
Interpretation:
Two differences apparent in arrangement of water about the hydrated ions have to be identified.
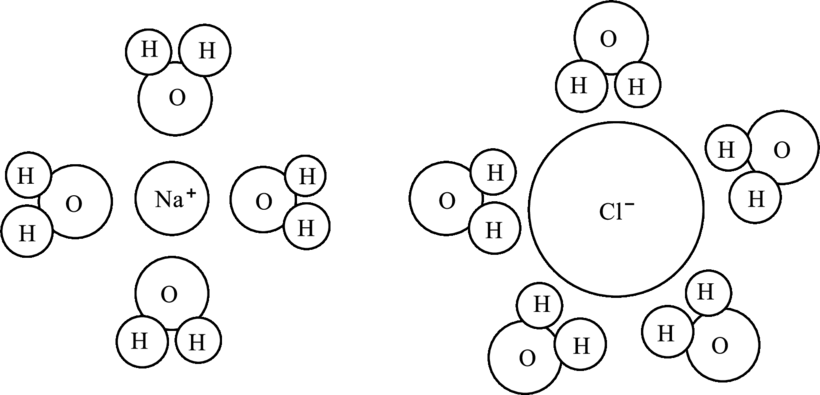
Concept Introduction:
An electrolyte refers to an ionic compound that on solvation in polar protic solvents ionizes to yield cationic and anionic species. The free movement of such ionic species results in the conduction of electricity.
Three subcategories exist for electrolyte namely strong electrolyte weak electrolyte and non-electrolyte. The strong electrolytes on dissolution exhibit
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
FOUNDATIONS OF COLLEGE CHEM +KNEWTONALTA
- Indicate the product(s) A, B C and D that are formed in the reaction: H + NH-NH-CH [A+B] [C+D] hydrazonesarrow_forwardHow can you prepare a 6 mL solution of 6% H2O2, if we have a bottle of 30% H2O2?arrow_forwardHow many mL of H2O2 from the 30% bottle must be collected to prepare 6 mL of 6% H2O2.arrow_forward
- Indicate the product(s) B and C that are formed in the reaction: HN' OCH HC1 B + mayoritario C minoritario OCH3arrow_forwardIndicate the product(s) that are formed in the reaction: NH-NH, OCH3 -H₂O OCH3arrow_forward21.38 Arrange the molecules in each set in order of increasing acidity (from least acidic to most acidic). OH OH SH NH2 8 NH3 OH (b) OH OH OH (c) & & & CH3 NO2 21.39 Explain the trends in the acidity of phenol and the monofluoro derivatives of phenol. OH OH OH OH PK 10.0 PK 8.81 PK 9.28 PK 9.81arrow_forward
- identify which spectrum is for acetaminophen and which is for phenacetinarrow_forwardThe Concept of Aromaticity 21.15 State the number of 2p orbital electrons in each molecule or ion. (a) (b) (e) (f) (c) (d) (h) (i) DA (k) 21.16 Which of the molecules and ions given in Problem 21.15 are aromatic according to the Hückel criteria? Which, if planar, would be antiaromatic? 21.17 Which of the following structures are considered aromatic according to the Hückel criteria? ---0-0 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (h) H -H .8.0- 21.18 Which of the molecules and ions from Problem 21.17 have electrons donated by a heteroatom?arrow_forward1. Show the steps necessary to make 2-methyl-4-nonene using a Wittig reaction. Start with triphenylphosphine and an alkyl halide. After that you may use any other organic or inorganic reagents. 2. Write in the product of this reaction: CH3 CH₂ (C6H5)₂CuLi H₂O+arrow_forward
- 3. Name this compound properly, including stereochemistry. H₂C H3C CH3 OH 4. Show the step(s) necessary to transform the compound on the left into the acid on the right. Bri CH2 5. Write in the product of this LiAlH4 Br H₂C OHarrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following reaction? Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following enolate alkylation reaction? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing as to how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning  Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning




