
(a)
Interpretation:
Hydrogen bonding between 2 water molecules should be depicted.
Concept introduction:
All types of molecules have some kind of attractive force that keeps them together. Polar molecules that have elements that are high in electro negativity like nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine directly attached to hydrogen atom, exhibit hydrogen bonding. They are held together by hydrogen bonding between molecules.
Hydrogen bonding is a special kind of dipole-dipole bond.
(a)
Answer to Problem 98A
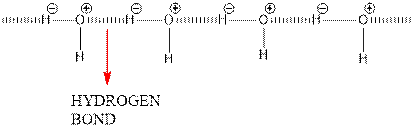
Hydrogen bonding between 2 water molecules is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
In case of
Since oxygen is electronegative centre, it can easily attract hydrogen molecule of other water molecule and hence a partial positive charge develops on it and a partial negative charge develops on hydrogen. This results in intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
(b)
Interpretation:
Hydrogen bonding between 2 ammonia molecules should be depicted.
Concept introduction:
All types of molecules have some kind of attractive force that keeps them together. Polar molecules that have elements that are high in electro negativity like nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine directly attached to hydrogen atom, exhibit hydrogen bonding. They are held together by hydrogen bonding between molecules.
Hydrogen bonding is a special kind of dipole-dipole bond.
(b)
Answer to Problem 98A
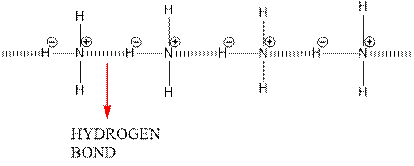
Hydrogen bonding between 2 ammonia molecules is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
In case of
Since nitrogen is electronegative centre, it can easily attract hydrogen molecule of other ammonia molecule and hence a partial positive charge develops on it and a partial negative charge develops on hydrogen. This results in intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
(c)
Interpretation:
Hydrogen bonding between water and ammonia molecules should be depicted.
Concept introduction:
All types of molecules have some kind of attractive force that keeps them together. Polar molecules that have elements that are high in electro negativity like nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine directly attached to hydrogen atom, exhibit hydrogen bonding. They are held together by hydrogen bonding between molecules.
Hydrogen bonding is a special kind of dipole-dipole bond.
(c)
Answer to Problem 98A
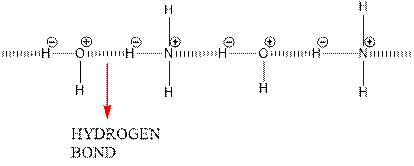
Hydrogen bonding between water and ammonia molecules is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
In case of
Similarly in case of
Since oxygen is electronegative centre, it can easily attract hydrogen molecule of other ammonia molecule and nitrogen can attract hydrogen molecules of water molecules and hence a partial positive charge develops on oxygen and nitrogen atom. A partial negative charge develops on hydrogen. This results in intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Chapter 24 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- First I wanted to see if you would mind checking my graphs behind me. (They haven't been coming out right)? Second, could you help me explain if the rate of reaction is proportional to iodide and persulfate of each graph. I highlighted my answer and understanding but I'm not sure if I'm on the right track. Thank you in advance.arrow_forwardThe heat of combustion for ethane, C2H6C2H6 , is 47.8 kJ/g. How much heat is produced if 1.65 moles of ethane undergo complete combustion?arrow_forwardReview of this week's reaction: H2NCN (cyanamide) + CH3NHCH2COOH (sarcosine) + NaCl, NH4OH, H2O ----> H2NC(=NH)N(CH3)CH2COOH (creatine) Q7. Draw by hand the reaction of creatine synthesis listed above using line structures without showing the Cs and some of the Hs, but include the lone pairs of electrons wherever they apply. (4 pts) Q8. Considering the Zwitterion form of an amino acid, draw the Zwitterion form of Creatine. (2 pts) Q9. Explain with drawing why the C—N bond shown in creatine structure below can or cannot rotate. (3 pts)arrow_forward
- Would the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forwardPlease help me answer a. Please and thank you I advance.arrow_forwardDraw both of the chair flips for both the cis and trans isomers for the following compounds: 1,4-diethylcyclohexane 1-methyl-3-secbutylcyclohexanearrow_forward
- Ppplllleeeaaasssseeee hellppp wiithhh thisss physical chemistryyyyy I talked like this because AI is very annoyingarrow_forwardFor this question, if the product is racemic, input both enantiomers in the same Marvin editor. A) Input the number that corresponds to the reagent which when added to (E)-but-2-ene will result in a racemic product. Input 1 for Cl, in the cold and dark Input 2 for Oy followed by H₂O, Zn Input 3 for D₂ with metal catalyst Input 4 for H₂ with metal catalyst B) Draw the skeletal structure of the major organic product made from the reagent in part A Marvin JS Help Edit drawing C) Draw the skeletal structure of the major organic product formed when (2)-but-2-ene is treated with peroxyacetic acid. Marvin 35 Helparrow_forwardMichael Reactions 19.52 Draw the products from the following Michael addition reactions. 1. H&C CH (a) i 2. H₂O* (b) OEt (c) EtO H₂NEt (d) ΕΙΟ + 1. NaOEt 2. H₂O' H H 1. NaOEt 2. H₂O*arrow_forward
- Rank the labeled protons (Ha-Hd) in order of increasing acidity, starting with the least acidic. НОН НЬ OHd Онсarrow_forwardCan the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? ? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C :0 T Add/Remove step Garrow_forwardThe following equations represent the formation of compound MX. What is the AH for the electron affinity of X (g)? X₂ (g) → 2X (g) M (s) → M (g) M (g) M (g) + e- AH = 60 kJ/mol AH = 22 kJ/mol X (g) + e-X (g) M* (g) +X (g) → MX (s) AH = 118 kJ/mol AH = ? AH = -190 kJ/mol AH = -100 kJ/mol a) -80 kJ b) -30 kJ c) -20 kJ d) 20 kJ e) 156 kJarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





