
General Chemistry: Atoms First
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780321809261
Author: John E. McMurry, Robert C. Fay
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 16.7, Problem 16.9CP
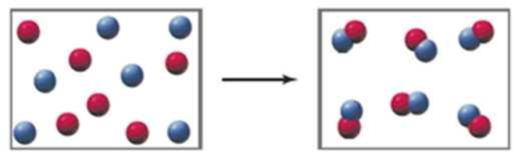
What are the signs (+, –, or 0) of ΔH, ΔS, and ΔG for the following spontaneous reaction of A atoms (red) and B atoms (blue)?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Sketch the intermediates for A,B,C & D.
Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating
the reactants?
O
? A
. If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like.
. If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead.
Explanation
Check
Click and drag to start drawing a structure.
ㅇ
80
F5
F6
A
2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cente
FIG
In methyl orange preparation, if the reaction started with 0.5 mole of sulfanilic acid to form the diazonium salt of this compound and then it converted to methyl orange [0.2 mole]. If the efficiency of the second step was 50%, Calculate: A. Equation(s) of Methyl Orange synthesis: Diazotization and coupling reactions. B. How much diazonium salt was formed in this reaction? C. The efficiency percentage of the diazotization reaction D. Efficiency percentage of the whole reaction.
Chapter 16 Solutions
General Chemistry: Atoms First
Ch. 16.1 - Predicting the Sign of S Predict the sign of S in...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.2PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.3CPCh. 16.3 - Which state has the higher entropy? Explain in...Ch. 16.5 - Calculate the standard entropy of reaction at 25C...Ch. 16.6 - By determining the sign of Stotal, show whether...Ch. 16.7 - Consider the decomposition of gaseous N2O4:...Ch. 16.7 - The following data apply to the vaporization of...Ch. 16.7 - What are the signs (+, , or 0) of H, S, and G for...Ch. 16.8 - Consider the thermal decomposition of calcium...
Ch. 16.8 - Consider the following endothermic decomposition...Ch. 16.9 - (a)Using values of Gf in Appendix B, calculate the...Ch. 16.10 - Calculate G for the formation of ethylene (C2H4)...Ch. 16.10 - Consider the following gas-phase reaction of A2...Ch. 16.11 - Given the data in Appendix B, calculate Kp at 25 C...Ch. 16.11 - Use the data in Appendix B to calculate the vapor...Ch. 16.11 - At 25 C, Kw for the dissociation of water is 1.0 ...Ch. 16.11 - Prob. 16.18PCh. 16.11 - Prob. 16.19PCh. 16 - Ideal gases A (red spheres) and B (blue spheres)...Ch. 16 - What are the signs (+, , or 0) of H, S, and G for...Ch. 16 - What are the signs (+, , or 0) of H, S, and G for...Ch. 16 - An ideal gas is compressed at constant...Ch. 16 - Consider the following spontaneous reaction of A2...Ch. 16 - Consider the dissociation reactionA2(g)2A(g). The...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.26CPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.27CPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.28CPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.29CPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.30SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.31SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.32SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.33SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.34SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.35SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.36SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.37SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.38SPCh. 16 - Predict the sign of S for each process in Problem...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.40SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.41SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.42SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.43SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.44SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.45SPCh. 16 - Which state in each of the following pairs has the...Ch. 16 - Which State in each of the following pairs has the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.48SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.49SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.50SPCh. 16 - Which substance in each of the following pairs...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.52SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.53SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.54SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.55SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.56SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.57SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.58SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.59SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.60SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.61SPCh. 16 - In lightning storms, oxygen is converted to ozone:...Ch. 16 - Sulfur dioxide emitted from coal-fired power...Ch. 16 - Elemental mercury can be produced from its oxide:...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.65SPCh. 16 - For the vaporization of benzene, Hvap = 30.7kJ/mol...Ch. 16 - For the melting of sodium chloride, Hfusion =...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.68SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.69SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.70SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.71SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.72SPCh. 16 - Given the data in Problem 16.67, calculate G for...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.74SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.75SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.76SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.77SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.78SPCh. 16 - Use the data in Appendix B to calculate H and S...