
Concept explainers
To graph: The polynomial function
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The given polynomial function
Concept used:
Leading coefficient test: If the polynomial function
Zeros of thepolynomial are the points
Graph:
The given polynomial is
(i) Since the leading coefficient of given function is positive, therefore, the graph of function falls to the left and rises to the right.
(ii) Since,
(iii) Some solutions of the function (computed by taking arbitrary values of x ) are :
| x | - 3.5 | -2 | -1 | 1 | 2 | 3.5 |
| -11.375 | 10 | 8 | -8 | -10 | 11.375 |
(iv). The continuous curve joining the calculated points (zeros and solutions), the graph of the polynomial function
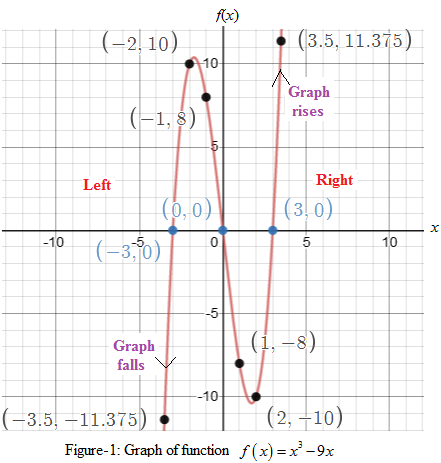
Interpretation of the Graph:
The function
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus with Limits: A Graphing Approach
- Differentiate the following functions. (a) y(x) = x³+6x² -3x+1 (b) f(x)=5x-3x (c) h(x) = sin(2x2)arrow_forwardx-4 For the function f(x): find f'(x), the third derivative of f, and f(4) (x), the fourth derivative of f. x+7arrow_forwardIn x For the function f(x) = find f'(x). Then find f''(0) and f''(9). 11x'arrow_forward
- Let f(x) = √√x+3 and g(x) = 6x − 2. Find each of the following composite functions and state the domain: (a) fog (b) gof, (c) fof (d) gogarrow_forwardCompute the following: (a) 8x³ + 3x dx (b) cos(2u) du (c) f² ebx dxarrow_forwardFind the following limits. (a) lim 3(x-1)² x→2 x (b) lim 0+x (c) lim 3x2-x+1 x²+3 x²+x-12 x-3 x-3arrow_forward
- For f(x) = (x+3)² - 2 sketch f(x), f(x), f(x − 2), and f(x) — 2. State the coordi- nates of the turning point in each graph.arrow_forwardFor f(x) = (x+3)² - 2 sketch f(x), f(x), f(x − 2), and f(x) — 2. State the coordi- nates of the turning point in each graph.arrow_forward4 For the function f(x) = 4e¯x, find f''(x). Then find f''(0) and f''(1).arrow_forward
- Solve the next ED: (see image)arrow_forwardWrite an equation for the polynomial graphed below. It will probably be easiest to leave your "a" value as a fraction. 8 7 + 9+ H 6 5 4 3 + 3 2 1 (-30) (-1,0) (1,0) (3,0) + -5 -4 -3 -2 2 3 4 7 2 -1 -2 3 (0,-3) f(x) = 456 -4 -5 -6+arrow_forwardWrite an equation for the polynomial graphed below 5+ 4 - 3 2 1 + + -5 4-3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 -1 -2 y(x) = -3 -4 5 -5+ Qarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





