
EBK ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220106714201
Author: HAMBLEY
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.100P
Solve for the actual value of i6 for the circuit of Figure P2.100, starting with the assumption that i6=1 A. Work back through the circuit to find the value of Is that results in i6=1 A. Then, use Proportionality to determine the value of i6 that results for Is=10A.
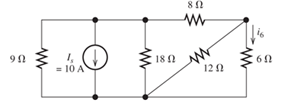
Figure P2.100
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Example2:-
8. = e.A nia +2.1 =
Find the maximum steady-state power capability of a system consisting of a
generator equivalent reactance of 0.4pu connected to an infinite bus through a
series reactance of 1.0 p.u. The terminal voltage of the generator is held at1.10 p.u.
and the voltage of the infinite bus is 1.0 p.u.
B) A 60-Hz generator is supplying 60% of P max to an infinite bus through a reactive network.
A fault occurs which increases the reactance of the network between the generator internal
voltage and the infinite bus by 400%. When the fault is cleared, the maximum power that can
be delivered is 80% of the original maximum value. Determine the critical clearing angle for
the condition described.
In the circuit shown, let Vs-9, R₁-8, R2-2, and R3-4. Use Nodal analysis to determine the current lo. In
particular find:
V2=
10=
A
The relative tolerance for this problem is 5 %.
R₁
V₁
+
ww
R₂
Vs
V₂
21
x
R3
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Ch. 2 - Reduce each of the networks shown in Figure P2.1...Ch. 2 - A 4- resistance is in series with the parallel...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance looking into...Ch. 2 - Suppose that we need a resistance of 1.5 k and...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance between terminals a...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance between terminals a...Ch. 2 - What resistance in parallel with 120 results in...Ch. 2 - Determine the resistance between terminals a and b...Ch. 2 - Two resistances having values of R and 2R are in...Ch. 2 - A network connected between terminals a and b...
Ch. 2 - Two resistances R1 and R2 are connected in...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance for the infinite...Ch. 2 - If we connect n 1000- resistances in parallel,...Ch. 2 - The heating element of an electric cook top has...Ch. 2 - We are designing an electric space heater to...Ch. 2 - Sometimes, we can use symmetry considerations to...Ch. 2 - The equivalent resistance between terminals a and...Ch. 2 - Three conductances G1 G2, and G3 are in series....Ch. 2 - Most sources of electrical power behave as...Ch. 2 - The resistance for the network shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - Often, we encounter delta-connected loads such as...Ch. 2 - What are the steps in solving a circuit by network...Ch. 2 - Find the values of i1 and i2 in Figure P2.23....Ch. 2 - Find the voltages v1 and v2 for the circuit shown...Ch. 2 - Find the values of v and i in Figure P2.25. Figure...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P2.24....Ch. 2 - Find the voltage v and the currents i1 and 12 for...Ch. 2 - Find the values of vs, v1, and i2 in Figure P2.28....Ch. 2 - Find the values of i1 and i2 in Figure P2.29....Ch. 2 - Consider the cirrcuit shown in Figure P2.30 Find...Ch. 2 - Solve for the values of i1, i2, and the powers for...Ch. 2 - The 12-V source in Figure P2.32 is delivering 36...Ch. 2 - Refer to the circuit shown in Figure P2.33. With...Ch. 2 - Find the values of i1 and i2 in Figure P2.34. Find...Ch. 2 - Find the values of i1 and i2 in Figure P2.35...Ch. 2 - Use the voltage-division principle to calculate...Ch. 2 - Use the current-division principle to calculate i1...Ch. 2 - Use the voltage-division principle to calculate...Ch. 2 - Use the current-division principle to calculate...Ch. 2 - Suppose we need to design a voltage-divider...Ch. 2 - A source supplies 120 V to the series combination...Ch. 2 - We have a 60- resistance, a 20- resistance, and...Ch. 2 - A worker is standing on a wet concrete floor,...Ch. 2 - Suppose we have a load that absorbs power and...Ch. 2 - We have a load resistance of 50 that we wish to...Ch. 2 - We have a load resistance of 1 k that we wish to...Ch. 2 - The circuit of Figure P2.47 is similar to networks...Ch. 2 - Write equations and solve for the node voltages...Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.49....Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.50....Ch. 2 - Given R1=4 , R2=5 , R2=8 , R4=10 , R5=2 , and...Ch. 2 - Determine the value of i1 in Figure P2.52 using...Ch. 2 - Given R1=15 , R5=5 , R3=20 , R4=10 , R5=8 , R6=4 ,...Ch. 2 - In solving a network, what rule must you observe...Ch. 2 - Use the symbolic features of MATLAB to find an...Ch. 2 - Solve for the values of the node voltages shown in...Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.57....Ch. 2 - Solve for the power delivered to the 8- ...Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages shown in Figure P2.59....Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance looking into...Ch. 2 - Find the equivalent resistance looking into...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.62 shows an unusual voltage-divider...Ch. 2 - Solve for the node voltages in the circuit of...Ch. 2 - We have a cube with 1- resistances along each...Ch. 2 - Solve for the power delivered to the 15- resistor...Ch. 2 - Determine the value of v2 and the power delivered...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the value of i1...Ch. 2 - Solve for the power delivered by the voltage...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the value of v...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the value of i3...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the values of i1...Ch. 2 - Find the power delivered by the source and the...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the values of i1...Ch. 2 - Use mesh-current analysis to find the values of i1...Ch. 2 - The circuit shown in Figure P2.75 is the dc...Ch. 2 - Use MATLAB and mesh-current analysis to determine...Ch. 2 - Connect a 1-V voltage source across terminals a...Ch. 2 - Connect a 1-V voltage source across the terminals...Ch. 2 - Use MATLAB to solve for the mesh currents in...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - We can model a certain battery as a voltage source...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin arid Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - An automotive battery has an open-circuit voltage...Ch. 2 - A certain two-terminal circuit has an open-circuit...Ch. 2 - If we measure the voltage at the terminals of a...Ch. 2 - Find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 2 - Find the maximum power that can be delivered to a...Ch. 2 - Find the maximum power that can be delivered to a...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.91 shows a resistive load RL connected...Ch. 2 - Starling from the Norton equivalent circuit with a...Ch. 2 - A battery can be modeled by a voltage source Vt in...Ch. 2 - Use superposition to find the current i in Figure...Ch. 2 - Solve for is in Figure P2.49 by using...Ch. 2 - Solve the circuit shown in Figure P2.48 by using...Ch. 2 - Solve for i1 in Figure P2.34 by using...Ch. 2 - Another method of solving the circuit of Figure...Ch. 2 - Use the method of Problem P2.98 for the circuit of...Ch. 2 - Solve for the actual value of i6 for the circuit...Ch. 2 - Device A shown in Figure P2.101 has v=3i2 for i 0...Ch. 2 - The Wheatstone bridge shown in Figure 2.66 is...Ch. 2 - The Wheatstone bridge shown in Figure 2.66has...Ch. 2 - In theory, any values can be used for R1 and R3 in...Ch. 2 - Derive expressions for the Thévenin voltage and...Ch. 2 - Derive Equation 2.93 for the bridge circuit of...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.107PCh. 2 - Explain what would happen if, in wiring the bridge...Ch. 2 - Match each entry in Table T2.1(a) with the best...