
Concept explainers
17-30 Answer true or false.
(a) The reduction of an
(b) The reduction of a
(c) The oxidation of an aldehyde gives a
(d) The oxidation of a primary alcohol gives a ketone.
(e) Tollens’ reagent can be used to distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone.
(f) Sodium borohydride, NaBH4, reduces an aldehyde to a primary alcohol.
(g) The addition of one molecule of alcohol to the carbonyl group of a ketone gives a hemiacetal.
(h) The reaction of an aldehyde with two molecules of alcohol gives an acetal, plus a molecule
of water.
(j) The formation of hemiacetals and acetals is reversible.
(j) The cyclic hemiacetal formed from 4-hydroxy-pentanal has two stereocenters and can exist as
a mixture of 22 = 4 stereoisomers.
(a)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The reduction of an aldehyde always gives an alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
Reduction is the addition of a hydrogen atom to a compound.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
In aldehydes, the functional group is
Oxidation of aldehydes forms primary alcohol. For example, reduction of pentanal gives 1-pentanol.

Therefore, the given statement is true.
(b)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The reduction of ketones always gives a secondary alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. Reduction is the addition of a hydrogen atom to a compound.
Answer to Problem 22P
Therefore, the given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Reduction of ketones, hydrogen is added to the carbonyl carbon and gives secondary alcohol.

Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The oxidation of aldehydes gives a carboxylic acid.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. Oxidation is the process in which oxygen is added to the molecule.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Oxidation of aldehydes, oxygen is added to the carbonyl group and form carboxylic acid.

