
EBK MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING & TECHNOL
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780100793439
Author: KALPAKJIAN
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 75QTP
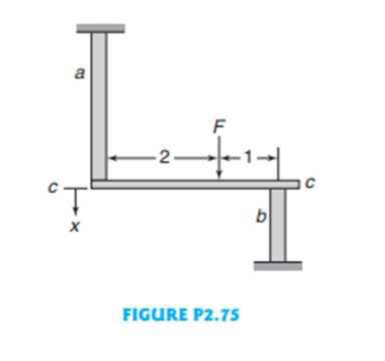
A horizontal rigid bar c–c is subjecting specimen a to tension and specimen b to frictionless compression such that the bar remains horizontal. (See Fig. P2.75.) The force F is located at a distance ratio of 2:1. Both specimens have an original cross-sectional area of 1 in2 and the original lengths are a = 8 in. and b = 4.5 in. The material for specimen a has a true stress–true strain curve of
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
100
As a spring is heated, its spring constant decreases. Suppose the spring is heated and then cooled so that the
spring constant at time t is k(t) = t sin + N/m. If the mass-spring system has mass m = 2 kg and a
damping constant b = 1 N-sec/m with initial conditions x(0) = 6 m and x'(0) = -5 m/sec and it is
subjected to the harmonic external force f (t) = 100 cos 3t N. Find at least the first four nonzero terms in
a power series expansion about t = 0, i.e. Maclaurin series expansion, for the displacement:
• Analytically (hand calculations)
Creating Simulink Model
Plot solutions for first two, three and four non-zero terms as well as the Simulink solution on the same graph
for the first 15 sec. The graph must be fully formatted by code.
Two springs and two masses are attached in a straight vertical line as shown in Figure Q3. The system is set
in motion by holding the mass m₂ at its equilibrium position and pushing the mass m₁ downwards of its
equilibrium position a distance 2 m and then releasing both masses. if m₁ = m² = 1 kg, k₁ = 3 N/m and
k₂ = 2 N/m.
(y₁ = 0)
www
k₁ = 3
Jm₁ = 1
k2=2
www
(Net change in
spring length
=32-31)
(y₂ = 0)
m₂ = 1
32
32
System in
static
equilibrium
System in
motion
Figure Q3 - Coupled mass-spring system
Determine the equations of motion y₁ (t) and y₂(t) for the two masses m₁ and m₂ respectively:
Analytically (hand calculations)
Using MATLAB Numerical Functions (ode45)
Creating Simulink Model
Produce an animation of the system for all solutions for the first minute.
Two large tanks, each holding 100 L of liquid, are interconnected by pipes, with the liquid flowing from tank
A into tank B at a rate of 3 L/min and from B into A at a rate of 1 L/min (see Figure Q1). The liquid inside each
tank is kept well stirred. A brine solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/L of salt flows into tank A at a rate of
6 L/min. The diluted solution flows out of the system from tank A at 4 L/min and from tank B at 2 L/min. If,
initially, tank A contains pure water and tank B contains 20 kg of salt.
A
6 L/min
0.2 kg/L
x(t)
100 L
4 L/min
x(0) = 0 kg
3 L/min
1 L/min
B
y(t)
100 L
y(0) = 20 kg
2 L/min
Figure Q1 - Mixing problem for interconnected tanks
Determine the mass of salt in each tank at time t≥ 0:
Analytically (hand calculations)
Using MATLAB Numerical Functions (ode45)
Creating Simulink Model
Plot all solutions on the same graph for the first 15 min. The graph must be fully formatted by code.
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING & TECHNOL
Ch. 2 - Distinguish between engineering stress and true...Ch. 2 - In a stress-strain curve, what is the proportional...Ch. 2 - Describe the events that take place when a...Ch. 2 - What is ductility, and how is it measured?Ch. 2 - In the equation =Kn, which represents the true...Ch. 2 - What is strain-rate sensitivity, and how is it...Ch. 2 - What test can measure the properties of a material...Ch. 2 - What testing procedures can be used to measure the...Ch. 2 - Describe the differences between brittle and...Ch. 2 - What is hardness? Explain.
