
(a)
Interpretation:
The reason for the isotope
Concept introduction:
The binding energy is defined as the energy required for breaking 1 mol of any nuclei into its individual nucleons.
Explanation of Solution
The graph is represented as follows:
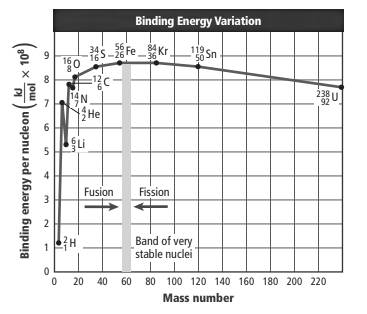
The above graph shows a change in binding energy per nucleon with an increase in mass numbers.
This can be seen from the graph that isotope
The binding energy is defined as the energy required breaking 1 mol of any nuclei into its individual nucleons. If the binding energy per nucleon is large, the force by which the nucleons are held together will be strong and the nucleus will be more stable. The binding energy per nucleon is lower for less stable atoms.
Here, the element with a mass number near 60 is most stable and it has maximum binding energy per nucleon.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether more stable isotopes are located higher or lower on the curve needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The binding energy is defined as the energy required breaking 1 mol of any nuclei into its individual nucleons. If the binding energy per nucleon is large, the force by which the nucleons are held together will be strong and nucleus will be more stable. The binding energy per nucleon is lower for less stable atoms.
Explanation of Solution
The more stable isotopes have large binding energy per nucleons. The energy increases on moving from bottom to top in the graph thus, the isotopes located higher on the curve have maximum binding energy per nucleons thus, they are more stable isotopes.
(c)
Interpretation:
The stability of Li-6 and He-4 needs to be compared.
Concept introduction:
The binding energy is defined as the energy required breaking 1 mol of any nuclei into its individual nucleons. If the binding energy per nucleon is large, the force by which the nucleons are held together will be strong and nucleus will be more stable. The binding energy per nucleon is lower for less stable atoms.
Explanation of Solution
The binding energy curve is represented as follows:
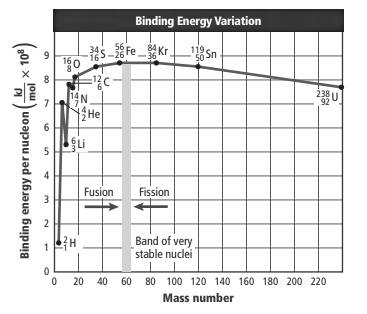
The points are represented for Li-6 and He-4. Here, mass number of Li is more than He but both are less than 60.
The binding energy per nucleon is less for Li-6 and it is approximately
Chapter 24 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- Draw the Michael adduct and final product of the Robinson annulation reaction. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardPost Lab Questions. 1) Draw the mechanism of your Diels-Alder cycloaddition. 2) Only one isomer of product is formed in the Diels-Alder cycloaddition. Why? 3) Imagine that you used isoprene as diene - in that case you don't have to worry about assigning endo vs exo. Draw the "endo" and "exo" products of the Diels-Alder reaction between isoprene and maleic anhydride, and explain why the distinction is irrelevant here. 4) This does not hold for other dienes. Draw the exo and endo products of the reaction of cyclohexadiene with maleic anhydride. Make sure you label your answers properly as endo or exo. 100 °C Xylenes ??? 5) Calculate the process mass intensity for your specific reaction (make sure to use your actual amounts of reagent).arrow_forwardIndicate the product(s) A, B C and D that are formed in the reaction: H + NH-NH-CH [A+B] [C+D] hydrazonesarrow_forward
- How can you prepare a 6 mL solution of 6% H2O2, if we have a bottle of 30% H2O2?arrow_forwardHow many mL of H2O2 from the 30% bottle must be collected to prepare 6 mL of 6% H2O2.arrow_forwardIndicate the product(s) B and C that are formed in the reaction: HN' OCH HC1 B + mayoritario C minoritario OCH3arrow_forward
- Indicate the product(s) that are formed in the reaction: NH-NH, OCH3 -H₂O OCH3arrow_forward21.38 Arrange the molecules in each set in order of increasing acidity (from least acidic to most acidic). OH OH SH NH2 8 NH3 OH (b) OH OH OH (c) & & & CH3 NO2 21.39 Explain the trends in the acidity of phenol and the monofluoro derivatives of phenol. OH OH OH OH PK 10.0 PK 8.81 PK 9.28 PK 9.81arrow_forwardidentify which spectrum is for acetaminophen and which is for phenacetinarrow_forward
- The Concept of Aromaticity 21.15 State the number of 2p orbital electrons in each molecule or ion. (a) (b) (e) (f) (c) (d) (h) (i) DA (k) 21.16 Which of the molecules and ions given in Problem 21.15 are aromatic according to the Hückel criteria? Which, if planar, would be antiaromatic? 21.17 Which of the following structures are considered aromatic according to the Hückel criteria? ---0-0 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (h) H -H .8.0- 21.18 Which of the molecules and ions from Problem 21.17 have electrons donated by a heteroatom?arrow_forward1. Show the steps necessary to make 2-methyl-4-nonene using a Wittig reaction. Start with triphenylphosphine and an alkyl halide. After that you may use any other organic or inorganic reagents. 2. Write in the product of this reaction: CH3 CH₂ (C6H5)₂CuLi H₂O+arrow_forward3. Name this compound properly, including stereochemistry. H₂C H3C CH3 OH 4. Show the step(s) necessary to transform the compound on the left into the acid on the right. Bri CH2 5. Write in the product of this LiAlH4 Br H₂C OHarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





