
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one
Answer to Problem 22.48P
No product is formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate with
Explanation of Solution
Esters do not undergo reaction with
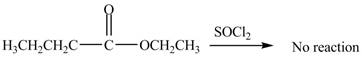
Figure 1
No product is formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate with
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons is known as a nucleophile. In nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, a nucleophile takes the position of a leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.48P
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
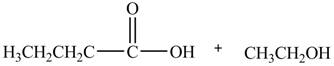
Explanation of Solution
Esters undergo hydrolysis under acidic and basic medium. In the given reaction, ester undergoes hydrolysis under acidic medium. One mole of

Figure 2
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons is known as a nucleophile. In nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, a nucleophile takes the position of a leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.48P
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
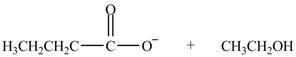
Explanation of Solution
Esters undergo hydrolysis under acidic and basic medium. In the given reaction, ester undergoes hydrolysis under basic medium. One mole of carboxylate ion and one mole of alcohol are produced from the hydrolysis of ethyl butanoate as shown in Figure 3.
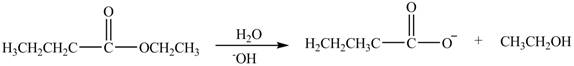
Figure 3
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
(d)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons is known as a nucleophile. In nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, a nucleophile takes the position of a leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.48P
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of ester with ammonia leads to the formation of amide and alcohol. The nitrogen atom of ammonia contains lone pair of electrons. The nitrogen atom acts as a nucleophile and attacks on the electron deficient carbonyl carbon atom of ester. The products formed by the reaction of ethyl butanoate with
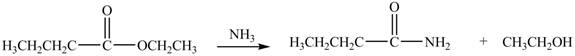
Figure 4
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
(e)
Interpretation:
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons is known as a nucleophile. In nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, a nucleophile takes the position of a leaving group.
Answer to Problem 22.48P
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
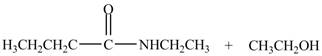
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of ester with primary
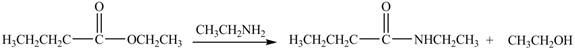
Figure 5
The product formed by the treatment of ethyl butanoate
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.200 M HClarrow_forwardCalculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
- Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


