
Concept explainers
Draw the products formed when phenol
a.
b.
c.
d.
(a)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
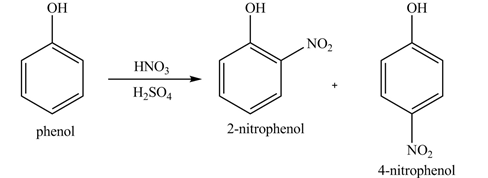
Explanation of Solution
Phenol undergoes nitration reaction on treatment with

Figure 1
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
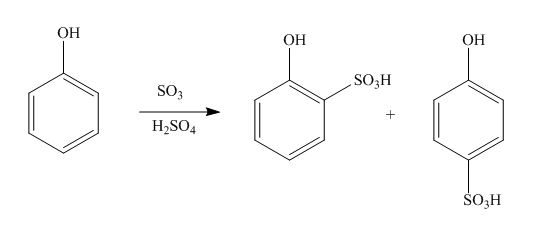
Explanation of Solution
An aromatic compound undergoes sulphonation on reaction with

Figure 2
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
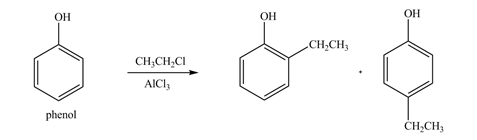
Explanation of Solution
An aromatic compound undergoes Friedel-Craft alkylation on reaction with

Figure 3
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
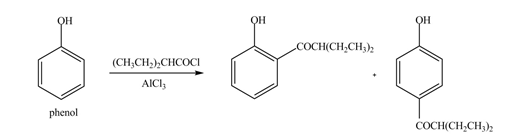
Explanation of Solution
An aromatic compound undergoes Friedel-Craft acylation on reaction with

Figure 4
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
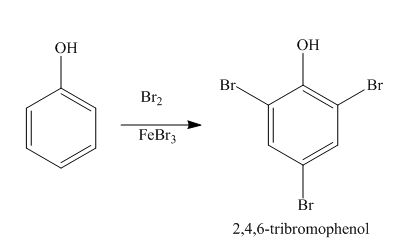
Explanation of Solution
The benzene ring is activated in phenol due to the presence of strong electron donating group. In bromination, bromonium acts as electrophile and produces

Figure 5
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
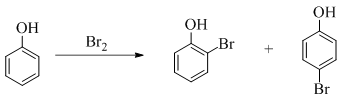
Explanation of Solution
Phenol undergoes mono bromination with bromine without catalyst. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.

Figure 6
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
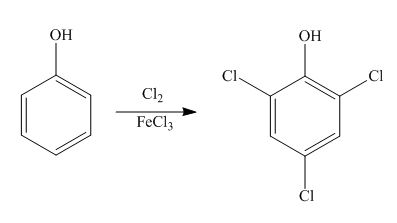
Explanation of Solution
The benzene ring is activated in phenol due to the presence of strong electron donating group. In chlorination, chloronium acts as electrophile and produces

Figure 7
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 7.
(h)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
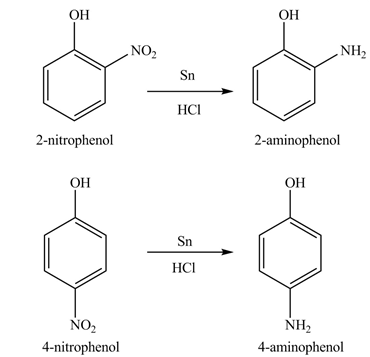
Explanation of Solution
The

Figure 8
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 8.
(i)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The carbonyl group

Figure 9
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 9.
(j)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
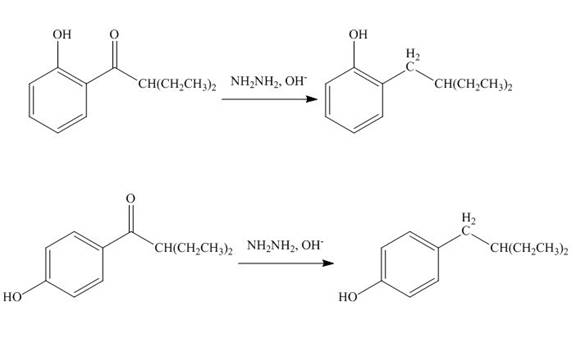
Explanation of Solution
The carbonyl group
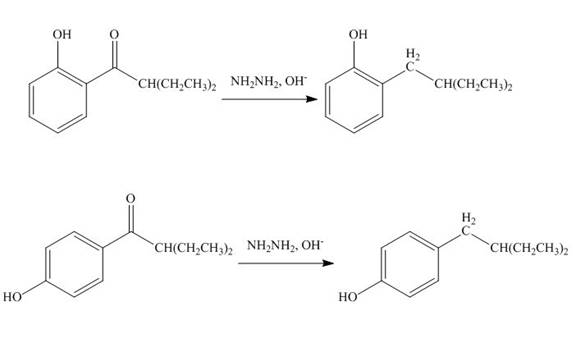
Figure 10
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 10.
(k)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
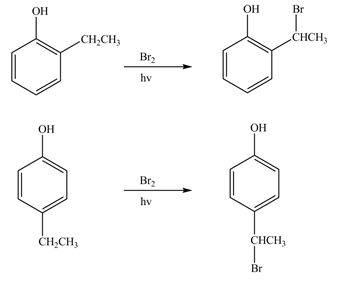
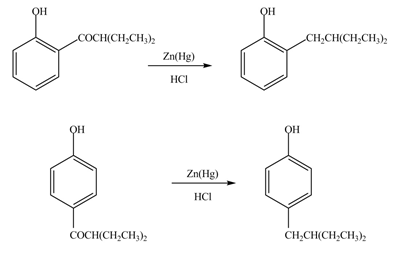
Explanation of Solution
The bromine group attaches to the side chain of the aromatic compound on reaction with

Figure 11
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 11.
(l)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
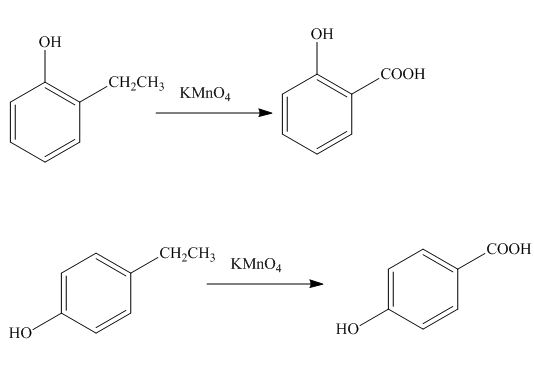
Explanation of Solution
The alkyl group oxidizes to

Figure 12
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 12.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- 2S2O2/3- (aq) + I2 (aq) ---> S4O2/6- (aq) +2I- (aq) Experiment I2 (M) S2O3- (M) Initital Rate (M/s) 1 0.01 0.01 0.0004 2 0.01 0.02 0.0004 3 0.02 0.01 0.0008 Calculate the overall order for this reaction using the table data a) 3b) 0c) 2d) 1arrow_forwardthe decomposition of N2O5 is the first order with a half-life of 1.98 minutes. If the inital concentration of N2O5 is 0.200 M, what is the concentration after 6 minutes?a) 0.612 Mb) 0.035 Mc) 0.024 Md) 0.100 Marrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M HCI is titrated with 0.075 M NaOH. What volume of NaOH is needed?a) 50 mLb) 20 mLc) 40 mLd) 26.66 mLarrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCI. What is the molarity of the HCI?a) 0.150 Mb) 0.079 Mc) 0.025 Md) 0.050 Marrow_forwardin the following reaction, the OH- acts as which of these?NO2- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ OH- (aq) + HNO2 (aq)a) not a weak acidb) basec) acidarrow_forwardfind the pH of a buffer made from 0.20 M HNO2 and 0.10 M NaNO2. Ka= 4.0 x 10-4a) 4.00b) 3.40c) 3.70d) 3.10arrow_forward
- the Ka for sodium dihydrogen phosphate is 6.32 x 10-8. Find the pH of a buffer made from 0.15 M H2PO4- and 0.15 M HPO42-.a) 6.98b) 7.42c) 7.00d) 7.20arrow_forwardFind the equilibrium concentration of H3O+ starting with 0.072 M solution of acetic acid. Ka = 1.8 x 10-5. Acetic acid is HC2H3O2 (aq).HC2H3O2 (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ H3O (aq) + C2H3O2- (aq) a) 1.3 x 10-6 b) 1.1 x 10-3 c) 1.5 x 10-2 d) 3.6 x 10-5arrow_forwardin VSEPR Theory, AX2 isarrow_forward
- calculate the pH of 0.066 M Ca(OH)2. Remember stoichiometry.arrow_forwardFind the equilibrium concentration of H3O+ starting with 0.072 M solution of acetic acid. Ka = 1.8 x 10-5. Acetic acid is HC2H3O2 (aq).HC2H3O2 (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ H3O (aq) + C2H3O2- (aq)arrow_forwardin VSEPR Theory AX2 isa) tetrahedralb) octahedralc) lineard) trigonal bipyramidarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





