
Concept explainers
A function f has the following verbal description: “Subtract 2, then cube the result.”
- (a) Find a formula that expresses f algebraically.
- (b) Make a table of values of f, for the inputs −1, 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4.
- (c) Sketch a graph of f, using the table of values from part (b) to help you.
- (d) How do we know that f has an inverse? Give a verbal description for f−1.
- (e) Find a formula that expresses f−1 algebraically.
(a)
To find: The formula that expresses f algebraically.
Answer to Problem 3T
The formula that expresses f algebraically is
Explanation of Solution
The given description is that “subtract 2, then cube the result”,
Let the function bex,
Subtract 2 from the function.
Cube the result of the above function.
Hence, the formula that expresses f algebraically is
(b)
To find: The values of f at the given inputs.
Answer to Problem 3T
The formula that expresses f algebraically is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given inputs are
Calculations:
From part (a) the formula is,
Substitute
The value of
Substitute
The value of
Substitute
The value of
Substitute
The value of
Substitute
The value of
Substitute
The value of
The value of
Write all the value in the table,
| x | y |
|
|
|
| 0 |
|
| 1 |
|
| 2 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 8 |
(c)
To sketch: The graph of f using the table values of part (b).
Explanation of Solution
From the part (b) plot all the points and connect the points to make a smooth curve.
The graph of f is shown in Figure (1),
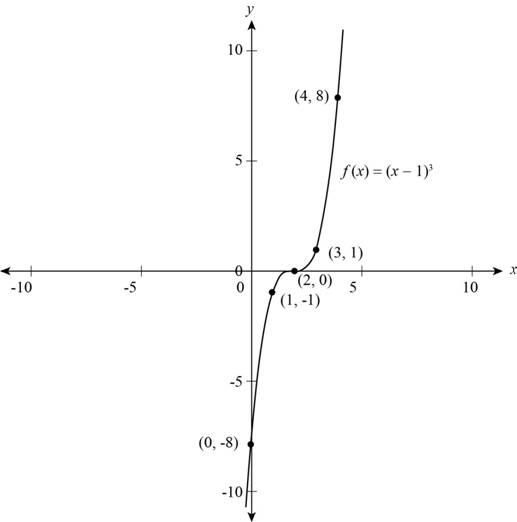
Figure (1)
Thus, Figure (1) shows the graph of function.
(d)
To explain: The f has inverse and verbal description for
Answer to Problem 3T
Inverse can check by horizontal line test and verbal description for
Explanation of Solution
Check by horizontal line test,
The given function is,
Take cube root of both side,
Add 2 on both side,
So, the inverse of f is
Inverse can check by horizontal line test and verbal description for
(e)
To find: The formula for algebraic expression of
Answer to Problem 3T
The inverse of f is
Explanation of Solution
From part (a) the function is,
Take cube root on both side of the function,
Add 2 on both sides of the function,
Hence, the inverse of f is
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS: MATHEMATICS FOR CALCUL
- Use Euler's method to numerically integrate dy dx -2x+12x² - 20x +8.5 from x=0 to x=4 with a step size of 0.5. The initial condition at x=0 is y=1. Recall that the exact solution is given by y = -0.5x+4x³- 10x² + 8.5x+1arrow_forwardFind an equation of the line tangent to the graph of f(x) = (5x-9)(x+4) at (2,6).arrow_forwardFind the point on the graph of the given function at which the slope of the tangent line is the given slope. 2 f(x)=8x²+4x-7; slope of the tangent line = -3arrow_forward
- please dont use chat gptarrow_forwardQuestion Given the graph of f(z) below, identify the graph of f'(z). Select the correct answer below: -7-6-5-4-3-2 1 2 3 4 5 6 + 123. -7-6-5-4-3 12 + 4-3-2-1 1arrow_forwardFind this expression in frequency domain in a expression y(t), in time, that is.arrow_forward
- please dont use chat gptarrow_forwardQuestion Given the graph of f(z) below, find the graph of the derivative of f(z). Select the correct answer below: ° 7-6-5-4-3 123 ° ° 2 -7-6-5-4-3- 123 -° 2-4 -°- °- -7-6-5-4-3-2-1 1 5 +arrow_forwardWhich of the functions shown below is differentiable at = 0? Select the correct answer below: -7-6-5-4- -6-5-4-3-21, -7-6-5-4-3-2 -7-6-5-4-3-2-1 2 4 5 6 -1arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





