The structural representation of sugar molecule in cyclic form is known as Haworth projection. Sugar molecule that has six-membered-ring is known as pyranose and sugar molecule that has five-membered-ring is called furanose. In Fischer projection formula, the horizontal and vertical line represents the bonds that are present above and below the plane, respectively. The verticals bonds are represented as dashed wedge and horizontal bonds as dark wedge.
Answer to Problem 28.47P
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is,
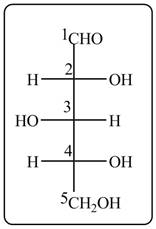
Figure 16
Explanation of Solution
The given cyclic monosaccharide is,
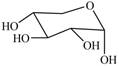
Figure 17
The steps for the conversion of Haworth projection into Fischer projection are as follow:
Step 1 In the Haworth projection, if
Step-2 The substituents which are present below the ring in the Haworth projection are drawn on the right side in the Fischer projection. Similarly, the substituents which are present above the ring in the Haworth projection are drawn on the left side in the Fischer projection.
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is,
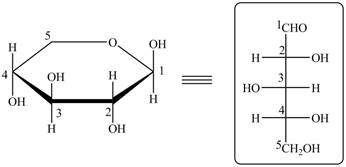
Figure 18
The acyclic form of given cyclic monosaccharide is shown in Figure 16.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- State the products (formulas) of the reaction of acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardExplanation Check Draw the skeletal ("line") structure of 5-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-pentanone. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cer ☐ : Carrow_forward1. Using a Model set Build a model for the following compound [CH2BrCI]. 2. Build another model of the mirror image of your first molecule. 3. Place the two models next to each other and take a picture which shows the differences between the two models. 4. Determine the absolute stereochemistry R or S for the two models. 5. Write or type a paragraph to Discuss the stereochemical relationship between the two models of CH2BrCl. You must provide an explanation for your conclusions also provide a description for the colors used to represent each atom in the model's images.arrow_forward
- What parameters are included in the specific rotation calculation of a pure substance based on measurement from a polarimeter? Select one or more: Density of the sample Pathlength of the sample container Enantiomeric excess of the sample Measured rotation of lightarrow_forwardV Determine whether the following molecule is a hemiacetal, acetal, or neither and select the appropriate box below. Also, highlight the hemiacetal or acetal carbon if there is one. Explanation O CH O Ohemiacetal Oacetal Oneither Check A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Cer 000 Ararrow_forward1. Using Online resources and chemical structures hand draw four different organic compounds (not those already shown in your handout) that are chiral, optically active (a pair of enantiomers will count as one). Pay attention to correct stereochemistry 2. Write or type a short paragraph to Discuss the stereochemical relationship between the four compounds.arrow_forward
- 1. Using a Model set Build a model for the following compound [CHBRIF] 2. Build another model of the mirror image of your first molecule. 3. Place the two models next to each other and take a picture which shows the differences between the two models. 4. Determine the absolute stereochemistry R or S for the two models. 5. Write or type a paragraph to Discuss the stereochemical relationship between the two models of CHBгCIF. You must provide an explanation for your conclusions also provide a description for the colors used to representarrow_forwardThe specific rotation of a sample depends upon measured angle of rotation, the density of the sample, and the pathway length of the light. True Falsearrow_forwardConsider the molecule A,B, C and D shown below, (1 x 4) Br NH2 A OH Br 边 H B C D 1. Assign the R/S configuration to each chiral center and identify by circling all the chiral centers. 2. Draw an image for the enantiomer of each of the compounds A, B, C and D.arrow_forward
- Could you crystallize one enantiomer of mandelic acid from a racemic mixture (using the typical achiral solvents found in our lab) without preparing a diastereomeric salt? Why or why not? No, because both enantiomers have the same solubility in achiral solvents. than the other. ооо Yes, because one enantiomer has a higher melting point No, because both enantiomers are liquids. Yes, because one enantiomer is more crystalline than the other.arrow_forwardIf the literature value of specific rotation for a chiral compound is -53.6°, what is the enantiomeric excess of a compound with a measured specific rotation of -40.5°?arrow_forwardThe process to determine the configuration, starts by placing the lowest priority substituent toward the back. If the substituents pointing forward decrease in priority in a clockwise order, the configuration is S. If the substituents decrease in priority in a counterclockwise order, the configuration is R. True Falsearrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





