
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Organic compounds are named systematically by using IUPAC rules.
Name of the organic compounds are given according to the number of carbon present in the molecule for example
A molecule having one carbon atom, the molecule name will start with meth etc.…

If any halogens are present in the molecule, the name of the halogens as follows.

Naming the substituted
- (1) Name the parent alkane (long alkyl chain)
- (2) Number the carbon
- (3) Name and number the substituent
If the molecules have the multiple substituents, the compound named as di, tri, tetra, Penta, etc.
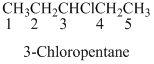
If the molecules having functional group, the name of the compound is given below. Numbering should be starts from the functional group of the given molecule.
The given compound is an alcohol
Example is given below
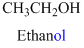

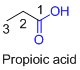
The given compound is an acid (
The amides are derivatives of acids and it is named as the ending of alkane with amide.
For example
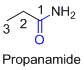
If the molecule is ester,
Esters end with “ate”
Example

The given compound is an
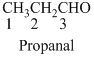
The given compound is
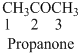
The given compound is an
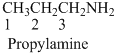
(b)
Interpretation:
The functional group should be identified for the given molecule.
Concept introduction:
Organic compounds are named systematically by using IUPAC rules.
Name of the organic compounds are given according to the number of carbon present in the molecule for example
A molecule having one carbon atom, the molecule name will start with meth etc.…

If any halogens are present in the molecule, the name of the halogens as follows.

Naming the substituted alkane:
- (4) Name the parent alkane (long alkyl chain)
- (5) Number the carbon
- (6) Name and number the substituent
If the molecules have the multiple substituents, the compound named as di, tri, tetra, Penta, etc.
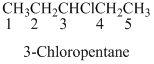
If the molecules having functional group, the name of the compound is given below. Numbering should be starts from the functional group of the given molecule.
The given compound is an alcohol
Example is given below
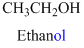

The given compound is an acid (

The amides are derivatives of acids and it is named as the ending of alkane with amide.
For example
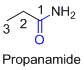
If the molecule is ester,
Esters end with “ate”
Example

The given compound is an aldehyde (
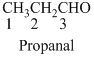
The given compound is ketone (
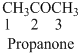
The given compound is an amine (
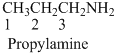
(c)
Interpretation:
The functional group should be identified for the given molecule.
Concept introduction:
Organic compounds are named systematically by using IUPAC rules.
Name of the organic compounds are given according to the number of carbon present in the molecule for example
A molecule having one carbon atom, the molecule name will start with meth etc.…

If any halogens are present in the molecule, the name of the halogens as follows.

Naming the substituted alkane:
- (7) Name the parent alkane (long alkyl chain)
- (8) Number the carbon
- (9) Name and number the substituent
If the molecules have the multiple substituents, the compound named as di, tri, tetra, Penta, etc.
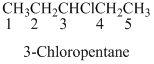
If the molecules having functional group, the name of the compound is given below. Numbering should be starts from the functional group of the given molecule.
The given compound is an alcohol
Example is given below
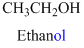

The given compound is an acid (

The amides are derivatives of acids and it is named as the ending of alkane with amide.
For example
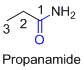
If the molecule is ester,
Esters end with “ate”
Example

The given compound is an aldehyde (
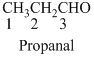
The given compound is ketone (
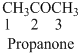
The given compound is an amine (
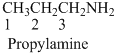
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry: Atoms First
- help draw the moleculearrow_forwardHow to draw this claisen condensation reaction mechanisms/arrow_forwardWrite all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forward
- How can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forwarddraw out these molecules pleasearrow_forward
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





