
Write the IUPAC name of each compound, showing stereochemistry where relevant.
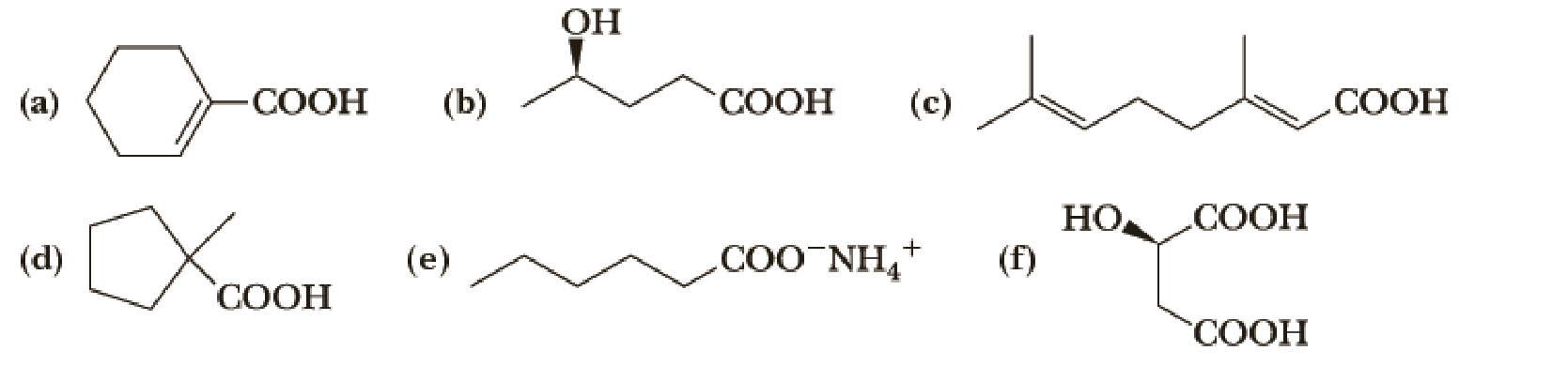
(a)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the compound has to be given and its configuration should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
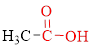
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid is,
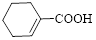
Let’s given numbering to this compound as follows,
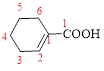
The parent hydrocarbon ring has 6 carbon atoms, one
Thus, according to IUPAC the compound can be named as, 1-Cyclohexenecarboxylic acid.
(b)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the compound has to be given and its configuration should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
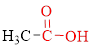
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid. If two or more carboxylic functional groups are present in the same compound then its number should be taken in to consideration and the prefix di, tri, tetra.. must be used.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid is,
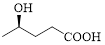
Let’s given numbering to this compound as follows,
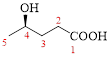
The parent hydrocarbon chain has five carbon atoms, there are two functional groups, one is –OH (which is attached to the fourth carbon atom) and the other one is –COOH. But, carboxylic acid has higher priority than the -OH, thus –OH will appeared in the name of the compound as the prefix – hydroxy.
Here, this compound has a chiral center (it is highlighted as *); its configuration can be specified as follows,
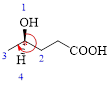
The numbering follows a clock wise direction and so molecule is in as R- configuration.
Thus, according to IUPAC the compound can be named as, (R)-4-hydroxypentanoic acid.
(c)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the compound has to be given and its configuration should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
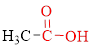
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
E-Z designators are used as like cis-trans terminology for non-similar groups attached alkenes.
In E-Z designations, the groups attached to vinylic positions are checked by their priority on the basis of higher molecular weight. If the higher priority groups are on the same sides, then the configuration is designated as Z. If the higher priority groups are on the opposite sides, then the configuration is designated as E.
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid is,
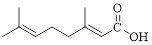
Let’s given numbering to this compound as follows,
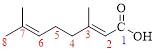
The parent hydrocarbon chain has eight carbon atoms, two methyl groups were attached to the third and seventh carbon atoms and these branches has lower priority over the carboxylic acid part.
The higher priority group (-COOH) are on the opposite sides, thus the configuration is designated as E.
Thus, according to IUPAC the compound can be named as, (E)-3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-octadienoic acid.
(d)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the compound has to be given and its configuration should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
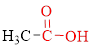
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
E-Z designators are used as like cis-trans terminology for non-similar groups attached alkenes.
