
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of formate ion
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure represents covalent bonds and describes valence electrons configuration of atoms. The covalent bonds are depicted by lines and unshared electron pairs by pairs of dots. The sequence to write Lewis structure of some molecule is given as follows:
- The central atom is identified and various other atoms are arranged around it. This central atom so chosen is often the least electronegative.
- Total valence electrons are estimated for each atom.
- single bond is first placed between each atom pair.
- The electrons left can be allocated as unshared electron pairs or as multiple bonds around
symbol of element to satisfy the octet (or duplet) for each atom. - Add charge on the overall structure in case of polyatomic cation or anion.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The molecule
The symbol for carbon is
The symbol for hydrogen is
The symbol for oxygen is
One negative charge on molecule is added up as one valence electron in the total count.
Thus total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons for each atom in
The skeleton structure
To complete the valence electrons of carbon, it forms a double bond with one oxygen atom.
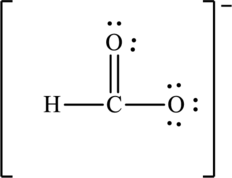
Hence, 10 electrons are allocated as 3 lone pairs on singly bonded oxygen atom and two lone pairs on doubly bonded oxygen atom. The Lewis structure of
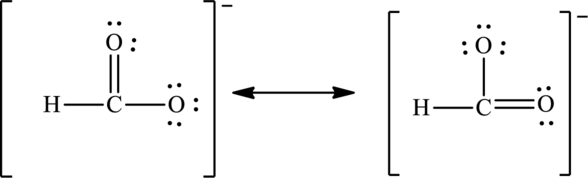
The negative charge on molecule is delocalized on each oxygen atom and since there are two oxygen atoms, therefore, two resonance structures are formed and possible resonance structures are as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of hydrogen phosphite ion
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The molecule
The symbol for oxygen is
The symbol for hydrogen is
The symbol for phosphorus is
Two negative charges on molecule are added up as two valence electrons in the total count.
Thus total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons for each atom in
The skeleton structure
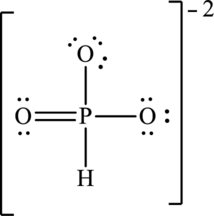
Hence, 18 electrons are allocated as 3 lone pairs on two singly bonded oxygen atoms and 2 lone pairs on doubly bonded oxygen atom to complete their octet. The Lewis structure is as follows:
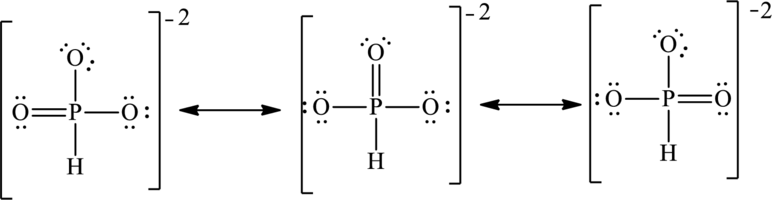
The negative charge on molecule is delocalized on three oxygen atoms therefore three resonance structures will be formed and possible resonance structures are as follows:
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of bromate ion
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The molecule
The symbol for oxygen is
The symbol for bromine is
One negative charge on molecule is added up to the total valence count.
Thus total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons for each atom in
The skeleton structure
To complete the valence electrons of bromine it forms two double bonds with two oxygen atoms.
Hence, 16 electrons are allocated as 3 lone pairs on the singly bonded oxygen atom, 2 lone pairs on doubly bonded oxygen atom and 1 lone pair on bromine to complete their respective octet. The Lewis structure is as follows:
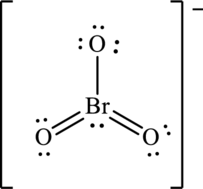
The negative charge on molecule participates in resonance by resonating on each oxygen atom. Since there are three oxygen atoms, therefore three resonating structures are drawn as:
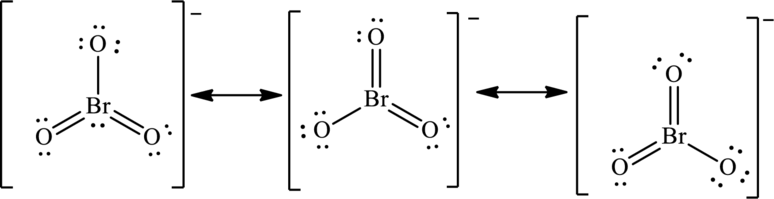
(d)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of selenate ion
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The molecule
The symbol for oxygen is
The symbol for selenium is
Two negative charges on molecule are added up as two valence electrons in the total count
Thus total valence electrons are sum of the valence electrons for each atom in
The skeleton structure
To complete the valence electrons of selenium, it forms double bond with two oxygen atom.
Hence, 20 electrons are allocated as 3 lone pairs on singly bonded oxygen atoms and 3 lone pairs on doubly bonded oxygen atoms to complete their octet. The Lewis structure is as follows:
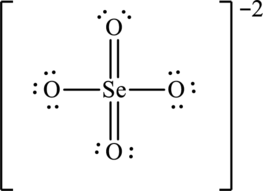
The two negative charges on molecule are delocalized on two oxygen atoms and since there are four oxygen atoms, therefore, four resonance structures will be formed and possible resonance structures are as follows:
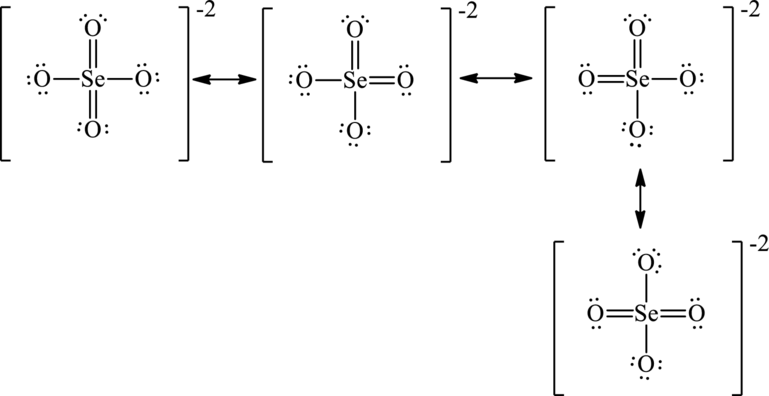
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
CHEM PRINCIPLES LL W/ACHIEVE ONE-SEM
- What is the hydronium ion concentration in a solution of water that has a hydroxide ion concentrationof 1.0 x 10-2 M?arrow_forwardIdentify conjugate acid-base pairs in the following reactions:HBr (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ H3O+ (aq) + Br- (aq) - OH (aq) + CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ H2O (l) + CH3COO- (aq)arrow_forward4:45 PM Tue Apr 1 K 77% Problem 9 of 10 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting structure, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Then draw any missing organic intermediates or products for this reaction. Include all lone pairs in the structures. Ignore inorganic byproducts, counterions, and solvents. :0: H Select to Add Arrows HI CH3OH H+ ·HO CH3OH, H+ 0:0 H H Select to Add Arrows tion Versirate CH3OH, H* Select to Draw Productarrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this graph? If you can show exactly where it needs to pass through.arrow_forwardG 1. PPh3, THF 2. 3. LiH, THF ' THF H Harrow_forwardPlease EnCircle or Fill-In your Choice CLEARLY: 21. Please Sketch the intermediates for each step below. Draw the Product which would result from the following series of reactions. Name each Type of Rx: 1. Br2, FeBr3 2. Mg, ether 3. ethylene oxide 4. H₂O+ 5. PBr3 6. Mg, ether 7. 8. H3O+, heat (-H₂O 9. HF ?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this question. All required information should be in data table.arrow_forwardesc For the reaction below: 1. Draw all reasonable elimination products to the right of the arrow. 2. In the box below the reaction, redraw any product you expect to be a major product. Major Product: Explanation Check C ☐ + X NaOH Br F1 F2 80 F3 F4 F5 F6 1 ! @ 2 3 $ 4 % 5 Q W LU E S D A F7 * C Click and dr drawing a 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserv ►II F8 4 F9 6 7 8 9 R T Y U LL F G H Jarrow_forwardCalculate equilibrium concentrations for the following reaction:N2 (g) + O2 (g) ⇋ 2 NO (g) Kc = 0.10 at 2273K initially [N2] = 0.200M; [O2] = 0.200arrow_forward
- For each scenario below, select the color of the solution using the indicator thymol blue during the titration. When you first add indicator to your Na2CO3solution, the solution is basic (pH ~10), and the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . At the equivalence point for the titration, the moles of added HCl are equal to the moles of Na2CO3. One drop (or less!) past this is called the endpoint. The added HCl begins to titrate the thymol blue indicator itself. At the endpoint, the indicator color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you weren't paying attention and added too much HCl (~12 mL extra), the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you really weren't paying attention and reached the second equivalence point of Na2CO3, the color isarrow_forwardThe following reaction is run in which the initial conditions include only methane (CH4) at a concentration of0.115 M. Once equilibrium was established, the concentration of acetylene (C2H2) was measured to be 0.035M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant, K?2 CH4 (g) ⇋ C2H2 (g) + 3 H2 (g)arrow_forwardCalculate the equilibrium concentration of carbon dioxide for the following reaction:2 COF2 (g) ⇋ CF4 (g) + CO2 (g) Kc = 2.00 at 10.00 °C. at equilibrium [COF2] = 0.255M; [CF4] = 0.118Marrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
