
(a)
Interpretation:
Aldehyde must contain the element nitrogen or not has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom.
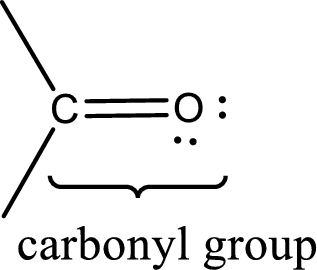
The groups that is attached to the carbonyl carbon atom can be either hydrogen or carbon atom. If the attached atoms are hydrogen and a carbon atom means then the compound is an aldehyde and if they are two carbon atoms means then the compound is a ketone. If the attached atom is a nitrogen atom to the carbonyl carbon atom means it is a amide. If a hydroxyl group is attached to a carbonyl carbon atom, then it is a
(b)
Interpretation:
Ketone must contain element nitrogen or not has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
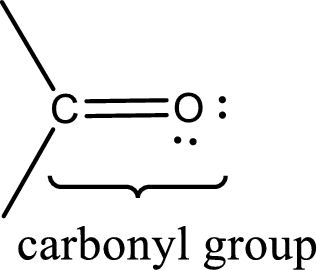
The groups that is attached to the carbonyl carbon atom can be either hydrogen or carbon atom. If the attached atoms are hydrogen and a carbon atom means then the compound is an aldehyde and if they are two carbon atoms means then the compound is a ketone. If the attached atom is a nitrogen atom to the carbonyl carbon atom means it is a amide. If a hydroxyl group is attached to a carbonyl carbon atom, then it is a carboxylic acid. If one of the bond in the carbonyl carbon atom is attached to an oxygen atom that is bonded with alkyl, cycloalkyl or aromatic system is known as ester.
(c)
Interpretation:
Ester must contain element nitrogen or not has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
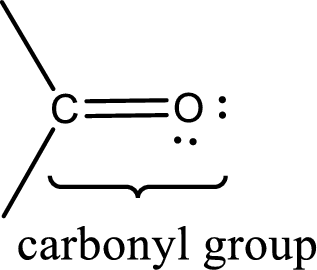
The groups that is attached to the carbonyl carbon atom can be either hydrogen or carbon atom. If the attached atoms are hydrogen and a carbon atom means then the compound is an aldehyde and if they are two carbon atoms means then the compound is a ketone. If the attached atom is a nitrogen atom to the carbonyl carbon atom means it is a amide. If a hydroxyl group is attached to a carbonyl carbon atom, then it is a carboxylic acid. If one of the bond in the carbonyl carbon atom is attached to an oxygen atom that is bonded with alkyl, cycloalkyl or aromatic system is known as ester.
(d)
Interpretation:
Amide must contain element nitrogen or not has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
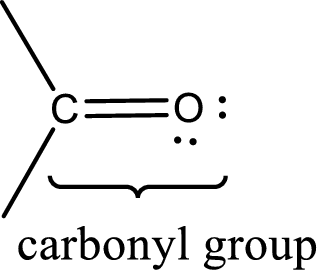
The groups that is attached to the carbonyl carbon atom can be either hydrogen or carbon atom. If the attached atoms are hydrogen and a carbon atom means then the compound is an aldehyde and if they are two carbon atoms means then the compound is a ketone. If the attached atom is a nitrogen atom to the carbonyl carbon atom means it is a amide. If a hydroxyl group is attached to a carbonyl carbon atom, then it is a carboxylic acid. If one of the bond in the carbonyl carbon atom is attached to an oxygen atom that is bonded with alkyl, cycloalkyl or aromatic system is known as ester.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Study Guide with Selected Solutions for Stoker's General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th
- 9 7 8 C 9 8 200 190 B 5 A -197.72 9 8 7 15 4 3 0: ང་ 200 190 180 147.52 134.98 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 90 OH 10 4 3 1 2 -143.04 140. 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 CI 3 5 1 2 141.89 140.07 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 ៖- 90 129. 126.25 80 70 60 -60 50 40 10 125.19 -129.21 80 70 3.0 20 20 -8 60 50 10 ppm -20 40 128.31 80 80 70 60 50 40 40 -70.27 3.0 20 10 ppm 00˚0-- 77.17 30 20 20 -45.36 10 ppm -0.00 26.48 22.32 ―30.10 ―-0.00arrow_forwardAssign all the carbonsarrow_forwardC 5 4 3 CI 2 the Righ B A 5 4 3 The Lich. OH 10 4 5 3 1 LOOP- -147.52 T 77.17 -45.36 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm B -126.25 77.03 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 TO LL <-50.00 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm 45.06 30.18 -26.45 22.36 --0.00 45.07 7.5 1.93 2.05 -30.24 -22.36 C A 7 8 5 ° 4 3 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 8 5 4 3 ཡི་ OH 10 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 5 4 3 2 that th 7 I 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 115 2.21 4.00 1.0 ppm 6.96 2.76 5.01 1.0 ppm 6.30 1.00arrow_forward
- Curved arrows were used to generate the significant resonance structure and labeled the most significant contribute. What are the errors in these resonance mechanisms. Draw out the correct resonance mechanisms with an brief explanation.arrow_forwardWhat are the: нсе * Moles of Hice while given: a) 10.0 ml 2.7M ? 6) 10.ome 12M ?arrow_forwardYou are asked to use curved arrows to generate the significant resonance structures for the following series of compounds and to label the most significant contributor. Identify the errors that would occur if you do not expand the Lewis structures or double-check the mechanisms. Also provide the correct answers.arrow_forward
- how to get limiting reactant and % yield based off this data Compound Mass 6) Volume(mL Ben zaphone-5008 ne Acetic Acid 1. Sam L 2-propanot 8.00 Benzopin- a col 030445 Benzopin a Colone 0.06743 Results Compound Melting Point (°c) Benzopin acol 172°c - 175.8 °c Benzoping to lone 1797-180.9arrow_forwardAssign ALL signals for the proton and carbon NMR spectra on the following pages.arrow_forward7.5 1.93 2.05 C B A 4 3 5 The Joh. 9 7 8 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 0.86 OH 10 4 3 5 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 CI 4 3 5 1 2 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 2.21 4.00 1.5 2.00 2.07 1.0 ppm 2.76arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





