
Concept explainers
The uniform rectangular block shown is moving along a frictionless surface with a velocity
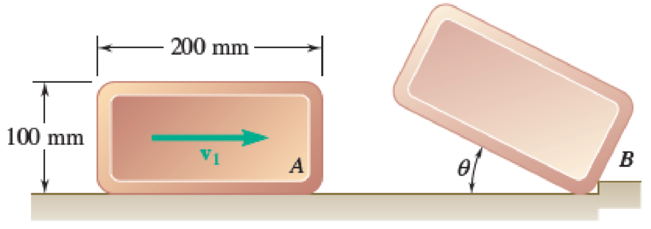
Fig. P17.115
Find the magnitude of the velocity
Answer to Problem 17.115P
The magnitude of the velocity
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length
The width
Calculation:
Write the equation of centroidal moment of inertia
Find the one half of the diagonal distance
Substitute 200 mm for a and 100 mm for b.
Before impact, let
Here, magnitude of velocity of the rectangular block is
After impact, the rectangular block rotates about small obstruction at B. Therefore,
Let
Find the equation of velocity
Consider the principle of impulse and momentum.
Sketch the impulse and momentum diagram of the rectangular block as shown in Figure (1).
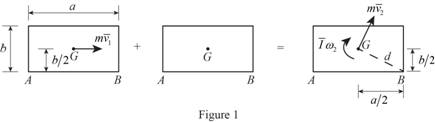
Take moment about B (positive sign in clockwise direction).
Substitute
Substitute
Sketch the free body diagram of the rectangular block after impact (position 2) and final position (position 3) as shown in Figure (2).
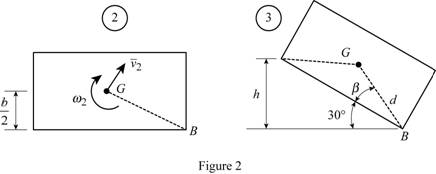
Write the equation of velocity
Refer Figure (2),
Find the angle
Substitute 200 mm for a and 100 mm for b.
Find the distance (h).
Substitute 0.1118 m for d and
At position 3, the angular velocity
Write the equation of the potential energy
Write the equation of the kinetic energy
Substitute
Substitute
Write the equation of the potential energy
The kinetic energy of the system at final position
Consider the conservation of energy.
Substitute
Substitute 200 mm for a, 100 mm for b, 0.1118 m for d,
Find the the magnitude of the velocity
Substitute 200 mm for a, 100 mm for b, and
Thus, the magnitude of the velocity
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
- Question 6 I need to show all work step by step dynamicsarrow_forwardQu. 3 The automobile is originally at rest s = 0. If it then starts to increase its speed at i = (0.05t2)ft/s?, where t is in seconds, determine the magnitudes of its velocity and acceleration at s = 550 ft. please show all work from dynamics step by step formulaarrow_forwardquestion 5 and 6 from dynamics I need to show all work step by step problemsarrow_forward
- Study Area Document Sharing User Settings Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists of a nest of barrels filled with an impact-absorbing material. The barrier stopping force is measured versus the vehicle penetration into the barrier. (Figure 1) Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Review Determine the distance a car having a weight of 4000 lb will penetrate the barrier if it is originally traveling at 55 ft/s when it strikes the first barrel. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 36 μΑ S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? Next >arrow_forwardWater is the working fluid in an ideal Rankine cycle. Saturated vapor enters the turbine at 12 MPa, and the condenser pressure is 8 kPa. The mass flow rate of steam entering the turbine is 50 kg/s. Determine: (a) the net power developed, in kW. (b) the rate of heat transfer to the steam passing through the boiler, in kW. (c) the percent thermal efficiency. (d) the mass flow rate of condenser cooling water, in kg/s, if the cooling water undergoes a temperature increase of 18°C with negligible pressure change in passing through the condenser.arrow_forward4. The figure below shows a bent pipe with the external loading FA 228 lb, and M₁ = M₂ = 1 kip-ft. The force Fernal loading FA = 300 lb, FB: parallel to the y-axis, and and yc = 60°. = 125 lb, Fc = acts parallel to the x-z plane, the force FB acts Cartesian resultan Coordinate direction angles of Fc are ac = 120°, ẞc = 45°, a. Compute the resultant force vector of the given external loading and express it in EST form. b. Compute the resultant moment vector of the given external loading about the origin, O, and express it in Cartesian vector form. Use the vector method while computing the moments of forces. c. Compute the resultant moment vector of the given external loading about the line OA and express it in Cartesian vector form. :00 PM EST k ghoufran@buffaternal du 2 ft M₁ A 40° FA M2 C 18 in 1 ft Fc 25 houfran@bald.edu - Feb 19, 3 ft FBarrow_forward
- The differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation: Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) . a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K? b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe? c. For the given transfer function, find tp, ts, tr, Mp . Plot the resulting step response. G(s) = 40/(s^2 + 4s + 40)arrow_forwardAuto Controls Perform the partial fraction expansion of the following transfer function and find the impulse response: G(s) = (s/2 + 5/3) / (s^2 + 4s + 6) G(s) =( 6s^2 + 50) / (s+3)(s^2 +4)arrow_forwardStudy Area Document Sharing User Settings mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The 150-lb skater passes point A with a speed of 6 ft/s. (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Determine his speed when he reaches point B. Neglect friction. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. με ? VB = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the normal force exerted on him by the track at this point. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ☐ о Α NB = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? ■Review Next >arrow_forward
- mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Study Area Document Sharing User Settings The 100-kg crate is subjected to the forces shown. The crate is originally at rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface is μk = 0.2. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the distance it slides in order to attain a speed of 8.1 m/s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 500 N 1 of 1 Α S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? ■Review Next >arrow_forwardThe differential equation of a DC motor can be described by the following equation Find the transfer function between the applied voltage ( Va)and the motor speed (thetadot m). What is the steady state speed of the motor after a voltage (Va = 10V) has been applied. Find the transfer function between the applied voltage (Va) and the shaft angle (thetadot m) .arrow_forwardStudy Area Document Sharing User Settings Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists of a nest of barrels filled with an impact-absorbing material. The barrier stopping force is measured versus the vehicle penetration into the barrier. (Figure 1) Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Review Determine the distance a car having a weight of 4000 lb will penetrate the barrier if it is originally traveling at 55 ft/s when it strikes the first barrel. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 36 μΑ S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? Next >arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





