
Concept explainers
Draw the product formed when pentanoyl chloride
a.
b.
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons is known as a nucleophile. In nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, a nucleophile takes the position of a leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
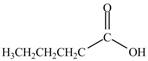
Explanation of Solution
Acyl chloride on reaction with
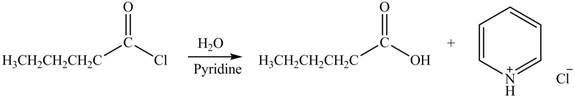
Figure 1
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons is known as a nucleophile. In nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, a nucleophile takes the position of a leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
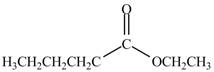
Explanation of Solution
The acyl chloride on reaction with alcohol converts into ester. The oxygen atom of alcoholic
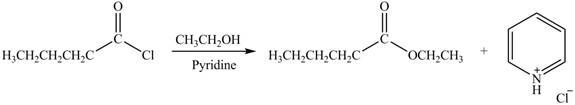
Figure 2
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons is known as a nucleophile. In nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, a nucleophile takes the position of a leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
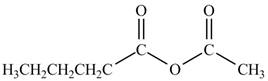
Explanation of Solution
The acyl chloride on reaction with acetate ion converts into acid anhydride. The oxygen atom of acetate ion contains negative charge. It undergoes nucleophilic attack on electron deficient carbonyl carbon atom and replaces chlorine atom. The reaction between pentanoyl chloride and
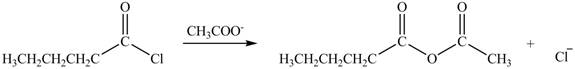
Figure 3
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
(d)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons is known as a nucleophile. In nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, a nucleophile takes the position of a leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
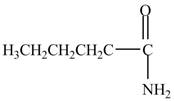
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of acyl chloride with ammonia
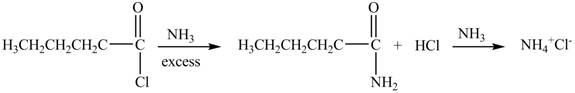
Figure 4
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
(e)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons is known as a nucleophile. In nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, a nucleophile takes the position of a leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
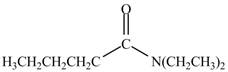
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of acyl chloride with secondary amine leads to the formation of amide. The nitrogen atom of
![]()
Figure 5
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
(f)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons is known as a nucleophile. In nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, a nucleophile takes the position of a leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.45P
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
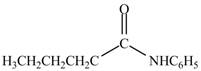
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of acyl chloride with primary amine leads to the formation of amide. The nitrogen atom of

Figure 6
The product formed by the treatment of pentanoyl chloride
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- Could you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but color-coded or step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you!arrow_forwardCould you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but (color-coded) and step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you! I want to see what they are doingarrow_forwardCan you please help mne with this problem. Im a visual person, so can you redraw it, potentislly color code and then as well explain it. I know im given CO2 use that to explain to me, as well as maybe give me a second example just to clarify even more with drawings (visuals) and explanations.arrow_forward
- Part 1. Aqueous 0.010M AgNO 3 is slowly added to a 50-ml solution containing both carbonate [co32-] = 0.105 M and sulfate [soy] = 0.164 M anions. Given the ksp of Ag2CO3 and Ag₂ soy below. Answer the ff: Ag₂ CO3 = 2 Ag+ caq) + co} (aq) ksp = 8.10 × 10-12 Ag₂SO4 = 2Ag+(aq) + soy² (aq) ksp = 1.20 × 10-5 a) which salt will precipitate first? (b) What % of the first anion precipitated will remain in the solution. by the time the second anion starts to precipitate? (c) What is the effect of low pH (more acidic) condition on the separate of the carbonate and sulfate anions via silver precipitation? What is the effect of high pH (more basic)? Provide appropriate explanation per answerarrow_forwardPart 4. Butanoic acid (ka= 1.52× 10-5) has a partition coefficient of 3.0 (favors benzene) when distributed bet. water and benzene. What is the formal concentration of butanoic acid in each phase when 0.10M aqueous butanoic acid is extracted w❘ 25 mL of benzene 100 mL of a) at pit 5.00 b) at pH 9.00arrow_forwardCalculate activation energy (Ea) from the following kinetic data: Temp (oC) Time (s) 23.0 180. 32.1 131 40.0 101 51.8 86.0 Group of answer choices 0.0269 kJ/mole 2610 kJ/mole 27.6 kJ/mole 0.215 kJ/mole 20.8 kJ/molearrow_forward
- Calculate activation energy (Ea) from the following kinetic data: Temp (oC) Time (s) 23.0 180. 32.1 131 40.0 101 51.8 86.0 choices: 0.0269 kJ/mole 2610 kJ/mole 27.6 kJ/mole 0.215 kJ/mole 20.8 kJ/molearrow_forwardCalculate activation energy (Ea) from the following kinetic data: Temp (oC) Time (s) 23.0 180. 32.1 131 40.0 101 51.8 86.0arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
