
EBK ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220106714201
Author: HAMBLEY
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.6PT
According to the superposition principle, what percentage of the total current flowing through the 5-
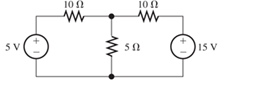
Figure T2.6
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Question 2
A transistor is used as a switch and the waveforms are shown in Figure 2. The parameters are
Vcc = 225 V, VBE(sat) = 3 V, IB = 8 A, VCE(sat) = 2 V, Ics = 90 A, td = 0.5 µs, tr = 1 µs, ts = 3 µs, tƒ
= 2 μs, and f
10 kHz. The duty cycle is k 50%. The collector- emitter leakage current is
ICEO = 2 mA. Determine the power loss due to the collector current:
=
=
=
(a) during turn-on ton = td + tr
VCE
Vcc
(b) during conduction period tn
V CE(sat)
0
toff"
ton
Ics
0.9 Ics
(c) during turn-off toff = ts + tf
(d) during off-time tot
(e) the total average power losses PT
ICEO
0
IBS
0
Figure 2
V BE(sat)
0
主
*
td
tr
In
Is
If
to
iB
VBE
T= 1/fs
Question 1:
The beta (B) of the bipolar transistor shown in Figure 1 varies from 12 to 60. The load resistance
is Rc = 5. The dc supply voltage is VCC = 40 V and the input voltage to the base circuit is
VB = 5 V. If VCE(sat) = 1.2 V, VBE(sat) = 1.6 V, and RB = 0.8 2, calculate:
(a) the overdrive factor ODF.
(b) the forced ẞ
(c) the power loss in the transistor PT.
IB
VB
RB
+
V BE
RC
Vcc'
Ic
+
IE
Figure 1
VCE
I need help in creating a matlab code to find the currents
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Ch. 2 - Reduce each of the networks shown in Figure P2.1...Ch. 2 - A 4- resistance is in series with the parallel...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance looking into...Ch. 2 - Suppose that we need a resistance of 1.5 k and...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance between terminals a...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance between terminals a...Ch. 2 - What resistance in parallel with 120 results in...Ch. 2 - Determine the resistance between terminals a and b...Ch. 2 - Two resistances having values of R and 2R are in...Ch. 2 - A network connected between terminals a and b...
Ch. 2 - Two resistances R1 and R2 are connected in...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance for the infinite...Ch. 2 - If we connect n 1000- resistances in parallel,...Ch. 2 - The heating element of an electric cook top has...Ch. 2 - We are designing an electric space heater to...Ch. 2 - Sometimes, we can use symmetry considerations to...Ch. 2 - The equivalent resistance between terminals a and...Ch. 2 - Three conductances G1 G2, and G3 are in series....Ch. 2 - Most sources of electrical power behave as...Ch. 2 - The resistance for the network shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - Often, we encounter delta-connected loads such as...Ch. 2 - What are the steps in solving a circuit by network...Ch. 2 - Find the values of i1 and i2 in Figure P2.23....Ch. 2 - Find the voltages v1 and v2 for the circuit shown...Ch. 2 - Find the values of v and i in Figure P2.25. Figure...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P2.24....Ch. 2 - Find the voltage v and the currents i1 and 12 for...Ch. 2 - Find the values of vs, v1, and i2 in Figure P2.28....Ch. 2 - Find the values of i1 and i2 in Figure P2.29....Ch. 2 - Consider the cirrcuit shown in Figure P2.30 Find...Ch. 2 - Solve for the values of i1, i2, and the powers for...Ch. 2 - The 12-V source in Figure P2.32 is delivering 36...Ch. 2 - Refer to the circuit shown in Figure P2.33. With...Ch. 2 - Find the values of i1 and i2 in Figure P2.34. Find...Ch. 2 - Find the values of i1 and i2 in Figure P2.35...Ch. 2 - Use the voltage-division principle to calculate...Ch. 2 - Use the current-division principle to calculate i1...Ch. 2 - Use the voltage-division principle to calculate...Ch. 2 - Use the current-division principle to calculate...Ch. 2 - Suppose we need to design a voltage-divider...Ch. 2 - A source supplies 120 V to the series combination...Ch. 2 - We have a 60- resistance, a 20- resistance, and...Ch. 2 - A worker is standing on a wet concrete floor,...Ch. 2 - Suppose we have a load that absorbs power and...Ch. 2 - We have a load resistance of 50 that we wish to...Ch. 2 - We have a load resistance of 1 k that we wish to...Ch. 2 - The circuit of Figure P2.47 is similar to networks...Ch. 2 - Write equations and solve for the node voltages...Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.49....Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.50....Ch. 2 - Given R1=4 , R2=5 , R2=8 , R4=10 , R5=2 , and...Ch. 2 - Determine the value of i1 in Figure P2.52 using...Ch. 2 - Given R1=15 , R5=5 , R3=20 , R4=10 , R5=8 , R6=4 ,...Ch. 2 - In solving a network, what rule must you observe...Ch. 2 - Use the symbolic features of MATLAB to find an...Ch. 2 - Solve for the values of the node voltages shown in...Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.57....Ch. 2 - Solve for the power delivered to the 8- ...Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.59....Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance looking into...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance looking into...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.62 shows an unusual voltage-divider...Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages in the circuit of...Ch. 2 - We have a cube with 1- resistances along each...Ch. 2 - Solve for the power delivered to the 15- resistor...Ch. 2 - Determine the value of v2 and the power delivered...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the value of i1...Ch. 2 - Solve for the power delivered by the voltage...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the value of v...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the value of i3...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the values of i1...Ch. 2 - Find the power delivered by the source and the...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the values of i1...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the values of i1...Ch. 2 - The circuit shown in Figure P2.75 is the dc...Ch. 2 - Use MATLAB and mesh-current analysis to determine...Ch. 2 - Connect a 1-V voltage source across terminals a...Ch. 2 - Connect a 1-V voltage source across the terminals...Ch. 2 - Use MATLAB to solve for the mesh currents in...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - We can model a certain battery as a voltage source...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin arid Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - An automotive battery has an open-circuit voltage...Ch. 2 - A certain two-terminal circuit has an open-circuit...Ch. 2 - If we measure the voltage at the terminals of a...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - Find the maximum power that can be delivered to a...Ch. 2 - Find the maximum power that can be delivered to a...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.91 shows a resistive load RL connected...Ch. 2 - Starling from the Norton equivalent circuit with a...Ch. 2 - A battery can be modeled by a voltage source Vt in...Ch. 2 - Use superposition to find the current i in Figure...Ch. 2 - Solve for is in Figure P2.49 by using...Ch. 2 - Solve the circuit shown in Figure P2.48 by using...Ch. 2 - Solve for i1 in Figure P2.34 by using...Ch. 2 - Another method of solving the circuit of Figure...Ch. 2 - Use the method of Problem P2.98 for the circuit of...Ch. 2 - Solve for the actual value of i6 for the circuit...Ch. 2 - Device A shown in Figure P2.101 has v=3i2 for i 0...Ch. 2 - The Wheatstone bridge shown in Figure 2.66 is...Ch. 2 - The Wheatstone bridge shown in Figure 2.66has...Ch. 2 - In theory, any values can be used for R1 and R3 in...Ch. 2 - Derive expressions for the Thévenin voltage and...Ch. 2 - Derive Equation 2.93 for the bridge circuit of...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.107PCh. 2 - Explain what would happen if, in wiring the bridge...Ch. 2 - Match each entry in Table T2.1(a) with the best...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit of Figure T2.2 with vs=96V ,...Ch. 2 - Write MATLAB code to solve for the node voltages...Ch. 2 - Write a set of equations that can be used to solve...Ch. 2 - Determine the Thévenin and Norton equivalent...Ch. 2 - According to the superposition principle, what...Ch. 2 - Determine the equivalent resistance between...Ch. 2 - Transform the 2-A current source and 6- ...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need help fixing this MATLAB code: as I try to get it working there were some problems:arrow_forwardI need help in construct a matlab code to find the voltage of VR1 to VR4, the currents, and the watts based on that circuit.arrow_forwardQ2: Using D flip-flops, design a synchronous counter. The counter counts in the sequence 1,3,5,7, 1,7,5,3,1,3,5,7,.... when its enable input x is equal to 1; otherwise, the counter count 0.arrow_forward
- From the collector characteristic curves and the dc load line given below, determine the following: (a) Maximum collector current for linear operation (b) Base current at the maximum collector current (c) VCE at maximum collector current. lc (mA) 600 ΜΑ 60- 500 με 50- 400 με 40- 300 μ Α 30- Q-point 200 ΜΑ 20- 10- 100 μ Α 0 VCE (V) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [6 Paarrow_forwardProcedure:- 1- Connect the cct. shown in fig.(2). a ADDS DS Fig.(2) 2-For resistive load, measure le output voltage by using oscilloscope ;then sketch this wave. 3- Measure the average values ::f VL and IL: 4- Repeat steps 2 & 3 but for RL load. Report:- 1- Calculate the D.C. output vcl age theoretically and compare it with the test value. 2- Calculate the harmonic cont :nts of the load voltage, and explain how filter components may be selected. 3- Compare between the three-phase half & full-wave uncontrolled bridge rectifier. 4- Draw the waveform for the c:t. shown in fig.(2) but after replaced Di and D3 by thyristors with a 30° and a2 = 90° 5- Draw the waveform for the cct. shown in fig.(2) but after replace the 6-diodes by 6- thyristor. 6- Discuss your results. Please solve No. 4 and 5arrow_forwardPlease I want solution by handwrittenarrow_forward
- 8 00 ! Required information Consider the circuit given below. 0/2 points awarded 3 ΚΩ www t=0 6kM Scored R 1.5i Vc 1 μF 10 V If R = 5.00 kQ, determine vao+). The value of va(0) is 1.4545 V.arrow_forwardI want to know what does it look in a breadboard circuit, because I want to created it but I not sure it is build properly, can you give me an illustuation base on this image, it do need to real, something like virutal examplearrow_forwardCharge neutrality Since doped semiconductor remains electroneutral, the concentration of negative charges equals the concentration of positive charges. n+ Na,ionized p+Nd,ionized np = n; 2 2 N-Na N N d d р + 2 2 n = Nd-Na 2 + Na - 2 Na +n₁ 2 71/2 1/2 2 2 +n Concentration of electrons and holes 1. Calculate concentrations of electrons and holes at room temperature in Si and Ge with donor concentration of 1.5x10¹7 cm³ and acceptor concentration of 8x1016 cm-3. 2. Will these concentrations change much with the temperature increase to 100°C?arrow_forward
- Answer the questions on the end of the image pleasearrow_forwardAnswer these two questions on the end of the image, please 1.Calculate intrinsic carrier concentration for Si, Ge and GaAs at temperatures -20°C, 20°C (room temperature) and 120°C 2.Compare the obtained data with n and p shown on previous slide 25arrow_forwardCan you help me achieve the requirements using Arduino? I have encountered some issues with these requirements. Q.2: Suppose you have two push buttons connected to ports (0 & 1) and four LED's connected to ports (6-9). Write a program to flash ON the odd LED's if we press the switch 0 for 4s, flash ON the even LED's if we press the switch 1 for 5s and flash ON all the LED's otherwise for 6s.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Current Divider Rule; Author: Neso Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hRU1mKWUehY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY