
(a)
Interpretation: The acceptable names for the given compounds are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
• The hydrocarbon is named after the longest carbon chain.
• The parent hydrocarbon containing ester group is named with suffix “ate”.
• The alkyl group bonded to oxygen through single bond forms the first part of the ester and alkyl group bonded to carbonyl group forms the second part.
Answer to Problem 22.38P
The acceptable name of the compound A is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound A is,
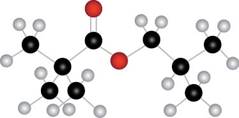
Figure 1
The red coloured ball has two bonds. So, this is the oxygen atom. The black coloured atoms have four single bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure of the compound is,
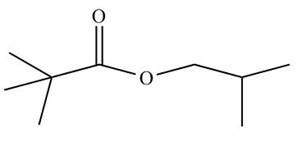
Figure 2
This compound contains ester group. The alkyl group attached to carbonyl group has longest chain of three carbon atoms with two methyl groups substituted at the second carbon atom. The alkyl group bonded to oxygen through single bond has longest chain of three carbon atoms with one methyl group substituted at the second carbon atom. The acceptable name of the compound is
The given compound B is,
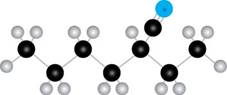
Figure 3
The blue coloured ball has three bonds. So, this is the nitrogen atom. The black coloured atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure of the compound is,
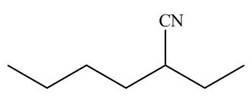
Figure 4
The given compound B contains longest chain of six carbon atoms with ethyl group substituted at the second carbon atom. The acceptable name of the compound is
The acceptable name of the compound A is
(b)
Interpretation: The products formed on treatment of A or B with given reagents: [1]
Concept introduction: The metal hydride reagents are good reducing agents such as
When the esters and nitriles are hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids in acidic medium and in basic medium carboxylate ions are formed.
Grignard reagents are organometallic compounds which are prepared using alkyl halides in the presence of magnesium metal in dry ether. These reagents act as strong nucleophiles and bases.
Answer to Problem 22.38P
The reaction of compound A with given reagents are shown below.
[1]
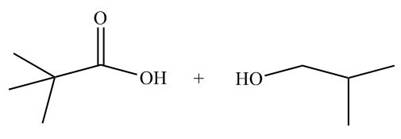
Figure 5
[2]
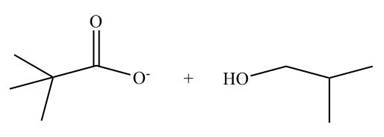
Figure 6
[3]
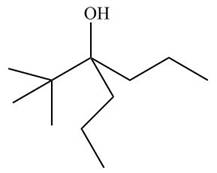
Figure 7
[4]
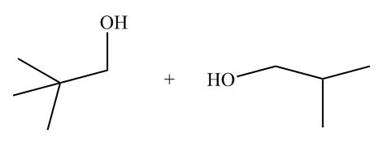
Figure 8
The reaction of compound B with given reagents are shown below.
[1]
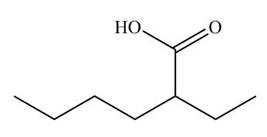
Figure 9
[2]
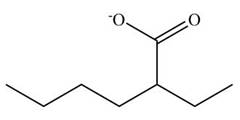
Figure 10
[3]
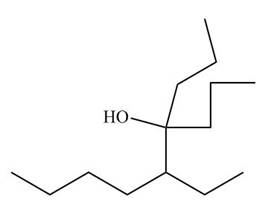
Figure 11
[4]
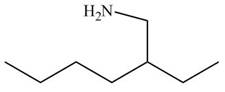
Figure 12
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of compound A with given reagents are shown below.
[1]
The ester group undergoes acidic hydrolysis to form alcohol and
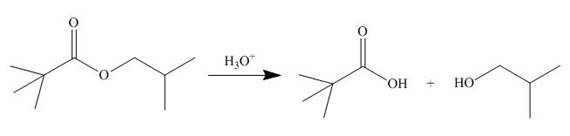
Figure 13
The products formed are
[2]
The ester group undergoes basic hydrolysis to form alcohol and carboxylic acid as shown below.
