
a.
To find: Distance invariant under half-turn.
a.
Answer to Problem 25WE
Distance is invariant under a half-turn.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Half-turn rotation
Concept Used:
A rotation is a transformation suggested by rotating a paddle wheel. When wheel stops, new position of a paddle referred as the image of initial position.
Invariant a
Calculation:
As per the given problem
There is a half-turn rotation.
For reference,
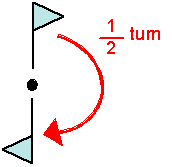
From diagram it can be understand that distance between the points i.e.
Hence,
Distance is invariant under a half-turn.
b.
To find:
b.
Answer to Problem 25WE
Angle measure is invariant under a half-turn.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Half-turn rotation
Concept Used:
A rotation is a transformation suggested by rotating a paddle wheel. When wheel stops, new position of a paddle referred as the image of initial position.
Invariant a function, quantity, or property which remains unchanged when a specified transformation is applied.
Calculation:
As per the given problem
There is a half-turn rotation.
For reference,
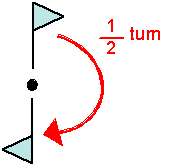
From diagram it can be understand that angle measure between the points i.e. triangle side angle remains same.
Hence,
Angle measure is invariant under a half-turn.
c.
To find: Area invariant under half-turn.
c.
Answer to Problem 25WE
Area is invariant under a half-turn.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Half-turn rotation
Concept Used:
A rotation is a transformation suggested by rotating a paddle wheel. When wheel stops, new position of a paddle referred as the image of initial position.
Invariant a function, quantity, or property which remains unchanged when a specified transformation is applied.
Calculation:
As per the given problem
There is a half-turn rotation.
For reference,
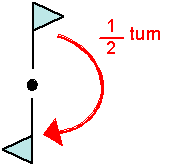
From diagram it can be understand that area between the points i.e. triangle area remains same.
Hence,
Area is invariant under a half-turn.
d.
To find: Orientation invariant under half-turn.
d.
Answer to Problem 25WE
Orientation is not invariant under a half-turn.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Half-turn rotation
Concept Used:
A rotation is a transformation suggested by rotating a paddle wheel. When wheel stops, new position of a paddle referred as the image of initial position.
Invariant a function, quantity, or property which remains unchanged when a specified transformation is applied.
Calculation:
As per the given problem
There is a half-turn rotation.
For reference,
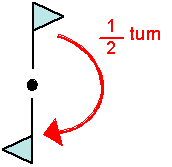
From diagram it can be understand that orientation of shape changes i.e. triangle face opposite to the previous orientation.
Hence,
Orientation is not invariant under a half-turn.
Chapter 14 Solutions
McDougal Littell Jurgensen Geometry: Student Edition Geometry
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

