
Concept explainers
Knowing that wheel A rotates with a constant angular velocity and that no slipping occurs between ring C and wheel A and wheel B, which of the following statements concerning the angular speeds of the three objects is true?
a.
b.
c.
d.
e. The contact points between A and C have the same acceleration.
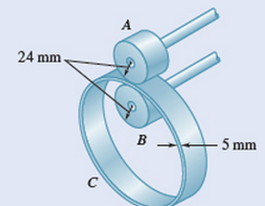
Fig. P15.CQ2
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
- please show presentation, drawing diagram, vector’s forces & position, etc.. and showing work steps. thank youarrow_forwardA 2.5-kg homogeneous disk of radius 80 mm rotates at the constant rate ω1 = 50 rad/s with respect to arm ABC, which is welded to a shaft DCE. Knowing that at the instant shown, shaft DCE has an angular velocity w2 = (12 rad/s)k and an angular acceleration a2= = (8 rad/s2)k, determine (a) the couple that must be applied to shaft DCE to produce that acceleration, (b) the corresponding dynamic reactions at D and E.arrow_forwardA disc rolls without slipping. The magnitude of the angular velocity ω= 1.0 rad/s, the angular acceleration α=1.0 rad/s2. The radius of the disc is r=2.0 m. (4) Determine the direction of the acceleration of the point A ________ A. down B. left C. up D. rightarrow_forward
- Ring C has an inside radius of 55 mm and an outside radius of 60 mm and is positioned between two wheels A and B, each of 24-mm outside radius. Knowing that wheel A rotates with a constant angular velocity of 300 rpm and that no slipping occurs, determine (a) the angular velocity of ring C and of wheel B, (b) the acceleration of the points on A and B that are in contact with C.arrow_forwardProblem 16.122 Member AB has the angular velocity ωAB = 2 rad/s and angular acceleration αAB = 7 rad/s2 . (Figure 1) Part A) Determine the angular velocity of member CD at the instant shown measured counterclockwise. Part B) Determine the angular acceleration of member CD at the instant shown measured counterclockwisearrow_forwardProblem 16.137 At the instant shown in (Figure 1), rod AB has an angular velocity WAB = 3.0 rad/s and an angular acceleration AB = 10 rad/s². The collar at C is pin-connected to CD and slides over AB. Figure 60° @AB αAB 0.75 m с 0.5 m B 1 of 1 Part A WCD= Determine the angular velocity of rod CD at this instant. Express your answer in radians per second to three significant figures. Enter positive value if the direction of velocity is counterclockwise and negative value if the direction of velocity is clockwise. IVE ΑΣΦΑ ↓↑ vec Submit Part B αCD = Request Answer Submit Determine the angular acceleration of rod CD at this instant. Express your answer in radians per second squared to three significant figures. Enter positive value if the direction of acceleration is counterclockwise and negative value if the direction of acceleration is clockwise. [Π ΑΣΦ Request Answer ? vec rad/s ? < rad/s² 8 of 8 Reviewarrow_forward
- Problem (1) A belt-driven pulley and attached disk are rotating with increasing angular velocity. If at a given instant, the speed of the belt is v = 1.5 m/s, and the total acceleration of point A is 100 m/s?, determine: (a) The angular acceleration a of the pulley and disk (b) The total acceleration of point B (c) The acceleration of point C on the belt. A 150 mm 200 mmarrow_forwardPlease solve it correctlyarrow_forwardA disc rolls without slipping. The magnitude of the angular velocity ω= 1.0 rad/s, the angular acceleration α=1.0 rad/s2. The radius of the disc is r=2.0 m. (2) Determine the direction of the acceleration of the point G ________ A. up B. down C. right D. leftarrow_forward
- Only need A, B, and C please.arrow_forwardThe outer gear A rotates with an angular velocity of 6 rad/s counterclockwise. Knowing that the angular velocity of the intermediate gear B is 3 rad/s clockwise, determine: 1. The angular velocity of the arm ABC 2. The angular velocity of the outer gear C. Select one: A. ωarm=3 ω a r m = 3 rad/s (CW); and ωC=1.5 ω C = 1.5 rad/s (CW) B. ωarm=5 ω a r m = 5 rad/s (CW); and ωC=3 ω C = 3 rad/s (CW) C. ωarm=0 ω a r m = 0 rad/s ; and ωC=1.5 ω C = 1.5 rad/s (CCW) D. ωarm=1 ω a r m = 1 rad/s (CW); and ωC=0 ω C = 0 rad/sarrow_forwardA The 18-in.-radius fly wheel is rigidly attached to a 1.5-in. -radius shaft that can roll along parallel rails. Knowing that at the instant shown the center of the shaft has a velocity of 1.2 in/s and an acceleration of 0.5 in/s?, both directed down to the left, determine the acceleration (a) of point A, (b) of point B. 18 in. 20 Вarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





