
Concept explainers
Answer the following questions about B, depicted in the ball-and-stick model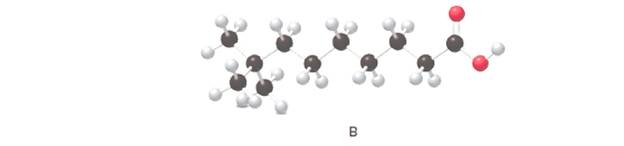
a. What is the IUPAC name for B?
b. Draw an isomer of B that has the same
c. Draw an isomer of B that has a different functional group.
d. What products are formed when B is treated with NaOH?
e. Predict the solubility properties of B in
f. What product is formed when B is treated with
g. What product is formed when B is heated with
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given ball and stick model should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
8,8-dimethylnonanoic acid.
Explanation of Solution
In the given ball and stick model of the compounds;
Black ball = C atom
White ball = H atom
Red ball = O atom
Blue ball = N atom
To assign the acceptable name to the compound, the IUPAC rules must be followed:
- Check the longest C chain and assign root word for that.
- Add prefix for the branch or side chain with its position.
- Add di, tri, tetra prefix for more than one prefix.
- The primary suffix indicates the single, double and triple bond in the molecule.
- Secondary suffix indicates the presence of functional group in the molecule.
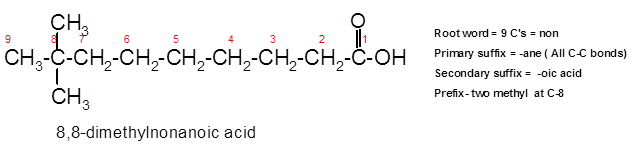
(b)
Interpretation:
The constitutional isomer of 8,8-dimethylnonanoic acid which has same functional group should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
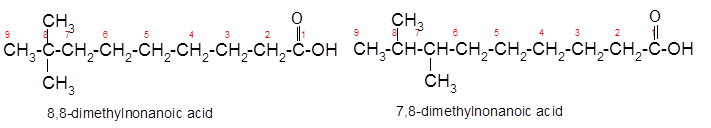
Explanation of Solution
Constitutional isomers are the isomers with same molecular formula but different arrangement of bonded atoms in the molecule. The constitutional isomer of 5-methylhexanoic acid which has same functional group must have same molecular formula but different structural arrangement of bonded atoms.
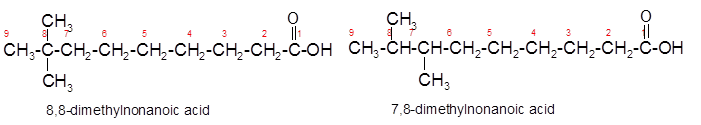
(c)
Interpretation:
The constitutional isomer of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid which has different functional group should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
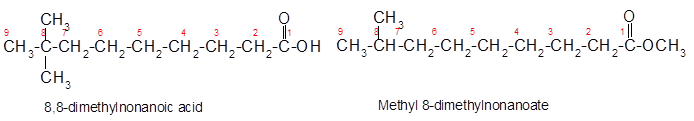
Explanation of Solution
Constitutional isomers are the isomers with same molecular formula but different arrangement of bonded atoms in the molecule. The constitutional isomer of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid which has different functional group must have same molecular formula but different functional group like ester as ester and carboxylic acid are functional isomers of each other.
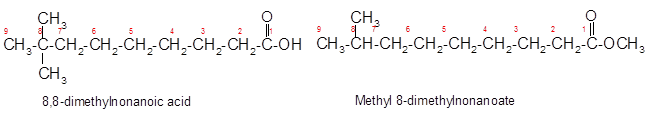
(d)
Interpretation:
The products formed when the given carboxylic 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid react with NaOH should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Amines are the organic compounds with general chemical formula of R-NH2 or R-NH-R whereas carboxylic acids are the organic molecules with R-COOH as general chemical formula.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
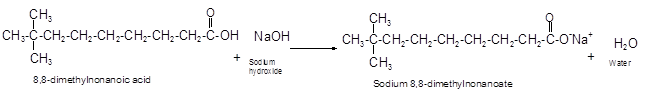
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of carboxylic acid with base like NaOH is an acid-base reaction that leads to the formation of salt and water.
It is also called as neutralization reaction. In these reactions the carboxylic acid gives H+ ions that combines with OH- ion from base and forms water. The carboxylate ion converts to sodium salt due to presence of Na+ ions in the solution.
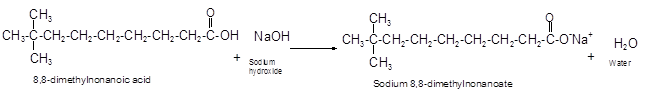
(e)
Interpretation:
The solubility of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid in water and organic solvent should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid is less soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Explanation of Solution
Organic compounds like hydrocarbons are composed of C and H atoms. They mainly have C-C and C-H bonds in their structure.
Since both C-C and C-H bonds are non-polar in nature therefore hydrocarbons like alkanes are non-polar compounds therefore it is soluble in non-polar solvents like organic solvents.
The 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid is a polar compound due to −COOH group and must form hydrogen bonds with water molecule but due to bulky alkyl group in the molecule it is very difficult for the molecule to form hydrogen bonds with water molecule. Therefore 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid is insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents.
(f)
Interpretation:
The reaction of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid with ethanol in the presence of H2SO4 should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Alcohols are the organic compounds with general chemical formula of R-OH whereas carboxylic acids are the organic molecules with R-COOH as general chemical formula.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
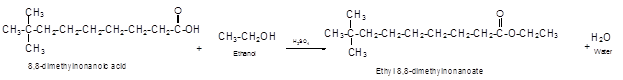
Explanation of Solution
The German chemist Emil Fischer purposed the reaction of carboxylic acid with alcohol in acidic medium to form ester and water. The reaction occurs in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid. In this reaction the alcohol carbon atom react with carbonyl carbon atom of carboxylic acid to form ester.
The reaction of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid with ethanol leads to formation of water and ester that must have −COO- group in the molecule.
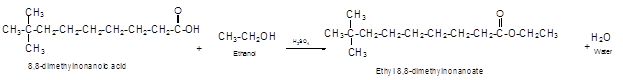
(g)
Interpretation:
The reaction of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid with ethylamine should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the groups of atoms or atoms which are bonded with parent carbon chain in the organic molecule and are responsible for the physical and chemical properties of the compound. In organic chemistry, there are different functional groups such as carboxylic acid, alcohol, ester, or amide.
Alcohols are the organic compounds with general chemical formula of R-OH whereas carboxylic acids are the organic molecules with R-COOH as general chemical formula.
Answer to Problem 17.92P
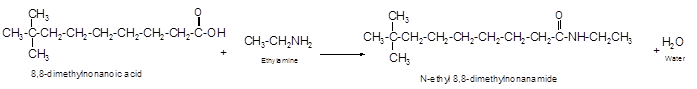
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of carboxylic acid with ammonia or amines forms amide molecules. It involves the formation of water molecule. In this reaction the amine nitrogen atom react with carbonyl carbon atom of carboxylic acid to form amide.
The reaction of 8, 8-dimethylnonanoic acid with ethylamine leads to formation of water and amide that must have −CONH- group in the molecule.
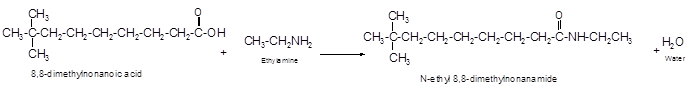
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. (CH3)2NH, TSOH Drawingarrow_forwardSo, the first image is what I'm trying to understand regarding my approach. The second image illustrates my teacher's method, and the third image includes my notes on the concepts behind these types of problems.arrow_forwardHAND DRAWarrow_forward
- Draw a mental model for calcium chloride mixed with sodium phosphatearrow_forwardhere is my question (problem number 20) please explain to me thanks!arrow_forwardThe bromination of anisole is an extremely fast reaction. Complete the resonance structures of the intermediate arenium cation for the reaction (Part 1), and then answer the question that follows (Part 2).arrow_forward
- Drawing of 3-fluro-2methylphenolarrow_forwardWhich compound(s) will be fully deprotonated (>99%) by reaction with one molar equivalent of sodium hydroxide? I, II, III I, || I, III I only II, III SH | H3C-C=C-H || III NH2arrow_forwardWill NBS (and heat or light) work for this reaction, or do we have to use Br2?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
