
Concept explainers
The uniform wire ABC, of unstretched length 2l, is attached to the supports shown and a vertical load P is applied at the midpoint B. Denoting by A the cross-sectional area of the wire and by E the modulus of elasticity, show that, for δ << l, the deflection at the midpoint B is
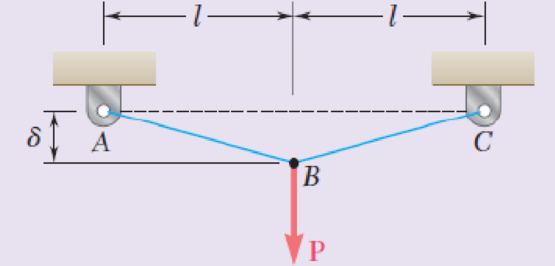
Fig. P2.124
To prove the deflection of uniform wire ABC at midpoint B is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The unstretched length is
The vertical load is P.
Calculation:
Sketch the uniform wire ABC as shown in Figure 1.
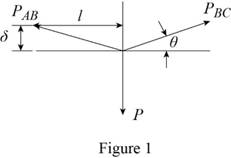
Refer to Figure 1.
The value of
Find the value of vertical load
Substitute for
Find the elongation at point AB using the relation:
Substitute
Sketch the right angle triangle as shown in Figure 2.
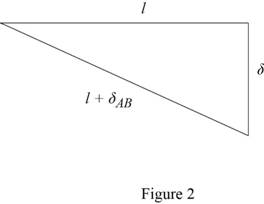
Refer to Figure 2.
Substitute
Hence, the deflection of uniform wire ABC at midpoint B is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
- Can you solve it analytically using laplace transforms and with Matlab code as well please. Thank Youarrow_forwardCan you solve it analytically using laplace transforms and with Matlab code as well please. Thank You.arrow_forwardQ11. Determine the magnitude of the reaction force at C. 1.5 m a) 4 KN D b) 6.5 kN c) 8 kN d) e) 11.3 KN 20 kN -1.5 m- C 4 kN -1.5 m B Mechanical engineering, No Chatgpt.arrow_forward
- aversity of Baoyion aculty of Engineering-AIMusyab Automobile Eng. Dep. Year: 2022-2023, st Course, 1st Attempt Stage: 3rd Subject: Heat Transfer I Date: 2023\01\23- Monday Time: 3 Hours Q4: A thick slab of copper initially at a uniform temperature of 20°C is suddenly exposed to radiation at one surface such that the net heat flux is maintained at a constant value of 3×105 W/m². Using the explicit finite-difference techniques with a space increment of Ax = = 75 mm, determine the temperature at the irradiated surface and at an interior point that is 150 mm from the surface after 2 min have elapsed. Q5: (12.5 M) A) A steel bar 2.5 cm square and 7.5 cm long is initially at a temperature of 250°C. It is immersed in a tank of oil maintained at 30°C. The heat-transfer coefficient is 570 W/m². C. Calculate the temperature in the center of the bar after 3 min. B) Air at 90°C and atmospheric pressure flows over a horizontal flat plate at 60 m/s. The plate is 60 cm square and is maintained at a…arrow_forwardUniversity of Baby on Faculty of Engineering-AIMusyab Automobile Eng. Dep. Year: 2022-2023. 1 Course, 1" Attempt Stage 3 Subject Heat Transfer I Date: 2023 01 23- Monday Time: 3 Hours Notes: Q1: • • Answer four questions only Use Troles and Appendices A) A flat wall is exposed to an environmental temperature of 38°C. The wall is covered with a layer of insulation 2.5 cm thick whose thermal conductivity is 1.4 W/m. C, and the temperature of the wall on the inside of the insulation is 315°C. The wall loses heat to the environment by convection. Compute the value of the convection heat-transfer coefficient that must be maintained on the outer surface of the insulation to ensure that the outer-surface temperature does not exceed 41°C. B) A vertical square plate, 30 cm on a side, is maintained at 50°C and exposed to room air at 20°C. The surface emissivity is 0.8. Calculate the total heat lost by both sides of the plate. (12.5 M) Q2: An aluminum fin 1.5 mm thick is placed on a circular tube…arrow_forwardSolve using graphical method and analytical method, only expert should solvearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