In E-Z designations, the groups attached to vinylic positions are checked by their priority on the basis of higher molecular weight. If the higher priority groups are on the same sides, then the configuration is designated as Z. If the higher priority groups are on the opposite sides, then the configuration is designated as E.
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid is,
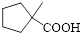
Let’s given numbering to this compound as follows,
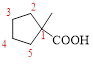
The parent hydrocarbon ring has five carbon atoms, one methyl groups is attached to the first carbon atom to this same carbon atom carboxylic acid is attached.
Thus, according to IUPAC the compound can be named as, 1-methylcyclopentane carboxylic acid.
(e)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the compound has to be given and its configuration should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
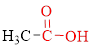
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound of acid is,
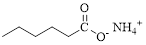
Let’s given numbering to this compound as follows,
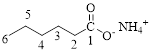
The parent hydrocarbon chain has six carbon atoms; an ammonium ion is attached with the carboxyl part of this compound.
Thus, according to IUPAC the compound can be named as, Ammonium hexanoate.
(f)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the compound has to be given and its configuration should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
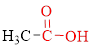
Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid. If two or more carboxylic functional groups are present in the same compound then its number should be taken in to consideration and the prefix di, tri, tetra.. must be used.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Explanation of Solution
Given carboxylic acid is,
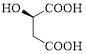
Let’s given numbering to this compound as follows,
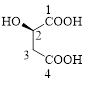
The parent hydrocarbon chain has four carbon atoms, there are three functional groups, one is –OH (which is attached to the second carbon atom) and the other two is –COOH. But, carboxylic acid has higher priority than the -OH, thus –OH will appeared in the name of the compound as the prefix – hydroxy.
Here, this compound has a chiral center (it is highlighted as *); its configuration can be specified as follows,
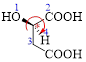
The numbering follows a clock wise direction and so molecule is in as R- configuration.
Thus, according to IUPAC the compound can be named as, (R)-2-hydroxybutanedioic acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
- 29. a) i Which energy diagram best represents the d-electrons in tetrahedral [Co(NH3)4]²+? b) ii c) iii d) iv 11 ་ ↑↓ ↑t t ↑↓ ↑↓ e) none of these ii In1 According to Slater's rules, what is the effective nuclear charge experienced by a 3d electron in 30. Ge? a) 32.00 b) 21.15 c) 16.05 d) 14.00 e) 10.85arrow_forwardRegarding Lowis structuros and geometrios, Draw Lewis structures for the following: SOF4, SO, ICI, XeO2F4, SeF and XeO3. For each one, indicate the observed molecular geometry it adopts.arrow_forwardExplain the following statements with equations: - The fusion product of an organic compund with sodium metal is an alkaline solution - The test for elements should be done before the solubility tests. - Using less sodium than the organic compound in the ignition test might cause a problem to detect the presence of the nitrogen and sulfur - Formation of colored product when adding ferric acid chloride to phenol solutionarrow_forward
- 31 Indicate the symbol, mass number and the atomic number of the missing product in each of the following nuclear reactions. a) 13/3 N 41 b) 11 Ca 20 c) 90 38 Sr → 133 C + ? + - 6 0 e →? 90 Y + ? 39 11 d) 22 Na → ? + + 1 B +1 β Toarrow_forwardPlease drawarrow_forward9. compore the Following two Venctions IN termy Of Ronction Rate and explan in detail the reasoning that led to your conclusion +He p₁₂ 11- ㅐ 15 .. +He H #H H / H b. Compare the Following too reactions 14 terms of reaction Rate and explain in detail the reasoning that led to your conclusion Н d-C- tłu Na +2446 е -ll +2n "Harrow_forward
- a. •Write all of the possible products For the Following ronction А ----- H - H H + H₂0 H+ Н b. in Rite the complete reaction Mechaniszn For the Formation of each product. ·C. Suggest what Reaction conditions could Result in each product being the major Product of the veaction:arrow_forwarda. Write the product For each of the Following reactions H 6-836-6 레 +H₂ N A H A-C-C=C-C-CH + 2 Na +2 NH3 - H H b. Write the reaction Mechanism For. reaction eacharrow_forwardhelp draw the moleculearrow_forward
- How to draw this claisen condensation reaction mechanisms/arrow_forwardWrite all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forwardHow can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


