
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100257063
Author: BEER
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.3, Problem 48P
The aluminum shell is fully bonded to the brass core and the assembly is unstressed at a temperature of 15°C. Considering only axial deformations, determine the stress in the aluminum when the temperature reaches 195°C.
2.48 Solve Prob. 2.47, assuming that the core is made of steel (Es = 200GPa, αs = 11.7 × 10-6/°C) Instead of brass.
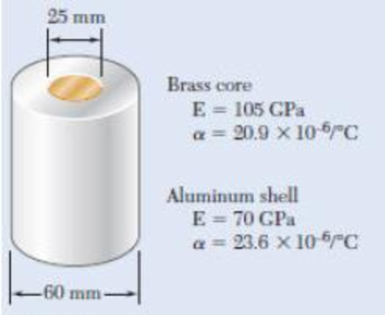
Fig. P2.47
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Sketch and desribe a balanced rudder and how it is suspended
A ship 140 m long and 18 m beam floats at a draught of9 m. The immersed cross-sectionai areas at equai intervais are 5,60, 116, 145, 152, 153, 153, 151, 142, 85 and 0 m2 respectively.Calculate:(a) displacement(b) block coefficient(c) midship section area coefficient(d) prismatic coefficient.
A steamer has waterplane area 1680m2 recorded in water with relative denisty 1.013. Displacement = 1200 t, calculate difference in draught in salwater reltive denisity 1.025.
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 2.1 - A nylon thread is subjected to a 8.5-N tension...Ch. 2.1 - A 4.8-ft-long steel wire of 14 -in.-diameter is...Ch. 2.1 - An 18-m-long steel wire of 5-mm diameter is to be...Ch. 2.1 - Two gage marks are placed exactly 250 mm apart on...Ch. 2.1 - An aluminum pipe must not stretch more than 0.05...Ch. 2.1 - A control rod made of yellow brass must not...Ch. 2.1 - A steel control rod is 5.5 ft long and must not...Ch. 2.1 - A cast-iron tube is used to support a compressive...Ch. 2.1 - A 4-m-long steel rod must not stretch more than 3...Ch. 2.1 - A nylon thread is to be subjected to a 10-N...
Ch. 2.1 - A block of 10-in. length and 1.8 1.6-in. cross...Ch. 2.1 - A square yellow-brass bar must not stretch more...Ch. 2.1 - Rod BD is made of steel (E = 29 106 psi) and is...Ch. 2.1 - The 4-mm-diameter cable BC is made of a steel with...Ch. 2.1 - A single axial load of magnitude P = 15 kips is...Ch. 2.1 - A 250-mm-long aluminum tube (E = 70 GPa) of 36-mm...Ch. 2.1 - The specimen shown has been cut from a...Ch. 2.1 - The brass tube AB (E = 105 GPa) has a...Ch. 2.1 - Both portions of the rod ABC are made of an...Ch. 2.1 - The rod ABC is made of an aluminum for which E =...Ch. 2.1 - For the steel truss (E = 200 GPa) and loading...Ch. 2.1 - For the steel truss (E = 29 106 psi) and loading...Ch. 2.1 - Members AB and BC are made of steel (E = 29 106...Ch. 2.1 - The steel frame (E = 200 GPa) shown has a diagonal...Ch. 2.1 - Link BD is made of brass (E = 105 GPa) and has a...Ch. 2.1 - Members ABC and DEF are joined with steel links (E...Ch. 2.1 - Each of the links AB and CD is made of aluminum (E...Ch. 2.1 - The length of the 332-in.-diameter steel wire CD...Ch. 2.1 - A homogenous cable of length L and uniform cross...Ch. 2.1 - The vertical load P is applied at the center A of...Ch. 2.1 - Denoting by the "engineering strain'' in a...Ch. 2.1 - The volume of a tensile specimen is essentially...Ch. 2.3 - An axial centric force of magnitude P = 450 kN is...Ch. 2.3 - An axial centric force of magnitude P = 450 kN is...Ch. 2.3 - The 4.5-ft concrete post is reinforced with six...Ch. 2.3 - The 4.5-ft concrete post is reinforced with six...Ch. 2.3 - An axial force of 200 kW is applied to the...Ch. 2.3 - The length of the assembly shown decreases by 0.40...Ch. 2.3 - A polystyrene rod consisting of two cylindrical...Ch. 2.3 - Three steel rods (E = 29 106 psi) support an...Ch. 2.3 - Fig. P2.41 2.41 Two cylindrical rods, one of steel...Ch. 2.3 - Solve Prob. 2.41, assuming that rod AC is made of...Ch. 2.3 - Each of the rods BD and CE is made of brass (E =...Ch. 2.3 - The rigid bar AD is supported by two steel wires...Ch. 2.3 - The rigid bar ABC is suspended from three wines of...Ch. 2.3 - The rigid bar AD is supported by two steel wires...Ch. 2.3 - The aluminum shell is fully bonded to the brass...Ch. 2.3 - The aluminum shell is fully bonded to the brass...Ch. 2.3 - The brass shell (b = 11.6 10-6/F) is fully bonded...Ch. 2.3 - The concrete post (Ec = 3.6 106) psi and c = 5.5 ...Ch. 2.3 - A rod consisting of two cylindrical portions AB...Ch. 2.3 - A rod consisting of two cylindrical portions AB...Ch. 2.3 - Fig. P2.52 2.52 A rod consisting of two...Ch. 2.3 - The steel rails of a railroad (rack (Es = 200GPa,...Ch. 2.3 - Two steel bars (Es = 200 GPa and s = 11.7 10-6/C)...