
Concept explainers
The synthesis of cyclobutanecarboxylic acid given in Section 18.7 was first carried out by William Perkin, Jr., in 1883, and it represent-ed one of the first syntheses of an organic compound with a ring smaller than six carbon atoms. (There was a general feeling at the time that such compounds would be too unstable to exist.) Earlier in 1883, Perkin reported what he mistakenly believed to be a cyclobutane derivative obtained from the reaction of acetoacetic ester and 1,3-dibromopropane. The reaction that Perkin had expected to take place was the following:
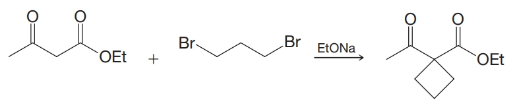
The molecular formula for his product agreed with the formulation given in the preceding reaction, and alkaline hydrolysis and acidification gave a nicely crystalline acid (also having the expected molecular formula). The acid, however, was quite stable to heat and resisted decarboxylation. Perkin later found that both the ester and the acid contained six-membered rings (five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom). Recall the charge distribution in the enolate ion obtained from acetoacetic ester and propose structures for Perkin’s ester and acid.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- Explanation O Conjugated Pi Systems Deducing the reactants of a Diels-Alder reaction Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardDiels Alder Cycloaddition: Focus on regiochemistry (problems E-F) –> match + of thedienophile and - of the diene while also considering stereochemistry (endo).arrow_forwardHELP! URGENT! PLEASE RESOND ASAP!arrow_forward
- Question 4 Determine the rate order and rate constant for sucrose hydrolysis. Time (hours) [C6H12O6] 0 0.501 0.500 0.451 1.00 0.404 1.50 0.363 3.00 0.267 First-order, k = 0.210 hour 1 First-order, k = 0.0912 hour 1 O Second-order, k = 0.590 M1 hour 1 O Zero-order, k = 0.0770 M/hour O Zero-order, k = 0.4896 M/hour O Second-order, k = 1.93 M-1-hour 1 10 ptsarrow_forwardDetermine the rate order and rate constant for sucrose hydrolysis. Time (hours) [C6H12O6] 0 0.501 0.500 0.451 1.00 0.404 1.50 0.363 3.00 0.267arrow_forwardDraw the products of the reaction shown below. Use wedge and dash bonds to indicate stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. OSO4 (cat) (CH3)3COOH Select to Draw ઘarrow_forward
- Calculate the reaction rate for selenious acid, H2SeO3, if 0.1150 M I-1 decreases to 0.0770 M in 12.0 minutes. H2SeO3(aq) + 6I-1(aq) + 4H+1(aq) ⟶ Se(s) + 2I3-1(aq) + 3H2O(l)arrow_forwardProblem 5-31 Which of the following objects are chiral? (a) A basketball (d) A golf club (b) A fork (c) A wine glass (e) A spiral staircase (f) A snowflake Problem 5-32 Which of the following compounds are chiral? Draw them, and label the chirality centers. (a) 2,4-Dimethylheptane (b) 5-Ethyl-3,3-dimethylheptane (c) cis-1,4-Dichlorocyclohexane Problem 5-33 Draw chiral molecules that meet the following descriptions: (a) A chloroalkane, C5H11Cl (c) An alkene, C6H12 (b) An alcohol, C6H140 (d) An alkane, C8H18 Problem 5-36 Erythronolide B is the biological precursor of erythromycin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic. How H3C CH3 many chirality centers does erythronolide B have? OH Identify them. H3C -CH3 OH Erythronolide B H3C. H3C. OH OH CH3arrow_forwardPLEASE HELP! URGENT! PLEASE RESPOND!arrow_forward
- 2. Propose a mechanism for this reaction. ہلی سے ملی N H (excess)arrow_forwardSteps and explanationn please.arrow_forwardProblem 5-48 Assign R or S configurations to the chirality centers in ascorbic acid (vitamin C). OH H OH HO CH2OH Ascorbic acid O H Problem 5-49 Assign R or S stereochemistry to the chirality centers in the following Newman projections: H Cl H CH3 H3C. OH H3C (a) H H H3C (b) CH3 H Problem 5-52 Draw the meso form of each of the following molecules, and indicate the plane of symmetry in each: OH OH (a) CH3CHCH2CH2CHCH3 CH3 H3C. -OH (c) H3C CH3 (b) Problem 5-66 Assign R or S configurations to the chiral centers in cephalexin, trade-named Keflex, the most widely prescribed antibiotic in the United States. H2N H IHH S Cephalexin N. CH3 CO₂Harrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

