
(a)
Interpretation:
To explain the following result obtain from theHammett equation.
Concept introduction:
Hammett reaction constant (
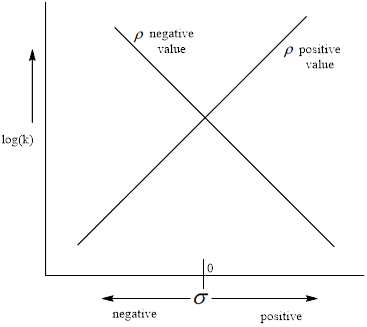
The negative value of the
(b)
Interpretation:
To explain the following result obtain from theHammett equation.
Concept introduction:
Hammett reaction constant (

The negative value of the
(c)
Interpretation:
To explain the following result obtain from theHammett equation.
Concept introduction: Hammett reaction constant (

The negative value of the
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- 7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forwardIndicate the compound formula: dimethyl iodide (propyl) sulfonium.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