Ch. 2 - Describe the features of a Rockwell hardness test.Ch. 2 - What is a Leeb test? How is it different from a...Ch. 2 - Differentiate between stress relaxation and creep.Ch. 2 - Describe the difference between elastic and...Ch. 2 - Explain what uniform elongation means in tension...Ch. 2 - Describe the difference between deformation rate...Ch. 2 - Describe the difficulties involved in conducting a...Ch. 2 - What is Hookes law? Youngs modulus? Poissons...Ch. 2 - Describe the difference between transgranular and...Ch. 2 - What is the reason that yield strength is...Ch. 2 - Why does the fatigue strength of a specimen or...Ch. 2 - If striations are observed under microscopic...Ch. 2 - What is an Izod test? Why are Izod tests useful?Ch. 2 - Why does temperature increase during plastic...Ch. 2 - What is residual stress? How can residual stresses...Ch. 2 - On the same scale for stress, the tensile true...Ch. 2 - What are the similarities and differences between...Ch. 2 - Can a material have a negative Poissons ratio?...Ch. 2 - It has been stated that the higher the value of m,...Ch. 2 - Explain why materials with high m values, such as...Ch. 2 - With a simple sketch, explain whether it is...Ch. 2 - Explain why the difference between engineering...Ch. 2 - Consider an elastomer, such as a rubber band. This...Ch. 2 - If a material (such as aluminum) does not have an...Ch. 2 - What role, if any, does friction play in a...Ch. 2 - Which hardness tests and scales would you use for...Ch. 2 - Consider the circumstance where a Vickers hardness...Ch. 2 - Which of the two tests, tension or compression,...Ch. 2 - List and explain briefly the conditions that...Ch. 2 - List the factors that you would consider in...Ch. 2 - On the basis of Fig. 2.5, can you calculate the...Ch. 2 - If a metal tension-test specimen is rapidly pulled...Ch. 2 - Comment on your observations regarding the...Ch. 2 - Will the disk test be applicable to a ductile...Ch. 2 - What hardness test is suitable for determining the...Ch. 2 - Wire rope consists of many wires that bend and...Ch. 2 - A statistical sampling of Rockwell C hardness...Ch. 2 - In a Brinell hardness test, the resulting...Ch. 2 - Some coatings are extremely thinsome as thin as a...Ch. 2 - Select an appropriate hardness test for each of...Ch. 2 - A paper clip is made of wire 0.5 mm in diameter....Ch. 2 - A 250-mm-long strip of metal is stretched in two...Ch. 2 - Identify the two materials in Fig. 2.5 that have...Ch. 2 - Plot the ultimate strength vs. stiffness for the...Ch. 2 - If you remove the layer of material ad from the...Ch. 2 - Prove that the true strain at necking equals the...Ch. 2 - Percent elongation is always defined in terms of...Ch. 2 - You are given the K and n values of two different...Ch. 2 - A cable is made of two strands of different...Ch. 2 - On the basis of the information given in Fig. 2.5,...Ch. 2 - In a disk test performed on a specimen 1.00 in. in...Ch. 2 - A piece of steel has a hardness of 300 HB....Ch. 2 - A metal has the following properties: UTS = 70,000...Ch. 2 - Using only Fig. 2.5, calculate the maximum load in...Ch. 2 - Estimate the modulus of resilience for a highly...Ch. 2 - A metal has a strength coefficient K = 100,000 psi...Ch. 2 - Plot the true stresstrue strain curves for the...Ch. 2 - The design specification for a metal requires a...Ch. 2 - Calculate the major and minor pyramid angles for a...Ch. 2 - If a material has a target hardness of 300 HB,...Ch. 2 - A Rockwell A test was conducted on a material and...Ch. 2 - For a cold-drawn 0.5% carbon steel, will a...Ch. 2 - A material is tested in tension. Over a 1-in. gage...Ch. 2 - A horizontal rigid bar cc is subjecting specimen a...Ch. 2 - List and explain the desirable mechanical...Ch. 2 - When making a hamburger, you may have observed the...Ch. 2 - An inexpensive claylike material called Silly...Ch. 2 - In tension testing of specimens, mechanical and...Ch. 2 - Demonstrate the impact toughness of a piece of...Ch. 2 - Using a large rubber band and a set of weights,...Ch. 2 - Find or prepare some solid circular pieces of...Ch. 2 - Take several rubber bands and pull them at...Ch. 2 - Devise a simple fixture for conducting the bend...Ch. 2 - By pressing a small ball bearing against the top...Ch. 2 - Describe your observations regarding Fig. 2.14c.Ch. 2 - Embed a small steel ball in a soft block of...Ch. 2 - Devise a simple experiment, and perform tests on...Ch. 2 - Obtain some solid and some tubular metal pieces,...Ch. 2 - Explain how you would obtain an estimate of the...Ch. 2 - Without using the words stress or strain, define...Ch. 2 - We know that it is relatively easy to subject a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. Estimate the friction pressure gradient in a 10.15 cm bore unheated horizontal pipe for the following conditions: Fluid-propylene Pressure 8.175 bar Temperature-7°C Mass flow of liquid-2.42 kg/s. Density of liquid-530 kg/m³ Mass flow of vapour-0.605 kg/s. Density of vapour-1.48 kg/m³arrow_forwardDescribe the following HVAC systems. a) All-air systems b) All-water systems c) Air-water systems Graphically represent each system with a sketch.arrow_forwardTwo large tanks, each holding 100 L of liquid, are interconnected by pipes, with the liquid flowing from tank A into tank B at a rate of 3 L/min and from B into A at a rate of 1 L/min (see Figure Q1). The liquid inside each tank is kept well stirred. A brine solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/L of salt flows into tank A at a rate of 6 L/min. The diluted solution flows out of the system from tank A at 4 L/min and from tank B at 2 L/min. If, initially, tank A contains pure water and tank B contains 20 kg of salt. A 6 L/min 0.2 kg/L x(t) 100 L 4 L/min x(0) = 0 kg 3 L/min 1 L/min B y(t) 100 L y(0) = 20 kg 2 L/min Figure Q1 - Mixing problem for interconnected tanks Determine the mass of salt in each tank at time t≥ 0: Analytically (hand calculations) Using MATLAB Numerical Functions (ode45) Creating Simulink Model Plot all solutions on the same graph for the first 15 min. The graph must be fully formatted by code.arrow_forward
- ased on the corresponding mass flow rates (and NOT the original volumetric flow rates) determine: a) The mass flow rate of the mixed air (i.e., the combination of the two flows) leaving the chamber in kg/s. b) The temperature of the mixed air leaving the chamber. Please use PyscPro software for solving this question. Notes: For part (a), you will first need to find the density or specific volume for each state (density = 1/specific volume). The units the 'v' and 'a' are intended as subscripts: · kgv = kg_v = kgv = kilogram(s) [vapour] kga = kg_a =kga = kilogram(s) [air]arrow_forwardThe answers to this question s wasn't properly given, I need expert handwritten solutionsarrow_forwardI need expert handwritten solutions to this onlyarrow_forward
- Two large tanks, each holding 100 L of liquid, are interconnected by pipes, with the liquid flowing from tank A into tank B at a rate of 3 L/min and from B into A at a rate of 1 L/min (see Figure Q1). The liquid inside each tank is kept well stirred. A brine solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/L of salt flows into tank A at a rate of 6 L/min. The diluted solution flows out of the system from tank A at 4 L/min and from tank B at 2 L/min. If, initially, tank A contains pure water and tank B contains 20 kg of salt. A 6 L/min 0.2 kg/L x(t) 100 L 4 L/min x(0) = 0 kg 3 L/min B y(t) 100 L y(0) = 20 kg 2 L/min 1 L/min Figure Q1 - Mixing problem for interconnected tanks Determine the mass of salt in each tank at time t > 0: Analytically (hand calculations)arrow_forwardTwo springs and two masses are attached in a straight vertical line as shown in Figure Q3. The system is set in motion by holding the mass m₂ at its equilibrium position and pushing the mass m₁ downwards of its equilibrium position a distance 2 m and then releasing both masses. if m₁ = m₂ = 1 kg, k₁ = 3 N/m and k₂ = 2 N/m. www.m k₁ = 3 (y₁ = 0). m₁ = 1 k2=2 (y₂ = 0) |m₂ = 1 Y2 y 2 System in static equilibrium (Net change in spring length =32-31) System in motion Figure Q3 - Coupled mass-spring system Determine the equations of motion y₁(t) and y₂(t) for the two masses m₁ and m₂ respectively: Analytically (hand calculations)arrow_forward100 As a spring is heated, its spring constant decreases. Suppose the spring is heated and then cooled so that the spring constant at time t is k(t) = t sin N/m. If the mass-spring system has mass m = 2 kg and a damping constant b = 1 N-sec/m with initial conditions x(0) = 6 m and x'(0) = -5 m/sec and it is subjected to the harmonic external force f(t) = 100 cos 3t N. Find at least the first four nonzero terms in a power series expansion about t = 0, i.e. Maclaurin series expansion, for the displacement: Analytically (hand calculations)arrow_forward
- this is answer to a vibrations question. in the last part it states an assumption of x2, im not sure where this assumption comes from. an answer would be greatly appreciatedarrow_forwardPlease answer with the sketches.arrow_forwardThe beam is made of elastic perfectly plastic material. Determine the shape factor for the cross section of the beam (Figure Q3). [Take σy = 250 MPa, yNA = 110.94 mm, I = 78.08 x 106 mm²] y 25 mm 75 mm I 25 mm 200 mm 25 mm 125 Figure Q3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Failure Theories (Tresca, von Mises etc...); Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xkbQnBAOFEg;License: Standard youtube license