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the maximum load P that can be applied...Ch. 2.3 - An aluminum rod (Ea = 70 GPa, a = 23.6 10-6/C)...Ch. 2.3 - Knowing that a 0.02-in. gap exists when the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine (a) the compressive force in the bars...Ch. 2.3 - At room temperature (20C) a 0.5-mm gap exists...Ch. 2.9 - A standard tension test is used to determine the...Ch. 2.9 - A 2-m length of an aluminum pipe of 240-nun outer...Ch. 2.9 - A line of slope 4:10 has been scribed on a...Ch. 2.9 - A 2.75-kN tensile load is applied to a test coupon...Ch. 2.9 - Fig. P2.65 2.65 In a standard tensile test a steel...Ch. 2.9 - The change in diameter of a large steel bolt is...Ch. 2.9 - The brass rod AD is fitted with a jacket that is...Ch. 2.9 - A fabric used in air-inflated structures is...Ch. 2.9 - A 1-in. square was scribed on the side of a large...Ch. 2.9 - The block shown is made of a magnesium alloy for...Ch. 2.9 - The homogeneous plate ABCD is subjected to a...Ch. 2.9 - For a member under axial loading, express the...Ch. 2.9 - In many situations it is known that the normal...Ch. 2.9 - In many situations physical constraints prevent...Ch. 2.9 - The plastic block shown is bonded to a rigid...Ch. 2.9 - The plastic block shown is bonded to a rigid...Ch. 2.9 - Two blocks of rubber with a modulus of rigidity G...Ch. 2.9 - Fig. P2.77 and P2.78 2.78 Two blocks of rubber...Ch. 2.9 - An elastomeric bearing (G = 130 psi) is used to...Ch. 2.9 - 2.80 For the elastomeric bearing In Prob. 2.79...Ch. 2.9 - A vibration isolation unit consists of two blocks...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 82PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 83PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 84PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 85PCh. 2.9 - A 2.75-kN tensile load is applied to a test coupon...Ch. 2.9 - A vibration isolation support consists of a rod A...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 88PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 89PCh. 2.9 - Show that for any given material, the ratio G/E of...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 91PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 92PCh. 2.13 - Knowing that, for the plate shown, the allowable...Ch. 2.13 - Knowing that P = 38 kN, determine the maximum...Ch. 2.13 - A hole is to be drilled in the plate at A. The...Ch. 2.13 - Fig. P2.95 and P2.96 2.96 (a) For P = 13 kips and...Ch. 2.13 - 2.97 Knowing that the hole has a diameter of 9 mm,...Ch. 2.13 - For P = 100 kN, determine the minimum plate...Ch. 2.13 - Prob. 99PCh. 2.13 - A centric axial force is applied to the steel bar...Ch. 2.13 - The cylindrical rod AB has a length L = 5 ft and a...Ch. 2.13 - Fig. P2.101 and P.102 2.102 The cylindrical rod AB...Ch. 2.13 - Rod AB is made of a mild steel that is assumed to...Ch. 2.13 - Prob. 104PCh. 2.13 - Rod ABC consists of two cylindrical portions and...Ch. 2.13 - Prob. 106PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 107PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 108PCh. 2.13 - Each cable has a cross-sectional area of 100 mm2...Ch. 2.13 - Prob. 110PCh. 2.13 - Two tempered-steel bars, each 316 in. thick, are...Ch. 2.13 - Prob. 112PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 113PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 114PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 115PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 116PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 117PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 118PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 119PCh. 2.13 - For the composite bar in Prob. 2.111, determine...Ch. 2.13 - Prob. 121PCh. 2.13 - Bar AB has a cross-sectional area of 1200 mm2 and...Ch. 2.13 - Bar AB has a cross-sectional area of 1200 mm2 and...Ch. 2 - The uniform wire ABC, of unstretched length 2l, is...Ch. 2 - The aluminum rod ABC (E = 10.1 106 psi), which...Ch. 2 - Two solid cylindrical rods are joined at B and...Ch. 2 - Prob. 127RPCh. 2 - Prob. 128RPCh. 2 - Prob. 129RPCh. 2 - A 4-ft concrete post is reinforced with four steel...Ch. 2 - The steel rods BE and CD each have a 16-mm...Ch. 2 - Prob. 132RPCh. 2 - Prob. 133RPCh. 2 - The aluminum test specimen shown is subjected to...Ch. 2 - Prob. 135RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- relative velocity 11.72 m/s is correct, need help finding the angle pleasearrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the two automobiles 2 s after A has passed through the intersection.arrow_forwardA box barge 65 m long and 12 m wide floats at a draught of5.5 m in sea water. Calculate:(a) the displacement of the barge,(b) its draught in fresh waterarrow_forward
- what is the angle of the velocity of block B? velocity is 7.46 in/s Determine the acceleration and angle of block B. (Round the acceleration value to three decimal places.)arrow_forwardDetermine the relative velocity of B with respect to A.arrow_forwardGenerate the kinematic diagram of the following mechanism. Then, draw their graphs and calculate their degrees of freedom (DoF) using Gruebler's formula.arrow_forward
- An elastic bar of length L = 1m and cross section A = 1cm2 spins with angular velocity ω about an axis, as shown in the figure below. The radial acceleration at a generic point x along the bar is a(x) = ω2x, where ω= 100rad/s is the angular velocity. The bar is pinned on the rotation axis at x = 0. A mass M = 1kg is attached to the right end of the bar. Due to the radial acceleration, the bar stretches along x with displacement function u(x). The displacement u(x) solves the BVP (strong form) sketched below: d dx (σ(x)) + ρa(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = E du dx Hooke’s law (1) u(0) =?? essential BC σ(L) =?? natural BC where σ(x) is the axial stress in the rod, ρ= 2700kg /m3 is the mass density, and E = 70GPa is the Young’s modulus 1. Define appropriate BCs for the strong BVP 2. Find the solution of the strong BVP analytically 3. Derive the weak form of the BVP.arrow_forwardGruebler's formula for the following mechanism?arrow_forwardw/I - | العنوان I need a detailed drawing with explanation SOLL эт 4 حكا The guide vane angle of a reaction turbine (Francis type make 20° with the tangent. The moving blade angle at entry is 120°. The external diameter of runner is 450 mm and the internal diameter is 300 mm. Runner width at entry is 62.5mm and at exit 100mm. Calculate the blade angle at exit for radial discharge. 96252 -20125 750 ×2.01arrow_forward
- Compressor Selection: (Q1) While a manufacturing cell is running, the calculated flow rate of air into a compressor is 40 SCFM. Which compressor from this list should be selected? A. A compressor that uses 80 SCFM B. A compressor that uses 40 SCFM C. A compressor that delivers 80 SCFM D. A compressor that delivers 40 SCFMarrow_forwardSCFM Calculation: (Q1) A pneumatic system running a manufacturing cell works on 80 psi and requires a flow rate of 10 CFM to operate. A compressor must be selected to run the cell. Calculate the amount of air going into the compressor to run this cell. (Hint: This will be in SCFM) Accurate to two decimals. Do not write the unit.arrow_forward: +00 العنوان >scóny : + 개 العنوان I need a actanicu urawing wit д い Ants nation Taxi pu +9635. The guide vane angle of a reaction turbine (Francis type make 20° with the tangent. The moving blade angle at entry is 120°. The external diameter of runner is 450 mm and the internal diameter is 300 mm. Runner width at entry is 62.5mm and at exit 100mm. Calculate the blade angle t exit for radial discharge. ۲/۱ = 44 985arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Strain energy and strain energy density introduced; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m14sqLGg4BQ;License: Standard youtube license