Therefore, the given statement is true.
(d)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The oxidation of primary alcohol gives ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. Oxidation is the process in which oxygen is added to the molecule.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Oxidation of primary alcohol first converted into aldehyde and followed by carboxylic acids.
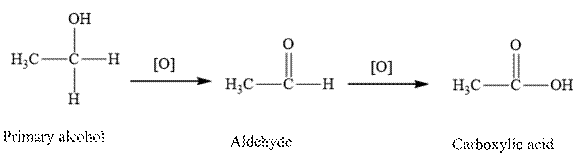
Therefore, the given statement is false.
(e)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
Tollen’s reagent can be used to distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Tollen’s reagent is a mild oxidizing agent.
Tollen’s reagent is reacts with the aldehyde group of a compound. The carbonyl group acts as a reducing agent and reduces the silver ion of the Tollen’s regent to silver metal.
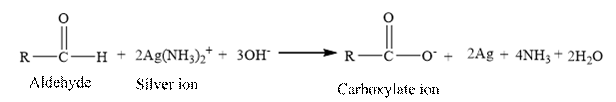
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes undergo oxidation easily, even with mild oxidizing agents and give carboxylic acid.
Ketone does not undergo oxidation with mild oxidizing agent due to selectivity of aldehyde and ketone for oxidation is used to differentiate an aldehyde and a ketone. Therefore, aldehyde and ketones are distinguished by using Tollen’s regent.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(f)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
Sodium borohydride,
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. The aldehydes undergoes a reduction reaction where in the addition of hydrogen occurs at the double bond between the oxygen and the carbon of the carbonyl group present in the aldehyde.
Answer to Problem 22P
Therefore, the given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
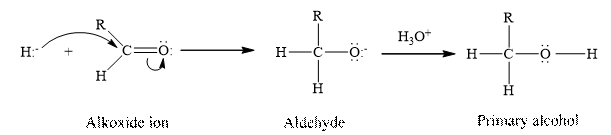
(g)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The addition of one molecule of alcohol to the carbonyl group of a ketone gives a hemiacetal.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. In Hemiacetal, carbon is added to hydroxyl group and alkoxy group.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
When a molecule of alcohol is added to a ketone, the hydrogen of the alcohol is added o the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group, while the alkoxy group of the alcohol is added to the carbon of the carbonyl group. Hence ketone forms hemiacetal when the reacts with one molecule of alcohol.
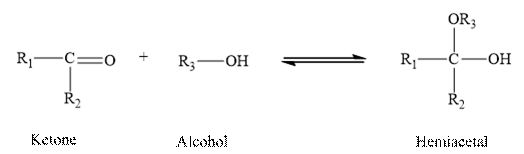
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(h)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The reaction of an aldehyde with two molecules of alcohol gives an acetal, plus a molecule of water.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. In acetal, carbon is bonded to two alkoxy groups.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Two molecules of an alcohol are added to an aldehyde to form hemiacetal. And it is unstable and it reacts with another molecule of an alcohol in the presence of an acid forms acetal and water.
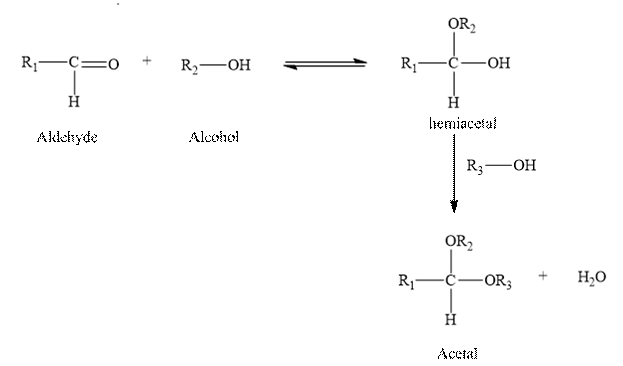
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(i)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The formation of hemiacetals and acetal is reversible.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. In Hemiacetal, carbon is added to hydroxyl group and alkoxy group. In acetal, carbon is added to a two alkoxy groups.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
By using large excess of alcohol hemiacetals and acetals are reversible by the removal of water molecules. To shift the equilibrium towards the left side by the hydrolysis of the acetal to the aldehyde or ketone and alcohol.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(j)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The cyclic hemiacetal formed from 4-hydroxypentanal has two stereocentres and can exists as a mixture of
Concept Introduction:
A stereocentre is a carbon atom with four different groups bonded to it. The stereocentres of molecule can be calculated by using
n= stereocentre.
Answer to Problem 22P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The cyclic hemiacetal; obtained from 4-hydroxypentanal has two stereocenters.
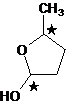
4- hydroxypentanal has two stereocenters, therefore it have 4 stereoisomers.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Introduction To General, Organic, And Biochemistry
- Dr. Mendel asked his BIOL 260 class what their height was and what their parent's heights were. He plotted that data in the graph below to determine if height was a heritable trait. A. Is height a heritable trait? If yes, what is the heritability value? (2 pts) B. If the phenotypic variation is 30, what is the variation due to additive alleles? (2 pts) Offspring Height (Inches) 75 67.5 60 52.5 y = 0.9264x + 4.8519 55 60 65 MidParent Height (Inches) 70 75 12pt v V Paragraph B IUA > AT2 v Varrow_forwardExperiment: Each team will be provided with 5g of a mixture of acetanilide and salicylic acid. You will divide it into three 1.5 g portions in separate 125 mL Erlenmeyer flasks savıng some for melting point analysis. Dissolve the mixture in each flask in ~60mL of DI water by heating to boiling on a hotplate. Take the flasks off the hotplate once you have a clear solution and let them stand on the bench top for 5 mins and then allow them to cool as described below. Sample A-Let the first sample cool slowly to room temperature by letting it stand on your lab bench, with occasional stirring to promote crystallization. Sample B-Cool the second sample 1n a tap-water bath to 10-15 °C Sample C-Cool the third sample in an ice-bath to 0-2 °C Results: weight after recrystalization and melting point temp. A=0.624g,102-115° B=0.765g, 80-105° C=1.135g, 77-108 What is the percent yield of A,B, and C.arrow_forwardRel. Intensity Q 1. Which one of the following is true of the compound whose mass spectrum is shown here? Explain how you decided. 100 a) It contains chlorine. b) It contains bromine. c) It contains neither chlorine nor bromine. 80- 60- 40- 20- 0.0 0.0 TT 40 80 120 160 m/z 2. Using the Table of IR Absorptions how could you distinguish between these two compounds in the IR? What absorbance would one compound have that the other compound does not? HO CIarrow_forward
- Illustrate reaction mechanisms of alkenes with water in the presence of H2SO4, detailing each step of the process. Please show steps of processing. Please do both, I will thumb up for sure #1 #3arrow_forwardDraw the following molecule: (Z)-1-chloro-1-butenearrow_forwardIdentify the molecule as having a(n) E, Z, cis, or trans configuration. CH3 H₁₂C ○ E ○ z ○ cis transarrow_forward
- Identify the molecule as having a(n) E, Z, cis, or trans configuration. H₂C- CH3 О Е ○ cis ○ transarrow_forwardThe decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide according to the equation: 50°C 2 N2O5(g) 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) follows first-order kinetics with a rate constant of 0.0065 s-1. If the initial concentration of N2O5 is 0.275 M, determine: the final concentration of N2O5 after 180 seconds. ...arrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- CS2(g) →CS(g) + S(g) The rate law is Rate = k[CS2] where k = 1.6 × 10−6 s−¹. S What is the concentration of CS2 after 5 hours if the initial concentration is 0.25 M?arrow_forwardCS2(g) → CS(g) + S(g) The rate law is Rate = k [CS2] where k = 1.6 × 10-6 s−1. S Calculate the half-life.arrow_forwardThe following is a first order reaction where the rate constant, k, is 6.29 x 10-3 min-*** What is the half-life? C2H4 C2H2 + H2arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

