
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321879721
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 25, Problem 4P
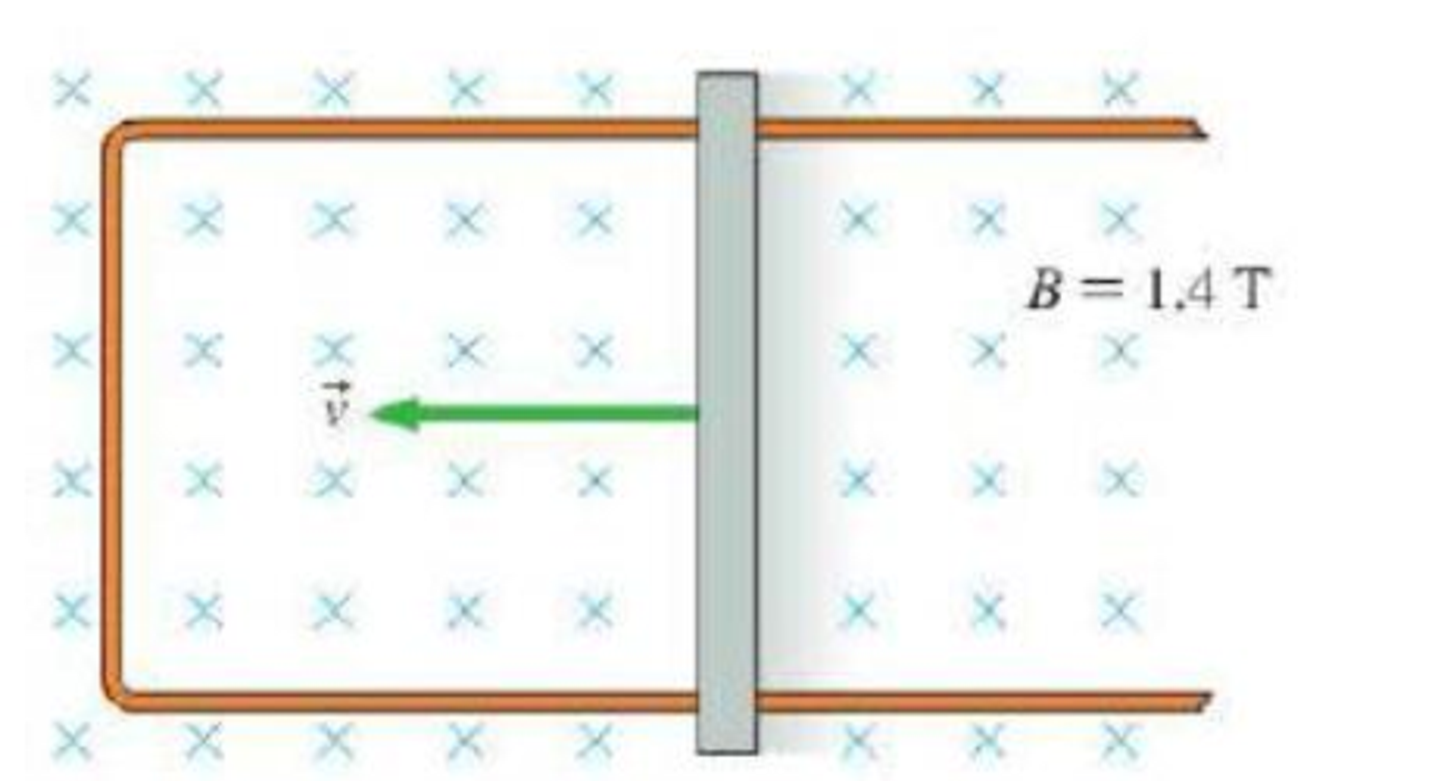
Figure P25.4 shows a 15-cm-long metal rod pulled along two frictionless,
a. What is the current induced in the rod?
b. What force is required to keep the rod moving at a constant speed?
FIGURE P25.4
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
i need step by step clear answers with the free body diagram clearly
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Review the data in Data Table 1 and examine the standard deviations and 95% Margin of Error calculations from Analysis Questions 3 and 4 for the Acceleration of the 1st Based on this information, explain whether Newton’s Second Law of Motion, Equation 1, was verified for your 1st Angle.
Equation: SF=ma
Please help with explaining the information I collected from a lab and how it relates to the equation and Newton's Second Law. This will help with additional tables in the lab. Thanks!
Chapter 25 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 25 - Prob. 1CQCh. 25 - The rapid vibration accompanying the swimming...Ch. 25 - Prob. 3CQCh. 25 - Prob. 4CQCh. 25 - Prob. 5CQCh. 25 - Prob. 6CQCh. 25 - The power lines that run through your neighborhood...Ch. 25 - The magnetic flux passing through a coil of wire...Ch. 25 - There is a counterclockwise induced current in the...Ch. 25 - A magnet dropped through a clear plastic tube...
Ch. 25 - The conducting loop in Figure Q25.11 is moving...Ch. 25 - Figure Q25.12 shows two concentric, conducting...Ch. 25 - Figure Q25.13 shows conducting loops next to each...Ch. 25 - Two loops of wire are stacked vertically, one...Ch. 25 - Prob. 15CQCh. 25 - A bar magnet is pushed toward a loop of wire, as...Ch. 25 - Prob. 17CQCh. 25 - A metal wire is resting on a U-shaped conducting...Ch. 25 - Prob. 19CQCh. 25 - Old-fashioned roof-mounted television antennas...Ch. 25 - An AM radio detects the oscillating magnetic field...Ch. 25 - Prob. 22CQCh. 25 - Prob. 23CQCh. 25 - The frequency of a beam of light is increased but...Ch. 25 - Arc welding uses electric current to make an...Ch. 25 - A circular loop of wire has an area of 0.30 m2. It...Ch. 25 - In Figure Q25.27, a square loop is rotating in the...Ch. 25 - A diamond-shaped loop of wire is pulled at a...Ch. 25 - Figure Q25.29 shows a triangular loop of wire in a...Ch. 25 - A device called a flip coil can be used to measure...Ch. 25 - The electromagnetic waves that carry FM radio...Ch. 25 - The beam from a laser is focused with a lens,...Ch. 25 - A spacecraft in orbit around the moon measures its...Ch. 25 - A 6.0 mW vertically polarized laser beam passes...Ch. 25 - Communication with submerged submarines via radio...Ch. 25 - Prob. 36MCQCh. 25 - Prob. 1PCh. 25 - Prob. 2PCh. 25 - A l0-cm-long wire is pulled along a U-shaped...Ch. 25 - Figure P25.4 shows a 15-cm-long metal rod pulled...Ch. 25 - Prob. 5PCh. 25 - In the rainy season, the Amazon flows fast and...Ch. 25 - A delivery truck with 2.8-m-high aluminum sides is...Ch. 25 - Prob. 8PCh. 25 - Prob. 9PCh. 25 - Prob. 10PCh. 25 - Prob. 11PCh. 25 - At a typical location in the United States, the...Ch. 25 - Prob. 13PCh. 25 - A magnet and a coil are oriented as shown in...Ch. 25 - A 1000-turn coil of wire 2.0 cm in diameter is in...Ch. 25 - Figure P25.I6 shows a 100-turn coil of wire of...Ch. 25 - Figure P25.17 shows a 10-cm-diameter loop in three...Ch. 25 - The plane of a loop of wire is perpendicular to a...Ch. 25 - Prob. 19PCh. 25 - Prob. 20PCh. 25 - Prob. 21PCh. 25 - A 5.0-cm-diameter loop of wire has resistance 1.2...Ch. 25 - Prob. 23PCh. 25 - Prob. 24PCh. 25 - Prob. 25PCh. 25 - Prob. 26PCh. 25 - A microwave oven operates at 2.4 GHz with an...Ch. 25 - The maximum allowed leakage of microwave radiation...Ch. 25 - Prob. 29PCh. 25 - Prob. 30PCh. 25 - At what distance from a 10 mW point source of...Ch. 25 - Prob. 32PCh. 25 - A radio antenna broadcasts a 1.0 MHz radio wave...Ch. 25 - A 200 MW laser pulse is focused with a lens to a...Ch. 25 - The intensity of a polarized electromagnetic wave...Ch. 25 - Prob. 36PCh. 25 - Prob. 37PCh. 25 - Prob. 38PCh. 25 - The polarization of a helium-neon laser can change...Ch. 25 - Prob. 40PCh. 25 - Prob. 41PCh. 25 - Prob. 42PCh. 25 - One recent study has shown that x rays with a...Ch. 25 - Prob. 44PCh. 25 - Prob. 45PCh. 25 - Prob. 46PCh. 25 - Prob. 47PCh. 25 - Prob. 48PCh. 25 - Prob. 49PCh. 25 - A particular species of copepod, a small marine...Ch. 25 - Prob. 51PCh. 25 - Prob. 52PCh. 25 - While using a dimmer switch to investigate a new...Ch. 25 - Prob. 54PCh. 25 - Prob. 55PCh. 25 - A python can detect thermal radiation with...Ch. 25 - If astronomers look toward any point in outer...Ch. 25 - A 100-turn, 2.0-cm diameter coil is at rest in a...Ch. 25 - A 25-turn, 10.0-cm-diameter coil is oriented in a...Ch. 25 - People immersed in strong unchanging magnetic...Ch. 25 - Prob. 61GPCh. 25 - Prob. 62GPCh. 25 - A 20-cm-long, zero-resistance wire is pulled...Ch. 25 - A TMS (transeranial magnetic stimulation) device...Ch. 25 - The 10-cm-wide, zero-resistance wire shown in...Ch. 25 - Experiments to study vision often need to track...Ch. 25 - A LASIK vision correction system uses a laser that...Ch. 25 - When the Voyager 2 spacecraft passed Neptune in...Ch. 25 - A new cordless phone emits 4.0 mW at 5.8 GHz. The...Ch. 25 - In reading the instruction manual that came with...Ch. 25 - Unpolarized light passes through a vertical...Ch. 25 - Prob. 73GPCh. 25 - Prob. 74GPCh. 25 - What is the wavelength of 27 MHz radio waves? A....Ch. 25 - If the frequency of the radio waves is increased,...Ch. 25 - Prob. 77MSPPCh. 25 - The metal detector will not detect insulators...Ch. 25 - A metal detector can detect the presence of metal...Ch. 25 - Which of the following changes would not produce a...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What is the difference between cellular respiration and external respiration?
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
29. Consider the unbalanced equation for the reaction of solid lead with silver nitrate:
a. Balance the equati...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
The enzyme that catalyzes the C C bond cleavage reaction that converts serine to glycine removes the substitue...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 using a Born-Haber cycle and data from Appendices F and L and Table 7.5. ...
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
27. Consider the reaction.
Express the rate of the reaction in terms of the change in concentration of each of...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Plants use the process of photosynthesis to convert the energy in sunlight to chemical energy in the form of su...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvote instantarrow_forwardKirchoff's Laws. A circuit contains 3 known resistors, 2 known batteries, and 3 unknown currents as shown. Assume the current flows through the circuit as shown (this is our initial guess, the actual currents may be reverse). Use the sign convention that a potential drop is negative and a potential gain is positive. E₂ = 8V R₁₁ = 50 R₂ = 80 b с w 11 www 12 13 E₁ = 6V R3 = 20 a) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop abefa in the clockwise direction starting at point a. (2 pt). b) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop bcdeb in the clockwise direction starting at point b. (2 pt). c) Apply Kirchoff's Junction Rule at junction b (1 pt). d) Solve the above 3 equations for the unknown currents I1, 12, and 13 and specify the direction of the current around each loop. (5 pts) I1 = A 12 = A 13 = A Direction of current around loop abef Direction of current around loop bcde (CW or CCW) (CW or CCW)arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 4.) The diagram shows the electric field lines of a positively charged conducting sphere of radius R and charge Q. A B Points A and B are located on the same field line. A proton is placed at A and released from rest. The magnitude of the work done by the electric field in moving the proton from A to B is 1.7×10-16 J. Point A is at a distance of 5.0×10-2m from the centre of the sphere. Point B is at a distance of 1.0×10-1 m from the centre of the sphere. (a) Explain why the electric potential decreases from A to B. [2] (b) Draw, on the axes, the variation of electric potential V with distance r from the centre of the sphere. R [2] (c(i)) Calculate the electric potential difference between points A and B. [1] (c(ii)) Determine the charge Q of the sphere. [2] (d) The concept of potential is also used in the context of gravitational fields. Suggest why scientists developed a common terminology to describe different types of fields. [1]arrow_forward3.) The graph shows how current I varies with potential difference V across a component X. 904 80- 70- 60- 50- I/MA 40- 30- 20- 10- 0+ 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 VIV Component X and a cell of negligible internal resistance are placed in a circuit. A variable resistor R is connected in series with component X. The ammeter reads 20mA. 4.0V 4.0V Component X and the cell are now placed in a potential divider circuit. (a) Outline why component X is considered non-ohmic. [1] (b(i)) Determine the resistance of the variable resistor. [3] (b(ii)) Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit. [1] (c(i)) State the range of current that the ammeter can measure as the slider S of the potential divider is moved from Q to P. [1] (c(ii)) Describe, by reference to your answer for (c)(i), the advantage of the potential divider arrangement over the arrangement in (b).arrow_forward1.) Two long parallel current-carrying wires P and Q are separated by 0.10 m. The current in wire P is 5.0 A. The magnetic force on a length of 0.50 m of wire P due to the current in wire Q is 2.0 × 10-s N. (a) State and explain the magnitude of the force on a length of 0.50 m of wire Q due to the current in P. [2] (b) Calculate the current in wire Q. [2] (c) Another current-carrying wire R is placed parallel to wires P and Q and halfway between them as shown. wire P wire R wire Q 0.05 m 0.05 m The net magnetic force on wire Q is now zero. (c.i) State the direction of the current in R, relative to the current in P.[1] (c.ii) Deduce the current in R. [2]arrow_forward
- 2.) A 50.0 resistor is connected to a cell of emf 3.00 V. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the circuit are ideal. V A 50.00 (a) The current in the ammeter is 59.0 mA. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell. The circuit is changed by connecting another resistor R in parallel to the 50.0 resistor. V A 50.00 R (b) Explain the effect of this change on R is made of a resistive wire of uniform cross-sectional area 3.1 × 10-8 m², resistivity 4.9 × 10-70m and length L. The resistance of R is given by the equation R = KL where k is a constant. (b.i) the reading of the ammeter. [2] (b.ii) the reading of the voltmeter. [2] (c) Calculate k. State an appropriate unit for your answer. [3] [2]arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What is Electromagnetic Induction? | Faraday's Laws and Lenz Law | iKen | iKen Edu | iKen App; Author: Iken Edu;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3HyORmBip-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY