
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of 2-hydroxyheptanoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.53P
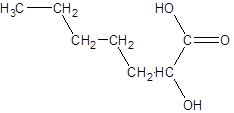
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid according to the following steps:
1. The parent (longest)
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is 2-hydroxyheptanoic acid where the parent chain is heptane that is 7 carbon atom chain having a hydroxy substituent at carbon-2. So, the structure of 2-hydroxyheptanoic acid is:
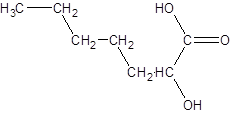
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of 4-chlorononanoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.53P
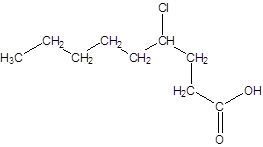
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid according to the following steps:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is 4-chlorononanoic acid where the parent chain is nonane that is 9 carbon atom chain having a chloro substituent at carbon-4. So, the structure of 4-chlorononanoic acid is:
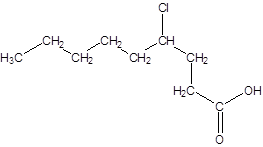
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of 3,4-dibromobenzoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.53P
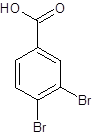
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid according to the following steps:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is 3,4-dibromobenzoic acid where the parent chain is benzene having 2 bromo substituents at carbon-3 and carbon-4. So, the structure of 3,4-dibromobenzoic acid is:
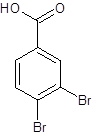
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of lithium propanoate should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.53P
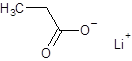
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H. When H of hydroxyl group present in carboxylic acid is replaced by an atom then it results in the formation of respective salt.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid salt according to the following steps:
- The parent (longest) carbon chain is identified.
- The name of metal is written first from which the salt is made up of.
- The ending of the for a carboxylic acid group is changed to -oate for naming salt of carboxylic acid.
- The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
- Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is lithium propanoate where the parent chain is propane having 3 carbon atoms and metal is lithium. So, the structure of lithium propanoate is:
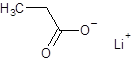
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of 2,2-dibromobutanoic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.53P
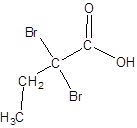
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H.
The IUPAC names are given to the carboxylic acid according to the following steps:
1. The parent (longest) alkane chain is identified.
2. The ending of the parent chain from alkane (-e) is changed to -oic acid for a carboxylic acid group.
3. The numbering is of the chain is done in such a way that carbonyl carbon gets the smaller number.
4. Name should be written in alphabetical order and other substituents are shown by the number.
For number of carbons atoms chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec
The given name is 2,2-dibromobutanoic acid where the parent chain is butane that is 4 carbon atom chain having two bromo substituents at carbon-2. So, the structure of 2,2-dibromobutanoic acid is:
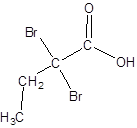
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of ethyl 2-methylpropanoate should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
The structure of organic compound is drawn in order to represent the arrangement of atoms in which they are present in a molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.53P
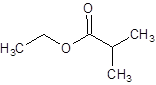
Explanation of Solution
An organic compound in which carboxy functional group that is -COOH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be a carboxylic acid. The general formula for carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H. When -H of the carboxylic acid is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group (-R') then it results in the formation of an ester having general formula RCOOR'.
The reaction which results in the formation of at least one ester along with water on heating acids with alcohols is said to be esterification.
So, in order to give the IUPAC name to the esters, the following steps are followed:
- The alkyl substituent from the alcohol is named first.
- The name of the parent chain from carboxylic acid part is replaced as carboxylate.
In order to write the common name of the esters, the common of acids are written from which the ester has been formed.
The given name is ethyl 2-methylpropanoate where ethyl name is derived from ethanol and 2-methylpropanoate is derived from the name 2-methylpropanoic acid. So, the structure of ethyl 2-methylpropanoate is:
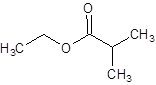
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning




