
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined:
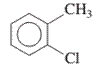
Concept Introduction: The ring structures of the compound having uncommon stability due to delocalized pi electron density shared in between all the carbon atoms of the ring is said to be an aromatic compound.
In order to give the name to the multiple substituted
- For single substituted aromatic compound (when the substituent contains six or fewer carbons), the name of the substituted group is written first followed by the name of the aromatic compound.
- For single substituted aromatic compound (when the substituent contains more than six carbons), the name of the aromatic compound is written first followed by the name of the substituted group.
- For single substituted aromatic compound, the numbering on the ring is done in such a way that the multiple substituents get the lowest number.
(b)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined:
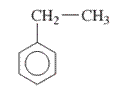
Concept Introduction: The ring structures of the compound having uncommon stability due to delocalized pi electron density shared in between all the carbon atoms of the ring is said to be an aromatic compound.
In order to give the name to the multiple substituted aromatic compounds, the following steps are followed:
- For single substituted aromatic compound (when the substituent contains six or fewer carbons), the name of the substituted group is written first followed by the name of the aromatic compound.
- For single substituted aromatic compound (when the substituent contains more than six carbons), the name of the aromatic compound is written first followed by the name of the substituted group.
- For single substituted aromatic compound, the numbering on the ring is done in such a way that the multiple substituents get the lowest number.
(c)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name of the following compound should be determined:
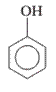
Concept Introduction: The ring structures of the compound having uncommon stability due to delocalized pi electron density shared in between all the carbon atoms of the ring is said to be an aromatic compound.
In order to give the name to the multiple substituted aromatic compounds, the following steps are followed:
- For single substituted aromatic compound (when the substituent contains six or fewer carbons), the name of the substituted group is written first followed by the name of the aromatic compound.
- For single substituted aromatic compound (when the substituent contains more than six carbons), the name of the aromatic compound is written first followed by the name of the substituted group.
- For single substituted aromatic compound, the numbering on the ring is done in such a way that the multiple substituents get the lowest number.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
Basic Chemistry
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forward

 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning




