
Concept explainers
- a. List the following alcohols in order from strongest acid to weakest acid:
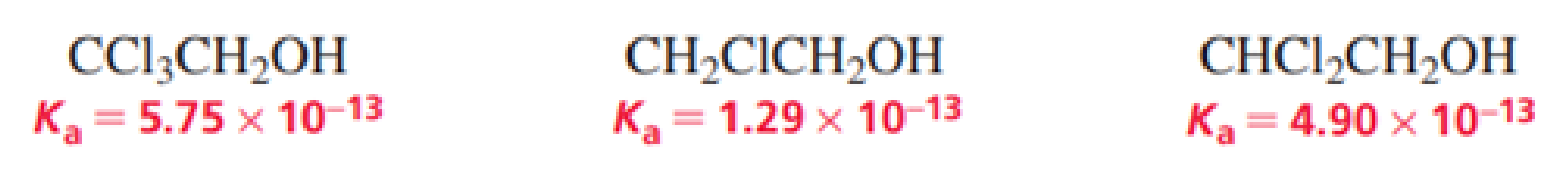
- b. Explain the relative acidities.
(a)
Interpretation:
The given alcohols have to be ranked from strongest to weakest acid.
Concept introduction:
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
If an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base. Weak base forms stronger conjugated acid.
Acidity of species depends on the electronegativity of atom attached to the acidic proton. Order of electronegativity of hybridization is
Acid dissociation constant
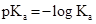
The strength of acid increases as the value of
Answer to Problem 38P
The given alcohols are ranked from strongest to weakest acid as follows,
Explanation of Solution
In hydrocarbons, if hydrogen atoms are replaced by electronegative atoms, it causes inductive electron withdrawal. It stabilizes its conjugate base thus increases the strength of the acid. The conjugated base of a weak acid is very strong. As the electronegativity of substituent increases, the greater will be the inductive electron withdrawal of the substituent making it a strong acid.
Therefore, the acidity order is:
The compound with three chlorine atoms near to the
The alcohol with high
(b)
Interpretation:
The relative acidities of the given alcohol compounds have to be explained briefly.
Concept introduction:
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
If an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base. Weak base forms stronger conjugated acid.
Acidity of species depends on the electronegativity of atom attached to the acidic proton. Order of electronegativity of hybridization is
Explanation of Solution
In hydrocarbons, if hydrogen atoms are replaced by electronegative atoms, it causes inductive electron withdrawal. It stabilizes its conjugate base thus increases the strength of the acid. The electron density near
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
- can someone draw out the reaction mechanism for this reaction showing all bonds, intermediates and side products Comment on the general features of the 1H-NMR spectrum of isoamyl ester provided belowarrow_forwardWhat would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1. PPh3 3 2. n-BuLi • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardIdentify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: X + Y H+ two steps Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H2O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х :arrow_forward
- I am struggling with the IUPAC (sys H Reply ☑Mark as Unreadarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solution and correct answerarrow_forwardH R Part: 1/2 :CI: is a/an electrophile Part 2 of 2 Draw the skeletal structure of the product(s) for the Lewis acid-base reaction. Include lone pairs and formal charges (if applicable) on the structures. 4-7: H ö- H Skip Part Check X :C1: $ % L Fi Click and drag to start drawing a structure. MacBook Pro & ㅁ x G 0: P Add or increase positive formal cha Save For Later Submit ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forward
- Draw the friedel-crafts acylation mechanism of m-Xylenearrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward1. Base on this experimental results, how do you know that the product which you are turning in is methyl 3-nitrobenzoate(meta substituted product ) rather than either of the other two products? 2. What observation suggests that at least a small amount of one or both of the other two isomers are in the mother liquor?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