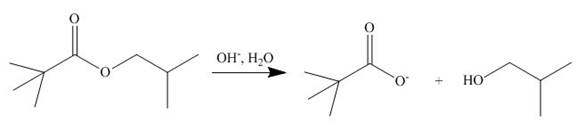
Figure 14
The products formed are
[3]
The given ester compound reacts with excess Grignard reagent followed by hydrolysis to form
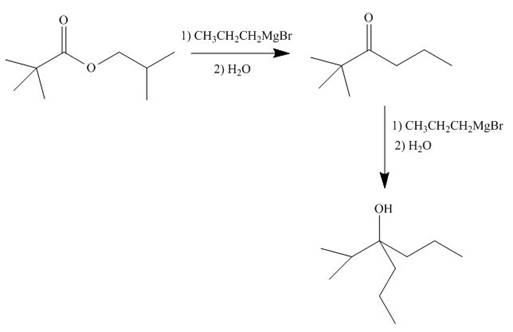
Figure 15
The product formed is form
[4]
In presence of lithium aluminium hydride, the ester group is reduced to two alcohols. The corresponding reaction is shown below.
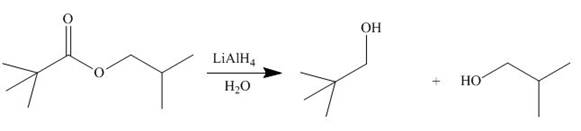
Figure 16
The products formed are
The reaction of compound B with given reagents are shown below.
[1]
The cyano group undergoes acidic hydrolysis to form carboxylic acid as shown below.
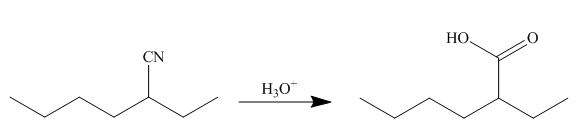
Figure 17
The products formed is
[2]
The cyano group undergoes basic hydrolysis to form carboxylate ion as shown below.
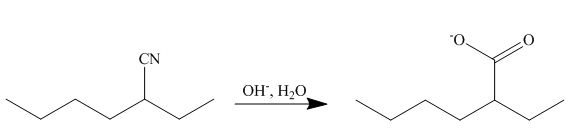
Figure 18
The product formed is
[3]
The nitrile compound reacts with Grignard reagent to form alcohol. The corresponding reaction is shown below.
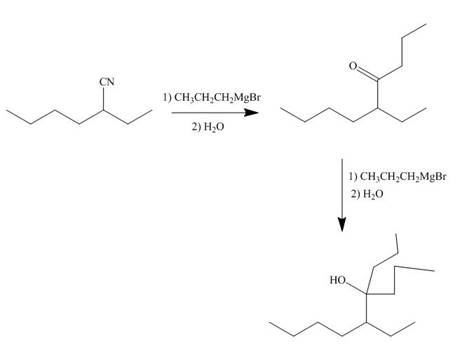
Figure 19
[4]
In the presence of lithium aluminium hydride, the ester group is reduced to two alcohols. The corresponding reaction is shown below.
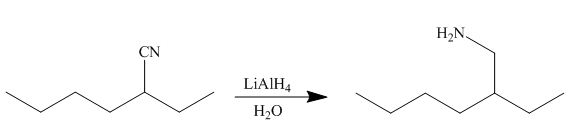
Figure 20
The product formed is
The products formed on treatment of A or B with given reagents: [1]
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- Draw the mechanism (including all curved arrows for electron movement) showing how the maleicanhydride is attacked by the anthracene and formation of the final Diels Alder product.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardI have a bottle of butanal that has been improperly used by lab workers. They allowed a traceamount NaOH (aq) to contaminate the bottle. What is now in my bottle of “butanal? What is the molecular name and functional group name? Draw the structure.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
- First image: Why can't the molecule C be formed in those conditions Second image: Synthesis for lactone C its not an examarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to show the mecanism for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion Second image: I have to show the mecanism of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primaryarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in those conditions. Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