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit of Figure T2.2 with vs=96V ,...Ch. 2 - Write MATLAB code to solve for the node voltages...Ch. 2 - Write a set of equations that can be used to solve...Ch. 2 - Determine the Thévenin and Norton equivalent...Ch. 2 - According to the superposition principle, what...Ch. 2 - Determine the equivalent resistance between...Ch. 2 - Transform the 2-A current source and 6- ...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Choose all nodes that must be included, if any, to construct the supernode for Nodal analysis. OV1, V3 OV1, V2 ○ V2, V3 OV1, V2, V4 OV1, V2, V3 O V2, V3, V4 2. Write KCL equation (Nodal equation) at super-node. Write your expression in terms of node voltages V1, V2, V3 and V4 and of the form (G11 V1+G12 V2+G13 V3+G14 V4 = 11), then enter the corresponding values: At super-node KCL: 1/Q G11 1/0 G12 1/Ω G13 1/Q G14 A 3. Use the above equation, the circuit and and super-node inner expression to calculate V3 and then lo : V3= V 10 = R3 Vst + A V₁ + VS2 V₂ V3 w W R₁ R₂ R4 ww R5 V4 V$3arrow_forwardEnter the matrix values (numerical) to solve for voltages at nodes v1, and v2, for the circuit shown, using Nodal equations. In the matrix, row 1, and row 2, correspond to node v1, and node v2 current expressions, respectively. Let Is1=14, Is2=7, R₁=5, R₂-8, R3=2, and R4-5. [G11 G12] [Vi₁ The matrix values are shown here: = G21 G22 [V2] [41] [12] {Hint: As discussed in class and to avoid sign errors, assume nodal currents are locally defined at each node (leaving) and use node labeling as indicated in the circuit. } The relative tolerance for this problem is 5%. VI R2 ww Isl 12 NODE v1 G11 G12 RI 1/Q 1/0 A 4= NODE v2 G21- 1/Q G22 1/0 12 W A === www R3 R4 www Use Cramer's rule (matrix), substitution, or any other method to calculate the voltages: v1 = V v2= V Is2arrow_forwardOnly expert should attemptarrow_forward
- For the circuit shown below, let l₁ = 9, 1₂ = 14, 13= 12, R₁ = 3, R₂ = 8, and R3 = 5. Use nodal equations to determine V1, V2 and I, as follows: • Consider Node 1, obtain a nodal equation in terms of V₁ and V₂ voltages. Simplify your equation to the format 1V1 + b,V₂ = c, then enter the corresponding values of coefficients b₁ and c₁ 1. b₁ =( C₁ = • Now consider Node 2, obtain a second nodal equation in terms of V₁ and V2 voltages. Simplify your equation to the format -1V₁+b2V2=c2 then enter the corresponding values of coefficients b₂ and c₂ 2. (b₂ = value.) ,၄၇ = - 3. Use (1) and (2) to determine V₂ = 4. Determine V₁ 5. Determine | = i 12 V₁ R1 20 www R2 ww I The relative tolerance for this problem is 5%. R3 This is not a decimal or integer www i3arrow_forwardFor the circuit shown, let V1 = 19 V, Vs2 = 76 V, R₁ = 9, R2 = 9, and R3 = 7. Use Nodal analysis to determine the voltage V2 and the current lo, choose the closet values: V2- 4.788 10 = ○ 2.28 11.978 17.761 35.522 23.957 -9.146 8.32 10.173 A O-7.435 O-5.783 10.531 V sl ་ ་ ་ ན ་་་ ་ ་ ་ ་ ་ ་ ་ ་ +1 ww R₁ R₂ ww R3 Io +1 VS2arrow_forwardNO AI PLEASEarrow_forward
- NO AI PLEASEarrow_forwardProblem 4 Consider the following system. In the figure, y(t) denotes the displacement of the mass and u(t) denotes the force applied to the mass. b1 u(t) y(t) + b2 M 0000 0000 K1 K2 a) Find the differential equation model of the system. b) Find the state-space model for the system. Write x, A, B, C and D clearly in your answer.arrow_forwardNO AI PLEASEarrow_forward
- Not use ai pleasearrow_forwardShow workarrow_forwardProblem 1 (a) Suppose the Laplace transform of a causal signal x₁ (t) is given by S X₁(s) = 52 +2 Using the Laplace transform properties, find the Laplace transform of the following signal x2(t). x2(t) = e2t+1 x₁(t − 1) - tx₁(2t - 1) (b) Suppose an LTI system T whose impulse response is given by h(t) e 2t 1(t) t 1(t) +28(t) What is the transfer function of the system? (c) If the input x2 (t) is applied to the system T, what will be the output Y₂(s)? Note, you just need to provide Laplace transform of the output y₂(t). Simplification is not needed in any part of this question.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Current Divider Rule; Author: Neso Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hRU1mKWUehY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY