
University Physics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133969290
Author: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 22.6E
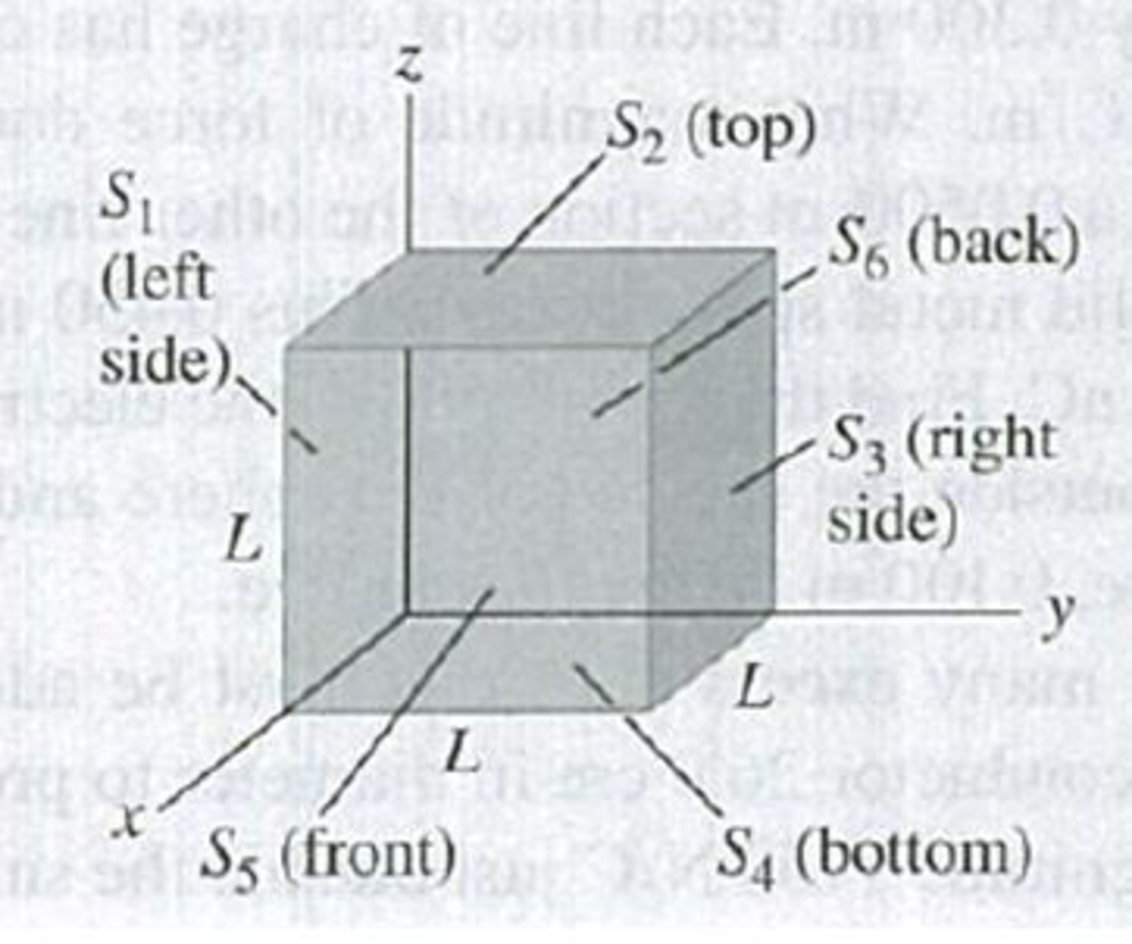
The cube in Fig. E22.6 has sides of length L = 10.0 cm. The electric field is uniform, has magnitude E = 4.00 × 103 N/C, and is parallel to the xy-plane at an angle of 53.1° measured from the +x-axis toward the +y-axis. (a) What is the electric flux through each of the six cube faces S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6? (b) What is the total electric flux through all faces of the cube?
Figure E22.6
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An electric field of magnitude E = 400 N/C points in the +x-direction for x > 0 and in the –x-direction for x < 0. A cylinder of length 30 cm and radius 10 cm has its center at the origin and its axis along the x-axis such that one end is at x = +15 cm and the other is at x = –15 cm. What is the flux through each end of the cylinder?
Group of answer choices
0.25 kN·m2/C
0.13 MN·m2/C
zero
1.3 kN·m2/C
13 N·m2/C
A circular loop of wire with a diameter of 0.626 m is rotated in a uniform electric field to a position where the electric flux through the
loop is a maximum. At this position, the electric flux is 7.50 x 105 N-m²/C. Determine the magnitude of the electric field.
O 2.44 × 106 N/C
O 4.24 × 106 N/C
O 1.07 x 106 N/C
O 8.88 x 105 N/C
O.6.00 x 106 N/C
eTextbook and Media
A thin, square, conducting plate 54.0 cm on a side lies in the xy plane. A total charge of 3.20 x 10-8 C is placed on the plate. You may assume the charge density is uniform.
