
(a)
Interpretation:
Structure of amine or quaternary ammonium salt that is obtained when trimethylamine and ethyl bromide is reacted in presence of strong base has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alkylation reaction is a reaction in which the transfer of alkyl group from one molecule to another molecule takes place. While considering
(a)
Answer to Problem 17.69EP
The structure of product obtained is,
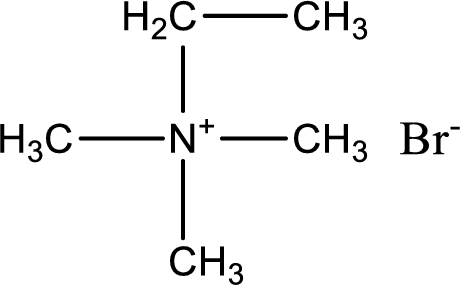
Explanation of Solution
Given reactants are trimethylamine and ethyl bromide. In this, the amine given is a tertiary amine. When tertiary amine is treated with an alkyl halide, the product obtained is a quaternary ammonium salt. The complete reaction and the structure of the product formed is given as,
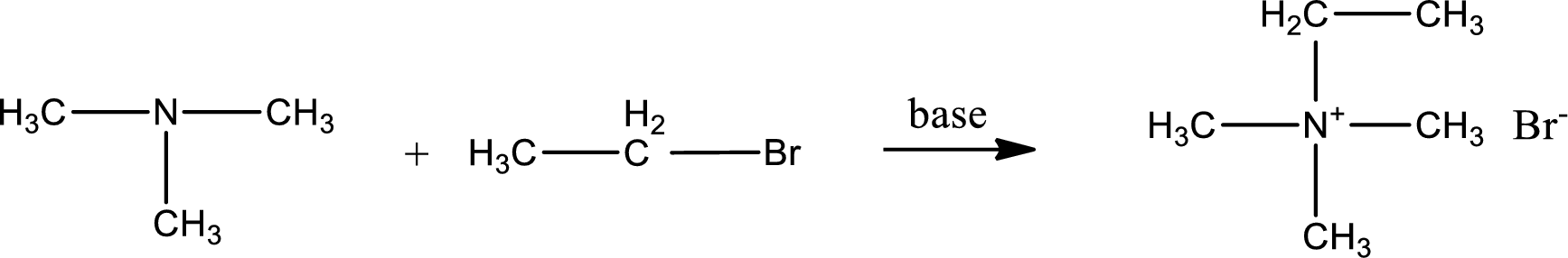
Structure of the product formed is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structure of amine or quaternary ammonium salt that is obtained when diisopropylamine and methyl bromide is reacted in presence of strong base has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alkylation reaction is a reaction in which the transfer of alkyl group from one molecule to another molecule takes place. While considering amines, the alkylating agent that is used is alkyl halides. Alkylation is done under basic conditions. The general equations for amines alkylation process is,
(b)
Answer to Problem 17.69EP
The structure of product obtained is,
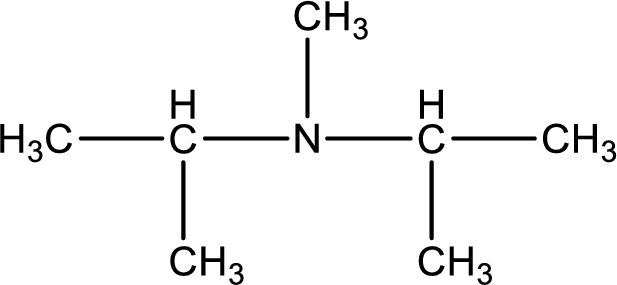
Explanation of Solution
Given reactants are diisopropylamine and methyl bromide. In this, the amine given is a secondary amine. When secondary amine is treated with an alkyl halide, the product obtained is a tertiary amine. The complete reaction and the structure of the product formed is given as,
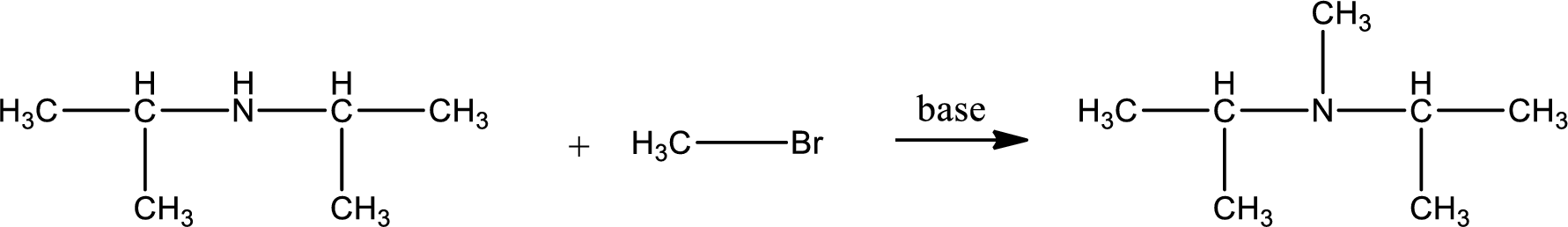
Structure of the product formed is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
Structure of amine or quaternary ammonium salt that is obtained when ethylmethylpropylamine and methyl chloride is reacted in presence of strong base has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alkylation reaction is a reaction in which the transfer of alkyl group from one molecule to another molecule takes place. While considering amines, the alkylating agent that is used is alkyl halides. Alkylation is done under basic conditions. The general equations for amines alkylation process is,
(c)
Answer to Problem 17.69EP
The structure of product obtained is,
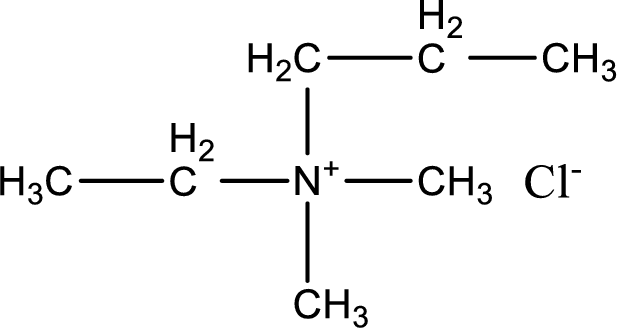
Explanation of Solution
Given reactants are ethylmethylpropylamine and methyl chloride. In this, the amine given is a tertiary amine. When tertiary amine is treated with an alkyl halide, the product obtained is a quaternary ammonium salt. The complete reaction and the structure of the product formed is given as,
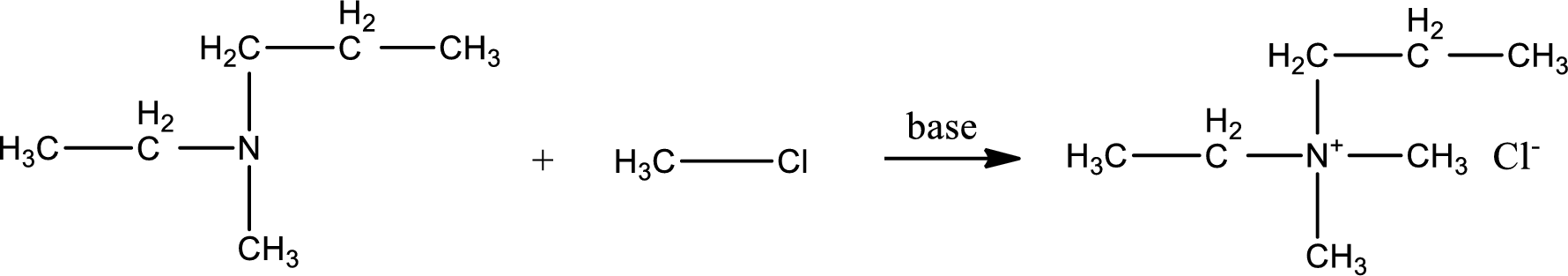
Structure of the product formed is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
Structure of amine or quaternary ammonium salt that is obtained when ethylamine and ethyl chloride is reacted in presence of strong base has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alkylation reaction is a reaction in which the transfer of alkyl group from one molecule to another molecule takes place. While considering amines, the alkylating agent that is used is alkyl halides. Alkylation is done under basic conditions. The general equations for amines alkylation process is,
(d)
Answer to Problem 17.69EP
The structure of product obtained is,
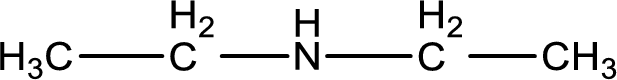
Explanation of Solution
Given reactants are ethylamine and ethyl chloride. In this, the amine given is a primary amine. When primary amine is treated with an alkyl halide, the product obtained is a secondary amine. The complete reaction and the structure of the product formed is given as,
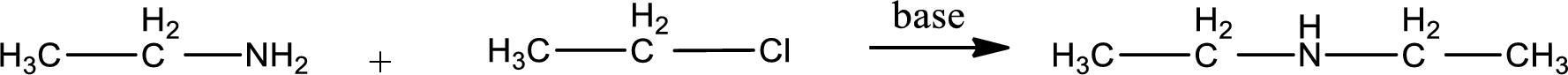
Structure of the product formed is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC,+BIO.CHEM.-MINDTAP
- The molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forwardWhat characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forward
- For a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forwardDescribe a sequence of photophysical processes that can be followed by radiation adsorbed by a molecule in the ground state to give rise to phosphorescent emission.arrow_forward
- State two similarities between fluorescence and phosphorescence.arrow_forwardState three photophysical processes that can be related to the effects of incident radiation on a molecule in its ground state. Consider that radiation can give rise to fluorescent emission, but not phosphorescent emission.arrow_forwardIn a photochemical reaction, how is the rate of the process related to its quantum yield?arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





