
(a)
To find: The translational symmetry of the pattern.
(a)
Answer to Problem 12CE
The pattern is not a translational symmetry.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given pattern design is shown below.
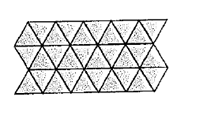
Calculation:
A design can also have translation symmetry if there is a translation that maps the figure onto itself.
Translational symmetry occurs only in pattern that cover a plane. But the given pattern is asymmetrical in nature so it is not a translational symmetry.
Therefore, the pattern is not a translational symmetry.
(b)
To find: Line symmetry of the pattern.
(b)
Answer to Problem 12CE
The given pattern is not a line symmetry.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given pattern design shown below.
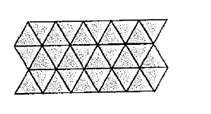
Calculation:
The line of symmetry is the imaginary line where fold the image and have both halves match exactly.
In the above pattern draw a line of axis then fold along that line the parts of object sides of the line not exactly coincide.
Hence the given pattern is not a line symmetry.
Therefore, the given pattern is not a line symmetry.
(c)
To find: Point symmetry of the pattern.
(c)
Answer to Problem 12CE
The pattern is not a point symmetry.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given pattern design shown below.
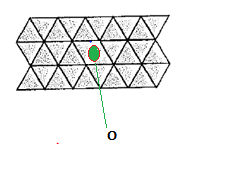
Calculation:
Point symmetry occurs when there exists a point on an object that splits the object into two parts in which each part has a matching part the same distance from the central point, and face different directions.
The given pattern is asymmetrical in nature , therefore the pattern is not a point symmetry.
Therefore, the pattern is not a point symmetry.
(d)
To find: The rotational symmetry of the pattern.
(d)
Answer to Problem 12CE
The pattern is not a rotational symmetry.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given pattern design is shown below.
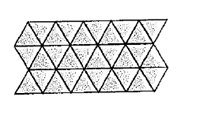
Calculation:
A shape has a rotational symmetry when it still looks the same after some rotation.
The given pattern is not symmetry if rotated because the shape is asymmetrical.
Therefore, the pattern is not a rotational symmetry.
Chapter 14 Solutions
McDougal Littell Jurgensen Geometry: Student Edition Geometry
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Elementary Statistics
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
- Mariela is in her classroom and looking out of a window at a tree, which is 20 feet away. Mariela’s line of sight to the top of the tree creates a 42° angle of elevation, and her line of sight to the base of the tree creates a 31° angle of depression. What is the height of the tree, rounded to the nearest foot? Be sure to show your work to explain how you got your answer.arrow_forward1arrow_forward20arrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

