
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To identify
Concept introduction: Pyruvate is the end product in the glycolysis. The production of the fate of pyruvate varies with the nature of the organism and the cellular conditions. The common fates of pyruvate are as follows:
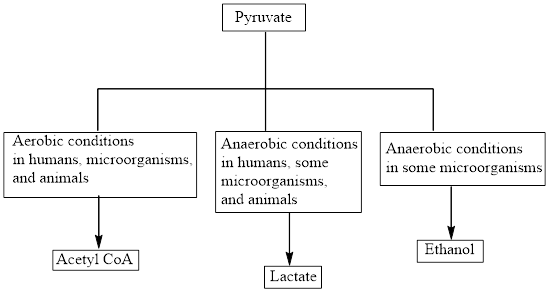
Aerobic reactions need oxygen while anaerobic reactions don’t need oxygen. Pyruvate forms
(a)
Answer to Problem 24.45EP
Carbon dioxide
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct choice:
Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to
The process of ethanol fermentation takes place in two steps. In step 1, the pyruvate molecule is converted to acetaldehyde by pyruvate decarboxylase enzymes. Carbon dioxide molecule is produced in this step. In step 2, acetaldehyde is reduced to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes. The ethanol fermentation equation is as follows:
Therefore,
Reason for incorrect choice:
The reaction equation for lactate fermentation is as follows:
(b)
Interpretation: To identify NADH is a reactant in which the fate of pyruvate-
Concept introduction: Pyruvate is the end product in the glycolysis. The production of the fate of pyruvate varies with the nature of the organism and the cellular conditions.
The common fates of pyruvate are as follows:

Aerobic reactions need oxygen while anaerobic reactions don’t need oxygen. Pyruvate forms
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is associated with the
A reactant is defined as the substance that is initially present in the
(b)
Answer to Problem 24.45EP
NADH is encountered as a reactant in the lactate and ethanol production from pyruvate.
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct choice:
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. In this reaction, NADH is oxidized to
Ethanol fermentation process occurs in some microorganisms (for example yeast) under the anaerobic conditions. The ethanol fermentation equation is as follows:
Therefore, NADH is encountered as a reactant in the lactate and ethanol production from pyruvate.
Reason for incorrect choice:
The reaction equation for the conversion of pyruvate to
Therefore, NADH is formed along with
(c)
Interpretation: To identify
Concept introduction: Pyruvate is the end product in the glycolysis. The production of the fate of pyruvate varies with the nature of the organism and the cellular conditions. The common fates of pyruvate are as follows:

Aerobic reactions need oxygen while anaerobic reactions don’t need oxygen. Pyruvate forms
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is associated with the redox reactions in metabolism. Its reduced form is NADH and oxidized form is
A reactant is defined as the substance that is initially present in the chemical reaction and gets consumed to form a new substance.
(c)
Answer to Problem 24.45EP
In the production of
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct choice:
The reaction equation for the conversion of pyruvate to
Therefore,
Reason for incorrect choice:
The reaction equation for the conversion of pyruvate to lactate is as follows:
Ethanol fermentation process occurs in some microorganisms (for example yeast) under the anaerobic conditions. The ethanol fermentation equation is as follows:
Therefore,
(d)
Interpretation: To identify the end product is a
Concept introduction: Pyruvate is the end product in the glycolysis. The production of the fate of pyruvate varies with the nature of the organism and the cellular conditions. The common fates of pyruvate are as follows:

Aerobic reactions need oxygen while anaerobic reactions don’t need oxygen. Pyruvate forms
Pyruvate
(d)
Answer to Problem 24.45EP
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct choice:
In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate is converted to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase enzymes in the human body. This anaerobic reduction is called lactate fermentation. The chemical reaction for the formation of lactate is as follows:

Lactate contains three carbon atoms. Therefore, lactate is a
Reason for incorrect choice:
In the ethanol fermentation process, pyruvate is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide by enzymes under the anaerobic conditions. The ethanol fermentation equation is as follows:
Ethanol
Pyruvate is converted to
Acetyl group
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- Including activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M KBr.arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the pH of a 0.010 M HCl solution with an ionic strength of 0.10 M.arrow_forward
- Can I please get the graph 1: Concentration vs. Density?arrow_forwardOrder the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forwardOrdene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forward
- Can I please get all final concentrations please!arrow_forwardState the detailed mechanism of the reaction of benzene with isopropanol in sulfuric acid.arrow_forwardDo not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction. For the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) · 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 -> NO2 + NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 →> N2O5 (k-1) → NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Give the expression for the acceptable rate. (A). d[N₂O] dt = -1 2k,k₂[N205] k₁+k₂ d[N₂O5] (B). dt =-k₁[N₂O₂] + k₁[NO2][NO3] - k₂[NO2]³ (C). d[N₂O] dt =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[N205] - K3 [NO] [N205] (D). d[N2O5] =-k₁[NO] - K3[NO] [N₂05] dtarrow_forward
- A 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 20.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFor the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 NO2 + NO3 (K1) | NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) | NO2 + NO3 NO2 + O2 + NO (k2) | NO + N2O51 NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) → Give the expression for the acceptable rate. → → (A). d[N205] dt == 2k,k₂[N₂O₂] k₁+k₁₂ (B). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[NO₂] [NO3] - k₂[NO₂]³ dt (C). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k [NO] - k₂[NO] [NO] d[N2O5] (D). = dt = -k₁[N2O5] - k¸[NO][N₂05] dt Do not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction.arrow_forwardFor the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 NO2 + NO3 (K1) | NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) | NO2 + NO3 NO2 + O2 + NO (k2) | NO + N2O51 NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) → Give the expression for the acceptable rate. → → (A). d[N205] dt == 2k,k₂[N₂O₂] k₁+k₁₂ (B). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[NO₂] [NO3] - k₂[NO₂]³ dt (C). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k [NO] - k₂[NO] [NO] d[N2O5] (D). = dt = -k₁[N2O5] - k¸[NO][N₂05] dt Do not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co




