
Concept explainers
A uniform disk, initially at rest and of constant thickness, is placed in contact with the belt shown, which moves at a constant speed v = 80 ft/s. Knowing that the coefficient of kinetic friction between the disk and the belt is 0.15, determine (a) the number of revolutions executed by the disk before it reaches a constant angular velocity, (b) the time required for the disk to reach that constant angular velocity.
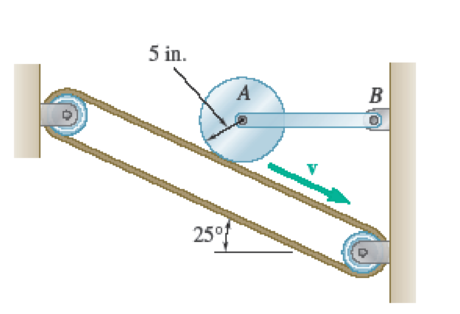
Fig. P17.135
(a)
Find the number of revolutions executed by the disk before it reaches a constant angular velocity.
Answer to Problem 17.135RP
The number of revolutions executed by the disk is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The speed of the belt is
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the disk and the belt is
The radius of the uniform disk is
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the disk as in Figure 1.
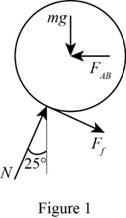
Find the frictional force
Here, the normal force is N.
Substitute 0.15 for
Resolve the vertical component of forces to find the normal force.
Here, the mass of the disk is m and the acceleration due to gravity is g.
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
Substitute 0.15N for
Substitute
Find the mass moment of inertia
Here, the radius of the disk is r.
Find the angular velocity
Find the work done
Here, the number of revolutions is
Substitute
The total kinetic energy at initial position is zero.
Find the total kinetic energy after reaching the constant angular velocity using the relation.
Substitute
Write the equation of conservation of energy and work as follows;
Substitute 0 for
Substitute 5 in. for r,
Therefore, the number of revolutions executed by the disk is
(b)
Find the time required for the disk to reach the constant angular velocity.
Answer to Problem 17.135RP
The time required for the disk is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The speed of the belt is
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the disk and the belt is
The radius of the uniform disk is
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the principle of impulse-momentum as in Figure 2.
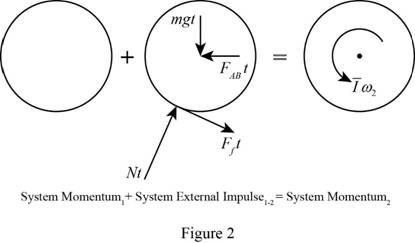
Take moment about point A as follows;
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the time required for the disk is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
- The hydraulic cylinder BC exerts on member AB a force P directed along line BC. The force P must have a 560-N component perpendicular to member AB. A M 45° 30° C Determine the force component along line AB. The force component along line AB is N.arrow_forward! Required information A telephone cable is clamped at A to the pole AB. The tension in the left-hand portion of the cable is given to be T₁ = 815 lb. A 15° 25° B T₂ Using trigonometry, determine the required tension T₂ in the right-hand portion if the resultant R of the forces exerted by the cable at A is to be vertical. The required tension is lb.arrow_forwardWhat are examples of at least three (3) applications of tolerance fitting analysis.arrow_forward
- The primary material used in the production of glass products is silica sand. True or Falsearrow_forwardWhich one of the following is the most common polymer type in fiber-reinforced polymer composites? thermosets thermoplastics elastomers none of the abovearrow_forwardA pattern for a product is larger than the actual finished part. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Two forces are applied as shown to a hook support. The magnitude of P is 38 N. 50 N 25° DG a 터 Using trigonometry, determine the required angle a such that the resultant R of the two forces applied to the support will be horizontal. The value of a isarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward101 the three shafts if the diameter ratio is 2 (D/d = 2)? Ans. na, tension = 1.21, na, bending = 1.19, na, torsion = 1.17. 6.32 A material with a yield strength of S₁ = 350 MPa is subjected to the stress state shown in Sketch c. What is the factor of safety based on the maximum shear stress and distortion energy theories? Ans. For MSST, n, = 11.67. 50 MPa 85 MPa 20 MPa 70 MPa Sketch c, for Problems 6.32 and 6.33arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





