
University Physics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133969290
Author: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 22.51P
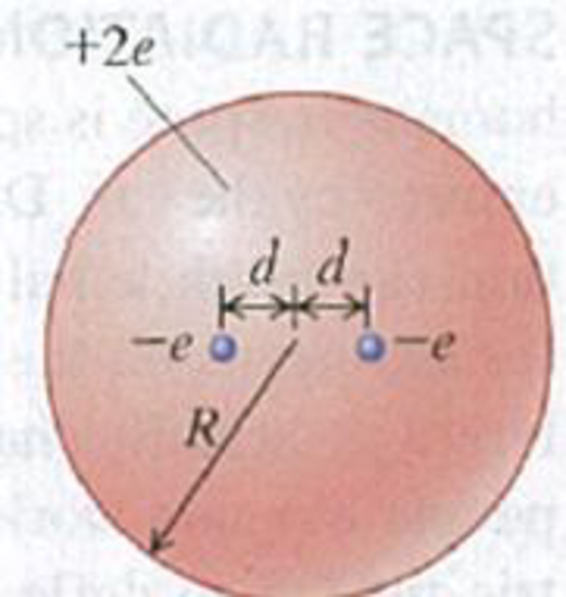
Thomson’s Model of the Atom, Continued. Using Thomson’s (outdated) model of (he atom described in Problem 22.50, consider an atom consisting of two electrons, each of charge −e, embedded in a sphere of charge +2e and radius R. In equilibrium, each electron is a distance d from the center of the atom (Fig. P22.51). Find the distanced in terms of the other properties of the atom.
Figure P22.51
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
2
3
Imagine you are out for a stroll on a sunny day when you encounter a lake. Unpolarized light from the sun is reflected off the lake into your eyes. However, you notice when you put on your vertically polarized sunglasses, the light reflected off the lake no longer reaches your eyes. What is the angle between the unpolarized light and the surface of the water, in degrees, measured from the horizontal? You may assume the index of refraction of air is nair=1 and the index of refraction of water is nwater=1.33 . Round your answer to three significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.
Chapter 22 Solutions
University Physics (14th Edition)
Ch. 22 - A rubber balloon has a single point charge in its...Ch. 22 - Suppose that in Fig. 22.15 both charges were...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22.15, suppose a third point charge were...Ch. 22 - A certain region of space bounded by an imaginary...Ch. 22 - A spherical Gaussian surface encloses a point...Ch. 22 - You find a sealed box on your doorstep. You...Ch. 22 - A solid copper sphere has a net positive charge....Ch. 22 - A spherical Gaussian surface encloses a point...Ch. 22 - In a conductor, one or more electrons from each...Ch. 22 - You charge up the Van de Graaff generator shown in...
Ch. 22 - Lightning is a flow of electrons. The lightning...Ch. 22 - A solid conductor has a cavity in its interior....Ch. 22 - Explain this statement: In a static situation, the...Ch. 22 - In a certain region of space, the electric field E...Ch. 22 - (a) In a certain region of space, the volume...Ch. 22 - A negative charge Q is placed inside the cavity of...Ch. 22 - A flat sheet of paper of area 0.250 m2 is oriented...Ch. 22 - A flat sheet is in the shape of a rectangle with...Ch. 22 - You measure an electric field of 1.25 106 N/C at...Ch. 22 - It was shown in Example 21.10 (Section 21.5) that...Ch. 22 - A hemispherical surface with radius r in a region...Ch. 22 - The cube in Fig. E22.6 has sides of length L =...Ch. 22 - BIO As discussed in Section 22.5, human nerve...Ch. 22 - The three small spheres shown in Fig. E22.8 carry...Ch. 22 - A charged paint is spread in a very thin uniform...Ch. 22 - A point charge q1 = 4.00 nC is located on the...Ch. 22 - C point charge is at the center of a cube with...Ch. 22 - Electric Fields in an Atom. The nuclei of large...Ch. 22 - Two very long uniform lines of charge are parallel...Ch. 22 - A solid metal sphere with radius 0.450 m carries a...Ch. 22 - How many excess electrons must be added to an...Ch. 22 - Some planetary scientists have suggested that the...Ch. 22 - A very long uniform line of charge has charge per...Ch. 22 - The electric field 0.400 m from a very long...Ch. 22 - A hollow, conducting sphere with an outer radius...Ch. 22 - (a) At a distance of 0.200 cm from the center or a...Ch. 22 - The electric field at a distance of 0.145 m from...Ch. 22 - A point charge of 3.00 C is located in the center...Ch. 22 - CP An electron is released from rest at a distance...Ch. 22 - Charge Q is distributed uniformly throughout the...Ch. 22 - A conductor with an inner cavity, like that shown...Ch. 22 - A very large, horizontal, nonconducting sheet of...Ch. 22 - Apply Gausss law to the Gaussian surfaces S2, S3,...Ch. 22 - A square insulating sheet 80.0 cm on a side is...Ch. 22 - An infinitely long cylindrical conductor has...Ch. 22 - Two very large, nonconducting plastic sheets, each...Ch. 22 - CP At time t = 0 a proton is a distance of 0.360 m...Ch. 22 - CP A very small object with mass 8.20 109 kg and...Ch. 22 - CP A small sphere with mass 4.00 106 kg and...Ch. 22 - A cube has sides of length L = 0.300 m. One corner...Ch. 22 - The electric field E in Fig. P22.35 is everywhere...Ch. 22 - CALC In a region of space there is an electric...Ch. 22 - The electric field E1 at one face of a...Ch. 22 - A long line carrying a uniform linear charge...Ch. 22 - The Coaxial Cable. A long coaxial cable consists...Ch. 22 - A very long conducting tube (hollow cylinder) has...Ch. 22 - A very long, solid cylinder with radius R has...Ch. 22 - A Sphere in a Sphere. A solid conducting sphere...Ch. 22 - A solid conducting sphere with radius R that...Ch. 22 - A conducting spherical shell with inner radius a...Ch. 22 - Concentric Spherical Shells. A small conducting...Ch. 22 - Repeat Problem 22.45, but now let the outer shell...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22.47PCh. 22 - A solid conducting sphere with radius R carries a...Ch. 22 - CALC An insulating hollow sphere has inner radius...Ch. 22 - CP Thomsons Model of the Atom. Early in the 20th...Ch. 22 - Thomsons Model of the Atom, Continued. Using...Ch. 22 - (a) How many excess electrons must be distributed...Ch. 22 - CALC A nonuniform, but spherically symmetric,...Ch. 22 - A Uniformly Charged Slab. A slab of insulating...Ch. 22 - CALC A Nonuniformly Charged Slab. Repeat Problem...Ch. 22 - CALC A nonuniform, but spherically symmetric,...Ch. 22 - (a) An insulating sphere with radius a has a...Ch. 22 - A very long, solid insulating cylinder has radius...Ch. 22 - DATA In one experiment the electric field is...Ch. 22 - DATA The electric field is measured for points at...Ch. 22 - DATA The volume charge density for a spherical...Ch. 22 - CP CALC A region in space contains a total...Ch. 22 - Suppose that to repel electrons in the radiation...Ch. 22 - What is the magnitude of E just outside the...Ch. 22 - SPACE RADIATION SHIELDING. One of the hazards...Ch. 22 - SPACE RADIATION SHIELDING. One of the hazards...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1.3 Obtain a bottle of multivitamins and read the list of ingredients. What are four chemicals from the list?
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
APPLY 1.2 Express the following quantities in scientific notation
using fundamental SI units of mass and lengt...
Chemistry (7th Edition)
With what geologic feature are the earthquakes in the mid-Atlantic associated?
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Give at least three examples of key ecosystem services that nature provides for people.
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Explain all answers clearly, with complete sentences and proper essay structure if needed. An asterisk (*) desi...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Match each of the following items with all the terms it applies to:
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on thesearrow_forward
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forward
- pls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY