
(a)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for Megatomoic acid has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
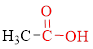
Nomenclature of
- Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- Replace the –e in the
alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
E-Z designators are used as like cis-trans terminology for non-similar groups attached
In E-Z designations, the groups attached to vinylic positions are checked by their priority on the basis of higher molecular weight. If the higher priority groups are on the same sides, then the configuration is designated as Z. If the higher priority groups are on the opposite sides, then the configuration is designated as E.
(b)
Interpretation: The number of possible stereoisomers for the given compound has to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
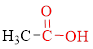
The stereoisomerism is the arrangement of atoms in molecules whose connectivity remains the same but their arrangement in different in each isomer.
The two molecules are described as stereoisomers if they are made of the same atoms connected in the same sequence, but the atoms are positions differently in space
E-Z designators are used as like cis-trans terminology for non-similar groups attached alkenes.
In E-Z designations, the groups attached to vinylic positions are checked by their priority on the basis of higher molecular weight. If the higher priority groups are on the same sides, then the configuration is designated as Z. If the higher priority groups are on the opposite sides, then the configuration is designated as E.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