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.80SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.81SPCh. 16 - Use the data in Appendix B to tell which of the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.83SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.84SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.85SPCh. 16 - Ethanol is manufactured in industry by the...Ch. 16 - Sulfur dioxide in the effluent gases from...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.88SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.89SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.90SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.91SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.92SPCh. 16 - What is G for the formation of solid uranium...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.94SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.95SPCh. 16 - What is the relationship between the standard...Ch. 16 - What is the relationship between the standard...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.98SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.99SPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.100SPCh. 16 - At 25 C, Ka for acid dissociation of aspirin...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.102SPCh. 16 - Calculate the equilibrium partial pressure of...Ch. 16 - Ethylene oxide, C2H4O, is used to make antifreeze...Ch. 16 - The first step in the commercial production of...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.106CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.107CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.108CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.109CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.110CHPCh. 16 - The standard free-energy change at 25 C for the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.112CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.113CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.114CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.115CHPCh. 16 - Use the data in Appendix B to calculate H, S, and...Ch. 16 - Troutons rule says that the ratio of the molar...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.118CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.119CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.120CHPCh. 16 - Use the data in Appendix B to calculate the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.122CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.123CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.124CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.125CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.126CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.127CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.128CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.129CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.130CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.131CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.132CHPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.133MPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.134MPCh. 16 - One step in the commercial synthesis of sulfuric...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.136MPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.137MPCh. 16 - A 1.00 L volume of gaseous ammonia at 25.0 C and...Ch. 16 - Consider the unbalanced equation:...Ch. 16 - A mixture of NO2 and N2O4, each at an initial...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hand written equations pleasearrow_forwardHand written equations pleasearrow_forward> each pair of substrates below, choose the one that will react faster in a substitution reaction, assuming that: 1. the rate of substitution doesn't depend on nucleophile concentration and 2. the products are a roughly 50/50 mixture of enantiomers. Substrate A Substrate B Faster Rate X Ś CI (Choose one) (Choose one) CI Br Explanation Check Br (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Farrow_forward
- NMR spectrum of ethyl acetate has signals whose chemical shifts are indicated below. Which hydrogen or set of hydrogens corresponds to the signal at 4.1 ppm? Select the single best answer. The H O HỌC—C—0—CH, CH, 2 A ethyl acetate H NMR: 1.3 ppm, 2.0 ppm, 4.1 ppm Check OA B OC ch B C Save For Later Submit Ass © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center |arrow_forwardHow many signals do you expect in the H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Br Br Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. 1 Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. Check For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. O ✓ No additional Hs to color in top molecule ง No additional Hs to color in bottom…arrow_forwardin the kinetics experiment, what were the values calculated? Select all that apply.a) equilibrium constantb) pHc) order of reactiond) rate contstantarrow_forward
- true or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forwardin the bromothymol blue experiment, pKa was measured. A closely related compound has a Ka of 2.10 x 10-5. What is the pKa?a) 7.1b) 4.7c) 2.0arrow_forwardcalculate the equilibrium concentration of H2 given that K= 0.017 at a constant temperature for this reaction. The inital concentration of HBr is 0.050 M.2HBr(g) ↔ H2(g) + Br2(g)a) 4.48 x 10-2 M b) 5.17 x 10-3 Mc) 1.03 x 10-2 Md) 1.70 x 10-2 Marrow_forward
- true or falsegiven these two equilibria with their equilibrium constants:H2(g) + CI2(l) ↔ 2HCI(g) K= 0.006 CI2(l) ↔ CI2(g) K= 0.30The equilibrium contstant for the following reaction is 1.8H2(g) + CI2 ↔ 2HCI(g)arrow_forwardI2(g) + CI2(g) ↔ 2ICIK for this reaction is 81.9. Find the equilibrium concentration of I2 if the inital concentration of I2 and CI2 are 0.010 Marrow_forwardtrue or false,the equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.50.PCI5(g) ↔ PCI3(g) + CI2(g)Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.25.2PCI5(g) ↔. 2PCI3(g) + 2CI2(g)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY