
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321879721
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 19CQ
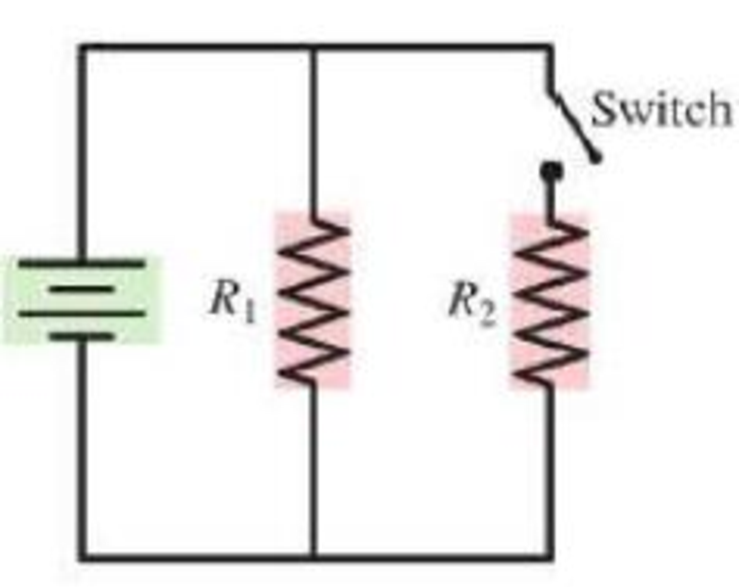
When the switch in Figure Q23.19 is closed,
a. Does the current through the battery increase, decrease, or stay the same? Explain.
b. Does the current through |R1 increase, decrease, or stay the same? Explain.
Figure Q23.19
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In order to increase the amount of exercise in her daily routine, Tara decides to walk up the four flights of stairs to her car instead of taking the elevator. Each of the steps she takes are 18.0 cm high, and there are 12 steps per flight.
(a) If Tara has a mass of 77.0 kg, what is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the Tara-Earth system (in J) when she reaches her car?
]
(b) If the human body burns 1.5 Calories (6.28 x 10³ J) for each ten steps climbed, how much energy (in J) has Tara burned during her climb?
]
(c) How does the energy she burned compare to the change in the gravitational potential energy of the system?
Eburned
Δυ
A 4.40 kg steel ball is dropped onto a copper plate from a height of 10.0 m. If the ball leaves a dent 2.75 mm deep, what is the average force exerted by the plate on the ball during the impact?
N
A block of mass m = 7.00 kg is released from rest from point and slides on the frictionless track shown in the figure below. (Assume h₂ = 7.80 m.)
a
m
ha
3.20 m
2.00 m
i
(a) Determine the block's speed at points ® and
point B
©.
m/s
m/s
point
(b) Determine the net work done by the gravitational force on the block as it moves from point
J
A
to point
Chapter 23 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 23 - The tip of a flashlight bulb is touching the top...Ch. 23 - A flashlight bulb is connected to a battery and is...Ch. 23 - Current Iin flows into three resistors connected...Ch. 23 - The circuit in Figure Q23.4 has two resistors,...Ch. 23 - The circuit in Figure Q23.5 has a battery and two...Ch. 23 - In the circuit shown in Figure Q23.6, bulbs A and...Ch. 23 - Figure Q23.7 shows two circuits. The two batteries...Ch. 23 - Figure Q23.8 shows two circuits. The two batteries...Ch. 23 - a. In Figure Q23.9, what fraction of current I...Ch. 23 - Two of the three resistors in Figure Q23.10 are...
Ch. 23 - Two of the three resistors in Figure Q23.11 are...Ch. 23 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 23 - The three bulbs in Figure Q23.13 are identical....Ch. 23 - The four bulbs in Figure Q23.14 are identical....Ch. 23 - Figure Q23.15 shows five identical bulbs connected...Ch. 23 - a. The three bulbs in Figure Q23.16 are identical....Ch. 23 - Initially, bulbs A and B in Figure Q23.17 are both...Ch. 23 - a. Consider the points a and b in Figure Q23.18....Ch. 23 - When the switch in Figure Q23.19 is closed, a....Ch. 23 - A voltmeter is (incorrectly) inserted into a...Ch. 23 - An ammeter is (incorrectly) inserted into a...Ch. 23 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 23 - Figure Q23.23 shows a circuit consisting of a...Ch. 23 - Figure Q23.24 shows the volt age as a function of...Ch. 23 - A charged capacitor could be connected to two...Ch. 23 - A flashing light is controlled by the charging and...Ch. 23 - A device to make an electrical measurement of skin...Ch. 23 - Consider the model of nerve conduction in...Ch. 23 - Adding a myelin sheath to an axon results in...Ch. 23 - What is the current in the circuit of Figure...Ch. 23 - Which resistor in Figure Q23.30 dissipates the...Ch. 23 - Normally, household lightbulbs are connected in...Ch. 23 - A metal wire of resistance R is cut into two...Ch. 23 - What is the value of resistor R in Figure Q23.34?...Ch. 23 - Two capacitors are connected in series. They are...Ch. 23 - If a cells membrane thickness doubles but the cell...Ch. 23 - If a cells diameter is reduced by 50% without...Ch. 23 - Draw a circuit diagram tor the circuit of Figure...Ch. 23 - Draw a circuit diagram for the circuit of Figure...Ch. 23 - Draw a circuit diagram for the circuit of Figure...Ch. 23 - In Figure P23.4, what is the current in the wire...Ch. 23 - The lightbulb in the circuit diagram of Figure...Ch. 23 - a. What are the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 23 - a. What are the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 23 - a. What is the potential difference across each...Ch. 23 - The current in a circuit with only one battery is...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent resistance of each group of...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent resistance of each group of...Ch. 23 - Prob. 12PCh. 23 - Prob. 13PCh. 23 - You have a collection of 1.0 k resistors. How can...Ch. 23 - You have a collection of six 1.0 k resistors. What...Ch. 23 - You have six 1.0 k resistors. How can you connect...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent resistance between points a...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent resistance between points a...Ch. 23 - The currents in two resistors in a circuit are...Ch. 23 - Two batteries supply current to the circuit in...Ch. 23 - Part of a circuit is shown in Figure P23.21. a....Ch. 23 - What is the value of resistor R in Figure P23.22?...Ch. 23 - What are the resistances R and the emf of the...Ch. 23 - The ammeter in Figure P23.24 reads 3.0 A. Find I1,...Ch. 23 - Find the current through and the potential...Ch. 23 - Find the current through and the potential...Ch. 23 - For the circuit shown in Figure P23.27, find the...Ch. 23 - Consider the potential differences between pairs...Ch. 23 - For the circuit shown in Figure P23.29, find the...Ch. 23 - A photoresistor, whose resistance decreases with...Ch. 23 - The two unknown resistors in Figure P23.31 have...Ch. 23 - A 6.0 F capacitor, a 10 F capacitor, and a 16 F...Ch. 23 - A 6.0 F capacitor, a 10 F capacitor, and a 16 F...Ch. 23 - You need a capacitance of 50 F, but you dont...Ch. 23 - You need a capacitance of 50 F, but you dont...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent capacitance of the three...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent capacitance of the three...Ch. 23 - For the circuit of Figure P23.38, a. What is the...Ch. 23 - For the circuit of Figure P23.39. a. What is the...Ch. 23 - What is the time constant for the discharge of the...Ch. 23 - What is the time constant for the discharge of the...Ch. 23 - After how many time constants has the voltage...Ch. 23 - A 10F capacitor initially charged to 20C is...Ch. 23 - A capacitor charging circuit consists of a...Ch. 23 - The switch in Figure P23.45 has been in position a...Ch. 23 - A 9.0-nm-thick cell membrane undergoes an action...Ch. 23 - A cell membrane has a resistance and a capacitance...Ch. 23 - Changing the thickness of the myelin sheath...Ch. 23 - A particular myelinated axon has nodes spaced 0.80...Ch. 23 - To measure signal propagation in a nerve in the...Ch. 23 - A myelinated axon conducts nerve impulses at a...Ch. 23 - How much power is dissipated by each resistor in...Ch. 23 - Two 75 W (120 V) lightbulbs are wired in series,...Ch. 23 - The corroded contacts in a lightbulb socket have...Ch. 23 - A real battery is not just an emf. We can If model...Ch. 23 - For the real battery shown in Figure P23.55,...Ch. 23 - Batteries are recharged by connecting them to a...Ch. 23 - When two resistors are connected in parallel...Ch. 23 - The 10 resistor in Figure P23.59 is dissipating 40...Ch. 23 - At this instant the current in the circuit of...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent resistance between points a...Ch. 23 - What is the current through the battery in Figure...Ch. 23 - What is the ratio P parallel/P series of the total...Ch. 23 - You have a device that needs a voltage reference...Ch. 23 - There is a current of 0.25 A in the circuit of...Ch. 23 - A circuit youre building needs an ammeter that...Ch. 23 - A circuit youre building needs a voltmeter that...Ch. 23 - For the circuit shown in Figure P23.68, find the...Ch. 23 - You have three 12 F capacitors. Draw diagrams...Ch. 23 - Initially, the switch in Figure P23.70 is in...Ch. 23 - The capacitor in an RC circuit with a time...Ch. 23 - The capacitor in Figure P23.72 is initially...Ch. 23 - What value resistor will discharge a 1.0 F...Ch. 23 - The charging circuit for the flash system of a...Ch. 23 - A capacitor is discharged through a 100 resistor....Ch. 23 - A 50 /F capacitor that had been charged to 30 V is...Ch. 23 - The switch in Figure P23.77 has been closed for a...Ch. 23 - Intermittent windshield wipers use a variable...Ch. 23 - In Example 23.14 we estimated the capacitance of...Ch. 23 - The giant axon of a squid is 0.5 mm in diameter,...Ch. 23 - A cell has a 7.0-nm-thick membrane with a total...Ch. 23 - The Defibrillator A defibrillator is designed to...Ch. 23 - The Defibrillator A defibrillator is designed to...Ch. 23 - The Defibrillator A defibrillator is designed to...Ch. 23 - A defibrillator is designed to pass a large...Ch. 23 - The voltage produced by a single nerve or muscle...Ch. 23 - The voltage produced by a single nerve or muscle...Ch. 23 - The voltage produced by a single nerve or muscle...Ch. 23 - The voltage produced by a single nerve or muscle...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Define histology.
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
The distances you obtained in Question 3 are for only one side of the ridge. Assuming that a ridge spreads equa...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
1.1 Write a one-sentence definition for each of the following:
a. chemistry
b. chemical
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Thiols such as ethanethiol and propanethiol can be used to reduce vitamin K epoxide to vitamin KH2, but they re...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
What are four functions of connective tissue?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Two culture media were inoculated with four different bacteria. After incubation, the following results were ob...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 1.10 x 10²-g particle is released from rest at point A on the inside of a smooth hemispherical bowl of radius R R B 2R/3 (a) Calculate its gravitational potential energy at A relative to B. ] (b) Calculate its kinetic energy at B. ] (c) Calculate its speed at B. m/s (d) Calculate its potential energy at C relative to B. J (e) Calculate its kinetic energy at C. ] = 26.5 cm (figure below).arrow_forwardReport on the percentage errors (with uncertainty) between the value of 'k' from the F vs displacement plot and each of the values of 'k' from the period measurements. Please comment on the goodness of the results. Value of k = Spring constant k = 50.00 N/m Each of the values of k from period measurements: Six Measurements of time for 5 osccilations: t1 = 7.76s, t2=8.00s, t3=7.40s, t4=7.00s, t5=6.90s, t6=7.10s (t1-tavg)^2 = (7.76-7.36)^2 = 0.16%(t2-tavg)^2 =(8.00-7.36)^2 = 0.4096%(t3-tavg)^2 =(7.40-7.36)^2 = 0.0016%(t4-tavg)^2 =(7.00-7.36)^2 = 0.1296%(t5-tavg)^2 =(6.90-7.36)^2 = 0.2116%(t6-tavg)^2 =(7.10-7.36)^2 = 0.0676arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Based on the two periods (from hand timed and ultrasonic sensor), find the value of 'k' they suggest from the physics and from the value of the hanging mass. hand time period is 1.472s and ultrasonic sensor time period is 1.44sarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardExperimental Research Report Template Title: Paper Airplane Flight. Materials: Paper, ruler, tape Procedure: Fold paper into different airplane designs, such as dart, glider, or classic. Measure and record the distances each design flies when thrown with the same force. Discuss aerodynamics and the factors that affect flight distance. Introduction: (What do you expect to learn? What is the purpose of this lab? List any questions this experiment will answer.) Hypothesis: (Predict the outcome(s) of the experiment, must be in an “if…then format.) Materials: (What equipment and materials did you need for this experiment assignment? Describe how any equipment was connected. Also mention any special hardware or connections. List the name and amount of each item used.) Procedures: (What steps did you take to accomplish this lab assignment? Include Safety Precautions.) Data Collection: (Record the data that is required at each step of the…arrow_forward
- Title: Studying the Relationship Between Drop Height and Bouncing Height of a Ball: You can drop balls of different materials (e.g., rubber, plastic, ping pong) from various heights onto a flat surface and measure the height of their bounce using a ruler. Introduction: (What do you expect to learn? What is the purpose of this lab? List any questions this experiment will answer.) Hypothesis: (Predict the outcome(s) of the experiment, must be in an “if…then format.) Materials: (What equipment and materials did you need for this experiment assignment? Describe how any equipment was connected. Also mention any special hardware or connections. List the name and amount of each item used.) Procedures: (What steps did you take to accomplish this lab assignment? Include Safety Precautions.) Data Collection: (Record the data that is required at each step of the lab: tables, charts, graphs, sketches, etc.) Data Analysis: (Explain you…arrow_forwardA traveler at an airport takes an escalator up one floor as in the figure below. The moving staircase would itself carry him upward with vertical velocity component v between entry and exit points separated by height h. However, while the escalator is moving, the hurried traveler climbs the steps of the escalator at a rate of n steps/s. Assume that the height of each step is hs. (a) Determine the amount of chemical energy converted into mechanical energy by the traveler's leg muscles during his escalator ride given that his mass is m. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: g.) energy = (b) Determine the work the escalator motor does on this person. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: g.) work =arrow_forwardWhich of the following is part of the interior of the Sun? photosphere the corona sunspots radiation zonearrow_forward
- Most craters on the surface of the Moon are believed to be caused by which of the following? faults asteroids volcanoes meteoroidsarrow_forwardAn object is subjected to a friction force with magnitude 5.49 N, which acts against the object's velocity. What is the work (in J) needed to move the object at constant speed for the following routes? y (m) C B (5.00, 5.00) A x (m) © (a) the purple path O to A followed by a return purple path to O ] (b) the purple path O to C followed by a return blue path to O ] (c) the blue path O to C followed by a return blue path to O ] (d) Each of your three answers should be nonzero. What is the significance of this observation? ○ The force of friction is a conservative force. ○ The force of friction is a nonconservative force.arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 2.50 kg is pushed d = 2.30 m along a frictionless horizontal table by a constant applied force of magnitude F = 10.0 N directed at an angle 25.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure below. m (a) Determine the work done by the applied force. ] (b) Determine the work done by the normal force exerted by the table. ] (c) Determine the work done by the force of gravity. ] (d) Determine the work done by the net force on the block. ]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What is Electromagnetic Induction? | Faraday's Laws and Lenz Law | iKen | iKen Edu | iKen App; Author: Iken Edu;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3HyORmBip-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY