
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781292089034
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.6, Problem 18P
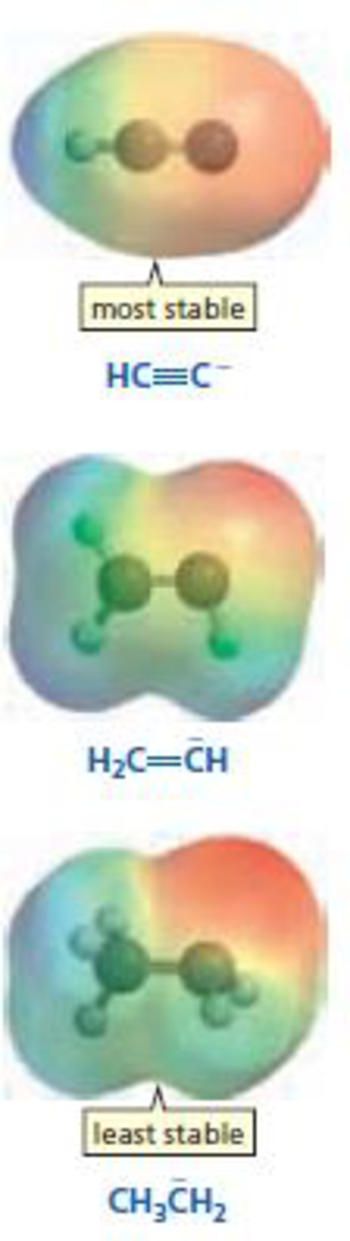
List the carbanions shown in the margin in order from most basic to least basic.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
None
Draw the Lewis structure of C2H4O
a)
5. Circle all acidic (and anticoplanar to the Leaving group) protons in the
following molecules, Solve these elimination reactions, and identify the
major and minor products where appropriate: 20 points
+
NaOCH3
Br
(2 product
Chapter 2 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
Ch. 2.1 - Which of the following are not acids? CH3COOH CO2...Ch. 2.1 - Draw the products of the acidbase reaction when a....Ch. 2.1 - a.What is the conjugate acid of each of the...Ch. 2.2 - a. Which is a stronger acid, one with a pKa of 5.2...Ch. 2.2 - Prob. 5PCh. 2.2 - Antacids are compounds that neutralize stomach...Ch. 2.2 - Are the following body fluids acidic or basic? a....Ch. 2.3 - Draw the conjugate acid of each of the following:...Ch. 2.3 - a. Write an equation showing CH3OH reacting as an...Ch. 2.3 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 2.3 - a. Which is a stronger base, CH3COO or HCOO? (The...Ch. 2.3 - Using the pKa values in Section 2.3, rank the...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 13PCh. 2.5 - Prob. 14PCh. 2.5 - Ethyne has a pKa value of 25, water has a pKa...Ch. 2.5 - Which of the following bases can remove a proton...Ch. 2.6 - List the ions (CH3, NH2, HO, and F) in order from...Ch. 2.6 - List the carbanions shown in the margin in order...Ch. 2.6 - Which is a stronger acid?Ch. 2.6 - a. Draw the products of the following reactions: A...Ch. 2.6 - List the halide ions (F, Cl, Br, and I) in order...Ch. 2.6 - a. Which is more electronegative, oxygen or...Ch. 2.6 - Which is a stronger acid? a. HCl or HBr b....Ch. 2.6 - a. Which of the halide ions (F, Cl, Br, and I) is...Ch. 2.6 - Which is a stronger base? a. H2O or HO b. H2O or...Ch. 2.7 - Which is a stronger acid? a. CH3OCH2CH2OH or...Ch. 2.7 - Which is a stronger base?Ch. 2.8 - Fosamax has six acidic groups. The structure of...Ch. 2.8 - Which is a stronger acid? Why?Ch. 2.10 - For each of the following compounds (shown in...Ch. 2.10 - Prob. 33PCh. 2.11 - Write the equation that shows how a buffer made by...Ch. 2.11 - What products are formed when each of the...Ch. 2 - a. List the following alcohols in order from...Ch. 2 - Which is a stronger base? a. HS or HO b. CH3O or...Ch. 2 - Prob. 40PCh. 2 - a. List the following carboxylic acids in order...Ch. 2 - For the following compound, a. draw its conjugate...Ch. 2 - List the following compounds in order from...Ch. 2 - For each of the following compounds, draw the form...Ch. 2 - Give the products of the following acidbase...Ch. 2 - Prob. 46PCh. 2 - For each compound, indicate the atom that is most...Ch. 2 - Tenormin, a member of the group of drugs known as...Ch. 2 - From which acids can HO remove a proton in a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 50PCh. 2 - Which is a stronger acid? a. CH29CHCOOH or...Ch. 2 - Prob. 52PCh. 2 - Prob. 53PCh. 2 - How could you separate a mixture of the following...Ch. 2 - Prob. 1PCh. 2 - Prob. 2PCh. 2 - Draw the products of the following acidbase...Ch. 2 - Prob. 4PCh. 2 - Prob. 5PCh. 2 - Prob. 6PCh. 2 - Prob. 7PCh. 2 - Prob. 8PCh. 2 - Prob. 9PCh. 2 - Prob. 10PCh. 2 - Prob. 11PCh. 2 - Prob. 12PCh. 2 - Prob. 13PCh. 2 - Prob. 14P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Nonearrow_forwardDr. Mendel asked his BIOL 260 class what their height was and what their parent's heights were. He plotted that data in the graph below to determine if height was a heritable trait. A. Is height a heritable trait? If yes, what is the heritability value? (2 pts) B. If the phenotypic variation is 30, what is the variation due to additive alleles? (2 pts) Offspring Height (Inches) 75 67.5 60 52.5 y = 0.9264x + 4.8519 55 60 65 MidParent Height (Inches) 70 75 12pt v V Paragraph B IUA > AT2 v Varrow_forwardExperiment: Each team will be provided with 5g of a mixture of acetanilide and salicylic acid. You will divide it into three 1.5 g portions in separate 125 mL Erlenmeyer flasks savıng some for melting point analysis. Dissolve the mixture in each flask in ~60mL of DI water by heating to boiling on a hotplate. Take the flasks off the hotplate once you have a clear solution and let them stand on the bench top for 5 mins and then allow them to cool as described below. Sample A-Let the first sample cool slowly to room temperature by letting it stand on your lab bench, with occasional stirring to promote crystallization. Sample B-Cool the second sample 1n a tap-water bath to 10-15 °C Sample C-Cool the third sample in an ice-bath to 0-2 °C Results: weight after recrystalization and melting point temp. A=0.624g,102-115° B=0.765g, 80-105° C=1.135g, 77-108 What is the percent yield of A,B, and C.arrow_forward
- Rel. Intensity Q 1. Which one of the following is true of the compound whose mass spectrum is shown here? Explain how you decided. 100 a) It contains chlorine. b) It contains bromine. c) It contains neither chlorine nor bromine. 80- 60- 40- 20- 0.0 0.0 TT 40 80 120 160 m/z 2. Using the Table of IR Absorptions how could you distinguish between these two compounds in the IR? What absorbance would one compound have that the other compound does not? HO CIarrow_forwardIllustrate reaction mechanisms of alkenes with water in the presence of H2SO4, detailing each step of the process. Please show steps of processing. Please do both, I will thumb up for sure #1 #3arrow_forwardDraw the following molecule: (Z)-1-chloro-1-butenearrow_forward
- Identify the molecule as having a(n) E, Z, cis, or trans configuration. CH3 H₁₂C ○ E ○ z ○ cis transarrow_forwardIdentify the molecule as having a(n) E, Z, cis, or trans configuration. H₂C- CH3 О Е ○ cis ○ transarrow_forwardThe decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide according to the equation: 50°C 2 N2O5(g) 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) follows first-order kinetics with a rate constant of 0.0065 s-1. If the initial concentration of N2O5 is 0.275 M, determine: the final concentration of N2O5 after 180 seconds. ...arrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardCS2(g) →CS(g) + S(g) The rate law is Rate = k[CS2] where k = 1.6 × 10−6 s−¹. S What is the concentration of CS2 after 5 hours if the initial concentration is 0.25 M?arrow_forwardCS2(g) → CS(g) + S(g) The rate law is Rate = k [CS2] where k = 1.6 × 10-6 s−1. S Calculate the half-life.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning



Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry | Acids & Bases; Author: Ninja Nerd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AOr_5tbgfQ0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY