
To prove: that the light ray follows the shortest possible path from A to C via the mirror by proving that for any point E on the mirror (other than B )
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given statement is that the condition can be proved by proving that for any point E on the mirror (other than B )
Concept used:
The
The sum of lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than length of third side.
Proof:
The geometric diagram to proof the condition.
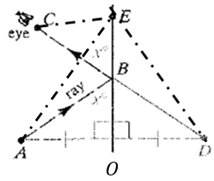
Since triangle BDO is reflection of triangle ABOin the line EOand
And triangle EDO is reflection of triangle AEO in the line EO and
In triangle CDE
The given condition is proved.
Therefore,
It is proved that light ray follows shortest path.
Chapter 14 Solutions
McDougal Littell Jurgensen Geometry: Student Edition Geometry
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

