
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321879721
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 14CQ
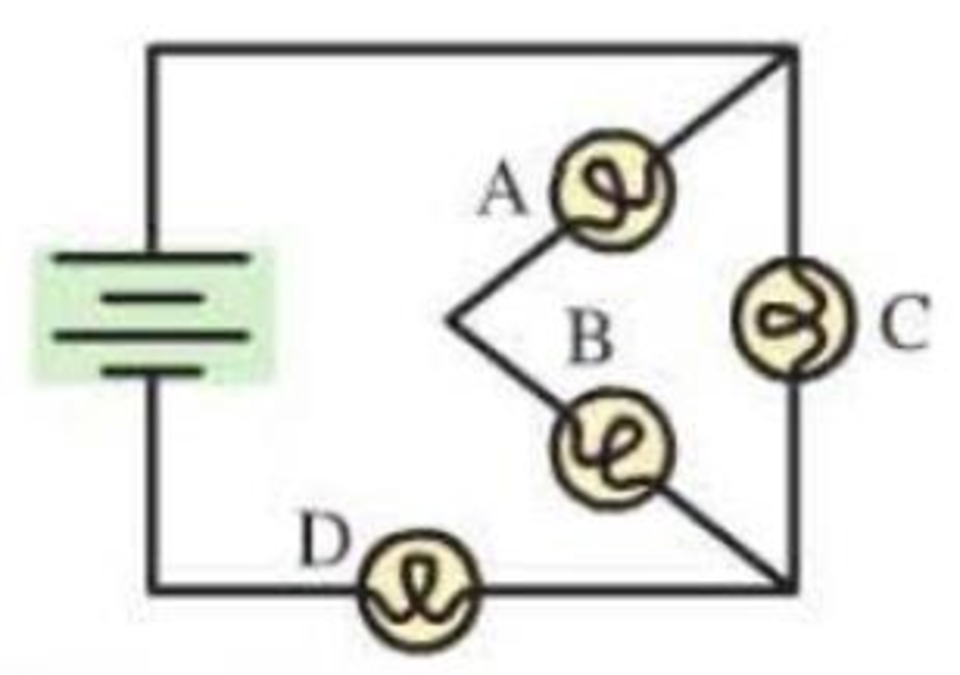
The four bulbs in Figure Q23.14 are identical. Rank the bulbs from brightest to dimmest. Explain.
Figure Q23.14
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The four bulbs shown are identical. Rank the bulbs from brightest to dimmest. Explain.
The three bulbs shown are identical. When bulb C is removed from the circuit, what happens to the brightness of bulb A? Of bulb B? Explain.
7. A4.50-volt
personal stereo uses 1950 joules
of electrical energy in one hour. What is the
electrical resistance of the personal stereo?
(1) 433 Q
(2) 96.3 Q
(3) 37.4 2
(4) 0.623 Q
7
Chapter 23 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 23 - The tip of a flashlight bulb is touching the top...Ch. 23 - A flashlight bulb is connected to a battery and is...Ch. 23 - Current Iin flows into three resistors connected...Ch. 23 - The circuit in Figure Q23.4 has two resistors,...Ch. 23 - The circuit in Figure Q23.5 has a battery and two...Ch. 23 - In the circuit shown in Figure Q23.6, bulbs A and...Ch. 23 - Figure Q23.7 shows two circuits. The two batteries...Ch. 23 - Figure Q23.8 shows two circuits. The two batteries...Ch. 23 - a. In Figure Q23.9, what fraction of current I...Ch. 23 - Two of the three resistors in Figure Q23.10 are...
Ch. 23 - Two of the three resistors in Figure Q23.11 are...Ch. 23 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 23 - The three bulbs in Figure Q23.13 are identical....Ch. 23 - The four bulbs in Figure Q23.14 are identical....Ch. 23 - Figure Q23.15 shows five identical bulbs connected...Ch. 23 - a. The three bulbs in Figure Q23.16 are identical....Ch. 23 - Initially, bulbs A and B in Figure Q23.17 are both...Ch. 23 - a. Consider the points a and b in Figure Q23.18....Ch. 23 - When the switch in Figure Q23.19 is closed, a....Ch. 23 - A voltmeter is (incorrectly) inserted into a...Ch. 23 - An ammeter is (incorrectly) inserted into a...Ch. 23 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 23 - Figure Q23.23 shows a circuit consisting of a...Ch. 23 - Figure Q23.24 shows the volt age as a function of...Ch. 23 - A charged capacitor could be connected to two...Ch. 23 - A flashing light is controlled by the charging and...Ch. 23 - A device to make an electrical measurement of skin...Ch. 23 - Consider the model of nerve conduction in...Ch. 23 - Adding a myelin sheath to an axon results in...Ch. 23 - What is the current in the circuit of Figure...Ch. 23 - Which resistor in Figure Q23.30 dissipates the...Ch. 23 - Normally, household lightbulbs are connected in...Ch. 23 - A metal wire of resistance R is cut into two...Ch. 23 - What is the value of resistor R in Figure Q23.34?...Ch. 23 - Two capacitors are connected in series. They are...Ch. 23 - If a cells membrane thickness doubles but the cell...Ch. 23 - If a cells diameter is reduced by 50% without...Ch. 23 - Draw a circuit diagram tor the circuit of Figure...Ch. 23 - Draw a circuit diagram for the circuit of Figure...Ch. 23 - Draw a circuit diagram for the circuit of Figure...Ch. 23 - In Figure P23.4, what is the current in the wire...Ch. 23 - The lightbulb in the circuit diagram of Figure...Ch. 23 - a. What are the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 23 - a. What are the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 23 - a. What is the potential difference across each...Ch. 23 - The current in a circuit with only one battery is...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent resistance of each group of...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent resistance of each group of...Ch. 23 - Prob. 12PCh. 23 - Prob. 13PCh. 23 - You have a collection of 1.0 k resistors. How can...Ch. 23 - You have a collection of six 1.0 k resistors. What...Ch. 23 - You have six 1.0 k resistors. How can you connect...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent resistance between points a...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent resistance between points a...Ch. 23 - The currents in two resistors in a circuit are...Ch. 23 - Two batteries supply current to the circuit in...Ch. 23 - Part of a circuit is shown in Figure P23.21. a....Ch. 23 - What is the value of resistor R in Figure P23.22?...Ch. 23 - What are the resistances R and the emf of the...Ch. 23 - The ammeter in Figure P23.24 reads 3.0 A. Find I1,...Ch. 23 - Find the current through and the potential...Ch. 23 - Find the current through and the potential...Ch. 23 - For the circuit shown in Figure P23.27, find the...Ch. 23 - Consider the potential differences between pairs...Ch. 23 - For the circuit shown in Figure P23.29, find the...Ch. 23 - A photoresistor, whose resistance decreases with...Ch. 23 - The two unknown resistors in Figure P23.31 have...Ch. 23 - A 6.0 F capacitor, a 10 F capacitor, and a 16 F...Ch. 23 - A 6.0 F capacitor, a 10 F capacitor, and a 16 F...Ch. 23 - You need a capacitance of 50 F, but you dont...Ch. 23 - You need a capacitance of 50 F, but you dont...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent capacitance of the three...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent capacitance of the three...Ch. 23 - For the circuit of Figure P23.38, a. What is the...Ch. 23 - For the circuit of Figure P23.39. a. What is the...Ch. 23 - What is the time constant for the discharge of the...Ch. 23 - What is the time constant for the discharge of the...Ch. 23 - After how many time constants has the voltage...Ch. 23 - A 10F capacitor initially charged to 20C is...Ch. 23 - A capacitor charging circuit consists of a...Ch. 23 - The switch in Figure P23.45 has been in position a...Ch. 23 - A 9.0-nm-thick cell membrane undergoes an action...Ch. 23 - A cell membrane has a resistance and a capacitance...Ch. 23 - Changing the thickness of the myelin sheath...Ch. 23 - A particular myelinated axon has nodes spaced 0.80...Ch. 23 - To measure signal propagation in a nerve in the...Ch. 23 - A myelinated axon conducts nerve impulses at a...Ch. 23 - How much power is dissipated by each resistor in...Ch. 23 - Two 75 W (120 V) lightbulbs are wired in series,...Ch. 23 - The corroded contacts in a lightbulb socket have...Ch. 23 - A real battery is not just an emf. We can If model...Ch. 23 - For the real battery shown in Figure P23.55,...Ch. 23 - Batteries are recharged by connecting them to a...Ch. 23 - When two resistors are connected in parallel...Ch. 23 - The 10 resistor in Figure P23.59 is dissipating 40...Ch. 23 - At this instant the current in the circuit of...Ch. 23 - What is the equivalent resistance between points a...Ch. 23 - What is the current through the battery in Figure...Ch. 23 - What is the ratio P parallel/P series of the total...Ch. 23 - You have a device that needs a voltage reference...Ch. 23 - There is a current of 0.25 A in the circuit of...Ch. 23 - A circuit youre building needs an ammeter that...Ch. 23 - A circuit youre building needs a voltmeter that...Ch. 23 - For the circuit shown in Figure P23.68, find the...Ch. 23 - You have three 12 F capacitors. Draw diagrams...Ch. 23 - Initially, the switch in Figure P23.70 is in...Ch. 23 - The capacitor in an RC circuit with a time...Ch. 23 - The capacitor in Figure P23.72 is initially...Ch. 23 - What value resistor will discharge a 1.0 F...Ch. 23 - The charging circuit for the flash system of a...Ch. 23 - A capacitor is discharged through a 100 resistor....Ch. 23 - A 50 /F capacitor that had been charged to 30 V is...Ch. 23 - The switch in Figure P23.77 has been closed for a...Ch. 23 - Intermittent windshield wipers use a variable...Ch. 23 - In Example 23.14 we estimated the capacitance of...Ch. 23 - The giant axon of a squid is 0.5 mm in diameter,...Ch. 23 - A cell has a 7.0-nm-thick membrane with a total...Ch. 23 - The Defibrillator A defibrillator is designed to...Ch. 23 - The Defibrillator A defibrillator is designed to...Ch. 23 - The Defibrillator A defibrillator is designed to...Ch. 23 - A defibrillator is designed to pass a large...Ch. 23 - The voltage produced by a single nerve or muscle...Ch. 23 - The voltage produced by a single nerve or muscle...Ch. 23 - The voltage produced by a single nerve or muscle...Ch. 23 - The voltage produced by a single nerve or muscle...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
3. A football coach sits on a sled while two of his players build their strength by dragging the sled across ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Express the unit vectors in terms of (that is, derive Eq. 1.64). Check your answers several ways Also work o...
Introduction to Electrodynamics
If you increase the rotation rate of a precessing gyroscope, will the precession rate increase or decrease?
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Consider the circuit shown below. Write equations for the three currents in terms of R and V.
University Physics Volume 2
The Rankine temperature scale (abbreviatedR) uses the same size degrees as Fahrenheit, but measured up from abs...
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (a) What is the terminal voltage of a large 1.54-V carbon-zinc dry cell used in a physics lab to supply 2.00 A to a circuit if the cell’s internal resistance is 0.100 ? (b) How much electrical power does the cell produce? (c) What power goes to its load?arrow_forwardThe resistance between terminals a and b in Figure P27.36 is 75.0 . If the resistors labeled R have the same value, determine R. Figure P27.36arrow_forwardThe current-versus-voltage behavior of a certain electrical device is shown in Figure OQ27.9. When the potential difference across the device is 2 V, what is its resistance? (a) 1 (b) 34 (c) (d) undefined (e) none of those answersarrow_forward
- (a) Can the circuit shown in Figure P27.21 be reduced to a single resistor connected to a battery? Explain. Calculate the currents (b) I1, (c) I2, and (d) I3. Figure P27.21arrow_forwardA battery is used to charge a capacitor through a resistor as shown in Figure P27.44. Show that half the energy supplied by the battery appears as internal energy in the resistor and half is stored in the capacitor. Figure P27.44arrow_forwardFour resistors are connected to a battery as shown in Figure P27.15. (a) Determine the potential difference across each resistor in terms of . (b) Determine the current in each resistor in terms of I. (c) What If? If R3 is increased, explain what happens to the current in each of the resistors. (d) In the limit that R3 , what are the new values of the current in each resistor in terms of I, the original current in the battery? Figure P27.15arrow_forward
- If you examine your smartphone battery, you will likely see two numbers: the battery's "capacity" labeled in mAh (milliamps x hours or milliamp-hours), and the battery's voltage or potential difference in V (volts). 1. What physical quantity is the battery's "capacity" measuring? Explain how you can tell. This answer has not been graded yet. 2. Suppose your phone's battery has a capacity of 2500 mAh and a potential difference of 3.7 V. What is the amount of charge, in C (coulombs), that is stored in your smartphone battery when it's fully charged? Charge = 3. Smartphone chargers are usually labeled with their current output in A (amps). Suppose your charger delivers a current of 1.1 A. If your phone's battery is completely drained, how long will it take to fully charge the battery using your charger? Charging time = hours 4. Smartphones are advertised with a certain amount of "talk time", i.e., how long the phone's battery will last if you are making a call. If your phone is advertised…arrow_forward1. FIGURE shows a 2 µF capacitor connected to a 10 V battery, a 2 MSN resistor and switches K1 and K2. 10 V 2 µF K2 2 ΜΩ a. Explain in words the meaning of capacitance. b. Calculate the charge of the capacitor when switch K1 is closed and switch K2 is opened. c. Switch K1 is then opened and switch K2 closed. Calculate the charge in the capacitor, 8.0 s after K2 is closed.arrow_forward2. Consider the circuit below. The values of the resistors and battery are: R₁ =5Q, R₂ =3Q, R₂ = 1 Q, R = 4, V₁ = 14 V R1 tr V R2 W R4 R3 a. What is I, through R.? b. What is the voltage across R.? c. Now imagine all the resistors have been replaced with capacitors. The values of capacitances are C₁ = 7 mF, C₂= 2 mF, C, = 1 mF, and C₂ = 5 mF. What is the equivalent capacitance of all capacitors in the circuit? d. How much charge is stored on C₁?arrow_forward
- Normally, household lightbulbs are connected in parallel to a power supply.Suppose a 40 W and a 60 W lightbulb are, instead, connected in series, as shown. Which bulb is brighter?A. The 60 W bulb.B. The 40 W bulb.C. The bulbs are equally bright.arrow_forward2o2 3052 352 552 652 2A A. The power dissipated in the 3 Ohms resistor is W. B. The total voltage is V. C. The power dissipated in the 5 Ohms resistor is W. Round all answers to whole numbers.arrow_forwardAnswer the the question:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
DC Series circuits explained - The basics working principle; Author: The Engineering Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VV6tZ3Aqfuc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY