
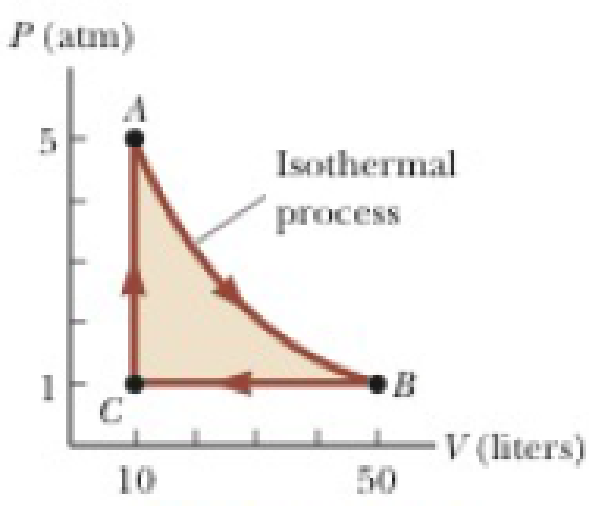
A 1.00-mol sample of an ideal monatomic gas is taken through the cycle shown in Figure P21.37. The process A → B is a reversible isothermal expansion. Calculate (a) the net work done by the gas, (b) the energy added to the gas by heat, (c) the energy exhausted from the gas by heat, and (d) the efficiency of the cycle. (e) Explain how the efficiency compares with that of a Carnot engine operating between the same temperature extremes.
Figure P21.37
(a)
The net work done by the gas.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The net work done by the gas is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The pressure and volume at A are
The formula for the net work done by the gas at
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the net work done by the gas at
The formula for the net work done by the gas at
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the net work done by the gas at BC is
The formula for the net work done by the gas at
As the change in the volume between processes
Thus, the net work done by the gas at
The formula for the total work done by the gas is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the total work done is
(b)
The energy added to the gas by heat.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The energy added to the gas by heat is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The pressure and volume at
The formula for the energy added by the gas in process
Substitute
Thus, the energy added by the gas in process
The formula for temperature at
Substitute
Thus, the temperature at
The formula for temperature at
Substitute
Thus, the temperature at
The formula for the energy added by the gas in process
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the energy added in process
The formula for the total energy added is,
Substitute
Thus, the total energy added is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the total energy added is
(c)
The energy exhausted from the gas by heat.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The energy exhausted from the gas by heat is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The pressure and volume at A are
The formula for the energy added by the gas in process
Substitute
Thus, the energy exhausted in process
Conclusion:
Therefore, the energy exhausted in process
(d)
The efficiency of the cycle.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The efficiency of the cycle is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The pressure and volume at A are
Formula to calculate the efficiency of the engine is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the efficiency of the engine is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the efficiency of the engine is
(e)
The comparison of efficiency to that of the Carnot engine.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The efficiency of Carnot engine is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The pressure and volume at A are
Formula to calculate the efficiency of the Carnot engine is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the efficiency of Carnot engine is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
- A square coil that has 17.5 cm on each side containing 17 loops lies flat on your desk as shown on this page. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 4.60 × 10-ST points into this page. If a 8.50-A clockwise Current flows through the coil. ca) determine the torque on the coil. N.m (b) which edge of the coil rises up? choose one 。 Bottom отор and explain. O Right • None of these О Left.arrow_forwardA circular loop of wire with a diameter of 13.0 cm is in the horizontal plane and carries of 1.70 A clockwise, as viewed from underneath. What is the magnitude magnetic field as the center of the loop? -T what is the direction of magnetic field at the center or down? please explain. of the loop? uparrow_forwardStarlord has a mass of 89.3 kg and Groot is pulling the bag with a force of 384. N at an angle of 35.0˚ as is shown in the figure below. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction if they are moving at a constant speed of 2.31 m/s?arrow_forward
- Early on in the video game Shadow of the Tomb Raider Lara Croft uses a winch to pull a heavy crate of stone up a 23.6° incline. If Lara causes the 66.0 kg crate to accelerate at 2.79 m/s2 up the ramp, what is the tension in the rope pulling the block? The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the ground is 0.503.arrow_forwardA player kicks a football at the start of the game. After a 4 second flight, the ball touches the ground 50 m from the kicking tee. Assume air resistance is negligible and the take-off and landing height are the same (i.e., time to peak = time to fall = ½ total flight time). (Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.) Calculate and answer all parts. Only use equations PROVIDED:arrow_forwardA shot putter releases a shot at 13 m/s at an angle of 42 degrees to the horizontal and from a height of 1.83 m above the ground. (Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.) Calculate and answer all parts. Only use equations PROVIDED:arrow_forward
- If a person jumps upwards with a vertical velocity of 5 m/s, What is their velocity 0.5 second into the jump?arrow_forwardA solid sphere 22 cm in radius carries 17 μC, distributed uniformly throughout its volume. Part A Find the electric field strength 12 cm from the sphere's center. Express your answer using two significant figures. E₁ = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ха Хь b Submit Previous Answers Request Answer <☑ × Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining ▾ Part B ? |X| X.10" <☑ Find the electric field strength 22 cm from the sphere's center. Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ E2 = Submit Request Answer ▾ Part C ? MN/C Find the electric field strength 44 cm from the sphere's center. Express your answer using two significant figures. ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ E3 = Submit Request Answer ? MN/C MN/Carrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forward
- In a naval battle, a battleship is attempting to fire on a destroyer. The battleship is a distance d1 = 2,150 m to the east of the peak of a mountain on an island, as shown in the figure below. The destroyer is attempting to evade cannon shells fired from the battleship by hiding on the west side of the island. The initial speed of the shells that the battleship fires is vi = 245 m/s. The peak of the mountain is h = 1,840 m above sea level, and the western shore of the island is a horizontal distance d2 = 250 m from the peak. What are the distances (in m), as measured from the western shore of the island, at which the destroyer will be safe from fire from the battleship? (Note the figure is not to scale. You may assume that the height and width of the destroyer are small compared to d1 and h.)arrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardThe law of reflection applies to Question 14Select one: a. specular reflection b. irregular reflection c. All of these d. diffuse reflectionarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