(a) Find the charge density on each face of the plate.
C/m²
(b) Find the electric field just above the plate.
magnitude
N/C
direction upward
◊
(c) Find the electric field just below the plate.
magnitude
N/C
direction downward ↑
Chapter 22 Solutions
University Physics (14th Edition)
Ch. 22 - A rubber balloon has a single point charge in its...Ch. 22 - Suppose that in Fig. 22.15 both charges were...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22.15, suppose a third point charge were...Ch. 22 - A certain region of space bounded by an imaginary...Ch. 22 - A spherical Gaussian surface encloses a point...Ch. 22 - You find a sealed box on your doorstep. You...Ch. 22 - A solid copper sphere has a net positive charge....Ch. 22 - A spherical Gaussian surface encloses a point...Ch. 22 - In a conductor, one or more electrons from each...Ch. 22 - You charge up the Van de Graaff generator shown in...
Ch. 22 - Lightning is a flow of electrons. The lightning...Ch. 22 - A solid conductor has a cavity in its interior....Ch. 22 - Explain this statement: In a static situation, the...Ch. 22 - In a certain region of space, the electric field E...Ch. 22 - (a) In a certain region of space, the volume...Ch. 22 - A negative charge Q is placed inside the cavity of...Ch. 22 - A flat sheet of paper of area 0.250 m2 is oriented...Ch. 22 - A flat sheet is in the shape of a rectangle with...Ch. 22 - You measure an electric field of 1.25 106 N/C at...Ch. 22 - It was shown in Example 21.10 (Section 21.5) that...Ch. 22 - A hemispherical surface with radius r in a region...Ch. 22 - The cube in Fig. E22.6 has sides of length L =...Ch. 22 - BIO As discussed in Section 22.5, human nerve...Ch. 22 - The three small spheres shown in Fig. E22.8 carry...Ch. 22 - A charged paint is spread in a very thin uniform...Ch. 22 - A point charge q1 = 4.00 nC is located on the...Ch. 22 - C point charge is at the center of a cube with...Ch. 22 - Electric Fields in an Atom. The nuclei of large...Ch. 22 - Two very long uniform lines of charge are parallel...Ch. 22 - A solid metal sphere with radius 0.450 m carries a...Ch. 22 - How many excess electrons must be added to an...Ch. 22 - Some planetary scientists have suggested that the...Ch. 22 - A very long uniform line of charge has charge per...Ch. 22 - The electric field 0.400 m from a very long...Ch. 22 - A hollow, conducting sphere with an outer radius...Ch. 22 - (a) At a distance of 0.200 cm from the center or a...Ch. 22 - The electric field at a distance of 0.145 m from...Ch. 22 - A point charge of 3.00 C is located in the center...Ch. 22 - CP An electron is released from rest at a distance...Ch. 22 - Charge Q is distributed uniformly throughout the...Ch. 22 - A conductor with an inner cavity, like that shown...Ch. 22 - A very large, horizontal, nonconducting sheet of...Ch. 22 - Apply Gausss law to the Gaussian surfaces S2, S3,...Ch. 22 - A square insulating sheet 80.0 cm on a side is...Ch. 22 - An infinitely long cylindrical conductor has...Ch. 22 - Two very large, nonconducting plastic sheets, each...Ch. 22 - CP At time t = 0 a proton is a distance of 0.360 m...Ch. 22 - CP A very small object with mass 8.20 109 kg and...Ch. 22 - CP A small sphere with mass 4.00 106 kg and...Ch. 22 - A cube has sides of length L = 0.300 m. One corner...Ch. 22 - The electric field E in Fig. P22.35 is everywhere...Ch. 22 - CALC In a region of space there is an electric...Ch. 22 - The electric field E1 at one face of a...Ch. 22 - A long line carrying a uniform linear charge...Ch. 22 - The Coaxial Cable. A long coaxial cable consists...Ch. 22 - A very long conducting tube (hollow cylinder) has...Ch. 22 - A very long, solid cylinder with radius R has...Ch. 22 - A Sphere in a Sphere. A solid conducting sphere...Ch. 22 - A solid conducting sphere with radius R that...Ch. 22 - A conducting spherical shell with inner radius a...Ch. 22 - Concentric Spherical Shells. A small conducting...Ch. 22 - Repeat Problem 22.45, but now let the outer shell...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.47PCh. 22 - A solid conducting sphere with radius R carries a...Ch. 22 - CALC An insulating hollow sphere has inner radius...Ch. 22 - CP Thomsons Model of the Atom. Early in the 20th...Ch. 22 - Thomsons Model of the Atom, Continued. Using...Ch. 22 - (a) How many excess electrons must be distributed...Ch. 22 - CALC A nonuniform, but spherically symmetric,...Ch. 22 - A Uniformly Charged Slab. A slab of insulating...Ch. 22 - CALC A Nonuniformly Charged Slab. Repeat Problem...Ch. 22 - CALC A nonuniform, but spherically symmetric,...Ch. 22 - (a) An insulating sphere with radius a has a...Ch. 22 - A very long, solid insulating cylinder has radius...Ch. 22 - DATA In one experiment the electric field is...Ch. 22 - DATA The electric field is measured for points at...Ch. 22 - DATA The volume charge density for a spherical...Ch. 22 - CP CALC A region in space contains a total...Ch. 22 - Suppose that to repel electrons in the radiation...Ch. 22 - What is the magnitude of E just outside the...Ch. 22 - SPACE RADIATION SHIELDING. One of the hazards...Ch. 22 - SPACE RADIATION SHIELDING. One of the hazards...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
To measure the heat capacity of an object, all you usually have to do is put it in thermal contact with another...
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
The Search for Life. Based on what you have learned about life on Earth, what are we searching for when we sear...
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
Write the SI unit for each abbreviation.
29. 27 mm
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
1. When is energy most evident?
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective
Choose the best answer to etch of the following. Explain your reasoning. Which of these stars is the most massi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A cylindrical metal can have a height of 27 cm and a radius of 11 cm. The electric field is directed outward along the entire surface of the can (including the top and bottom), with a uniform magnitude of 4.0x10^5 N/C. a.) What is the surface area of the cylinder?arrow_forwardA disk with a radius of 0.10 m is in a uniform electric field with a size E = 2x10 ^ 3 N / C. The normal unit vector of the disk makes an angle of 30 degrees with E. How much is the electric flux through the disk?arrow_forwardA solid insulating sphere of radius 0.06 cm carries a total charge of 30 nC. Concentric with this sphere is a conducting spherical shell with an inner radius of 0.13 cm and an outer radius of 0.17 cm and carrying a total charge of -15 nC. Find the magnitude of the electric field at r = 0.05 cm from the center of the two spheres and shell. O 1.248x105 A N O 1.248x108 N C 6.241x106 N O 6.241æ108 Narrow_forward
- A uniform electric field of magnitude 1.1 × 104 N/C is perpendicular to a square sheet with sides 2.0 m long. What is the electric flux through the sheet?arrow_forwarda circular surface with a radius of 0.061 m is exposed to a uniform electric field of magnitude 1.88E4 N/C. The electric flux through the surface is 77 Nm^2/C. What is the angle between the diraction of the electric field and the normal to the surfacearrow_forwardTwo parallel, infinitely long, z- axis oriented conducting cylinders of radius "a" are a distance "b" apart. "b" is much, much, greater than "a". One cylinder has a charge per unit length of pi on it, the other one has a charge per unit length of -Pi on it. The cylinders are in air. What is the approximate electric field at x = 103 "b" from the center of the two parallel cylinders?arrow_forward
- A solid metal cylinder of radius r = 1.9 cm is located coaxially inside a hollow metal cylinder of inner and outer radii rin = 13 cm and rout = 17 cm, respectively. Both cylinders have the same length L. Locations A and B are at distances da = 6.0 cm and dg = 24 cm, respectively. The electric fields at A and B are E = 1.25 x 10ªf N/C and Eg = -1.25 x 104f N/C, respectively. The diagram below shows the end view of the two cylinders. (a) What is the surface charge density on the outer surface of the inner cylinder? (b) What is the surface charge density on the inner surface of the outer cylinder? (c) What is the surface charge density on the outer surface of the outer cylinder?arrow_forwardA thin rod carries linear charge density according to the distribution X(z) = Aox/L, where Xo = 29.7 nC/cm and L is the length of the rod. The rod extends from x = 0 cm tc I=28 cm. What is the magnitude of the electric field at a location = 6.0 cm? (please provide your answer in kN/C to 1 decimal place) Type your answer.....arrow_forwardA 44.0-cm-diameter circular loop is rotated in a uniform electric field until the position of maximum electric flux is found. The flux in this position is measured to be 6.00 × 105 N. m²/C. What is the magnitude of the electric field?arrow_forward
- Figure P15.49 shows a closed cylinder with cross-sectional area A = 2.00 m². The con- stant electric field É has mag- nitude 3.50 x 10% N/C and is directed vertically upward, perpendicular to the cylinder's top and bottom surfaces so that no field lines pass through the curved surface. Calculate the electric flux through the cylinder's (a) top and (b) bottom surfaces. (c) Determine the amount of charge inside the cylinder. Figure P15.49arrow_forwardTwo conducting hollow spheres share a common center. The inner sphere has the radius a = 5.0 cm and charge +3.2x10-6 C. The outer sphere has the radius b = 32 cm and charge -4.0x10-6 C. What is the electric field (in N/C) at a point P, r = 20 cm from the center of the spheres?arrow_forwardThere is a rectangle of length 2.70 cm and width 1.50 cm in the xy-plane. If the electric field can be expressed by (50.0i^i^ +160. k^k^) N/C, what is the flux through the rectangle? 0.0648 N m2/C 0 N m2/C 0.0203 N m2/C 0.0679 N m2/Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY