
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915389
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.4, Problem 64P
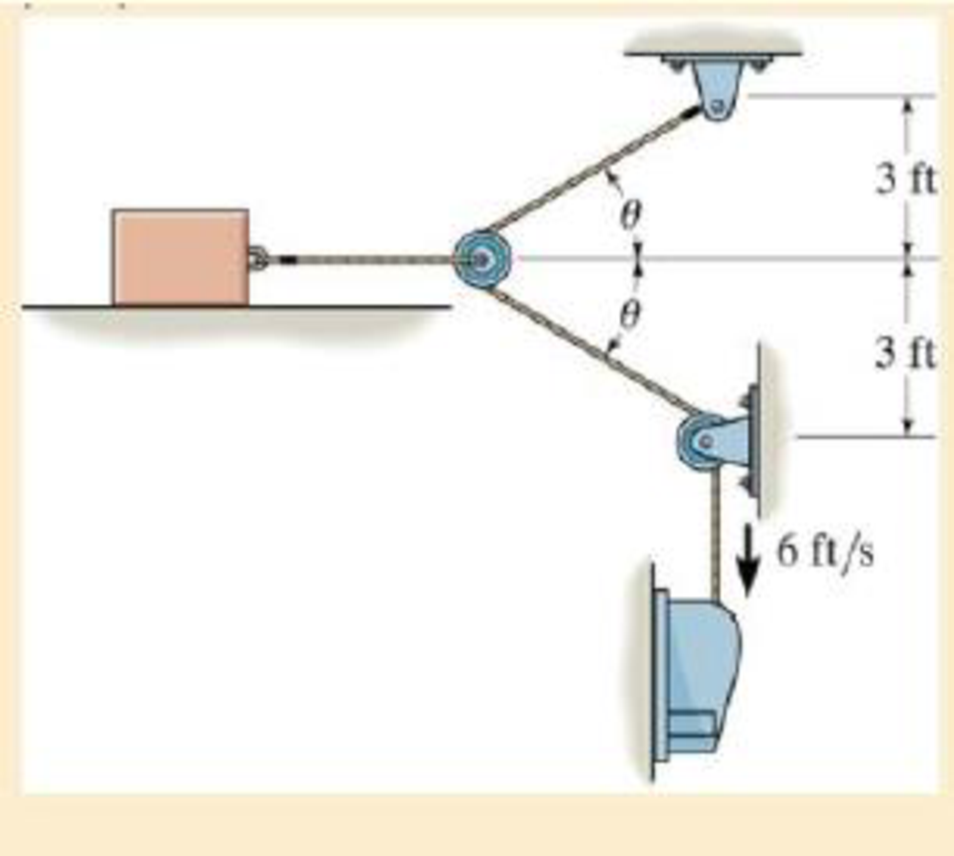
If the motor draws in the cable at a constant rate of 6 ft/ s, determine the output of the motor at the instant θ = 30°. Neglect the mass of the cable and pulleys.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Sketch and explain a PV Diagram and a Temperature Entropy Diagram for a 4 stroke diesel engine
please, please explain into detail the difference bewteen the two and referance the a diagram. Please include a sketch or an image of each diagram
Draw left view of the first orthographic projection
Sketch and Describe a timing diagram for a 2 stroke diesel engine
emphasis on the 2 stroke as my last answer explained 4 stroke
please include a diagram or sketch.
Chapter 14 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 14.3 - Determine the work of the force when it displaces...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the kinetic energy of the 10-kg block.Ch. 14.3 - The spring is placed between the wall and the...Ch. 14.3 - If the motor exerts a constant force of 300 N on...Ch. 14.3 - The crate is initially at rest on the ground.Ch. 14.3 - If the drag force of the parachute can be...Ch. 14.3 - When s = 0.5 m, the spring is unstretched and the...Ch. 14.3 - The 5-lb collar is pulled by a cord that passes...Ch. 14.3 - The 20-kg crate is subjected to a force having a...Ch. 14.3 - If the relation between the force and deflection...
Ch. 14.3 - If it is originally at rest, determine the...Ch. 14.3 - If it is originally at rest, determine the...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the required height h of the roller...Ch. 14.3 - How far will the truck skid if it is traveling 80...Ch. 14.3 - Show that this is so, by considering the 10-kg...Ch. 14.3 - A force of F = 250 N is applied to the end at B....Ch. 14.3 - If the block has a mass of 20 kg and is suspended...Ch. 14.3 - Determine how far the block must slide before its...Ch. 14.3 - If the 6-kg collar is orginally at rest, determine...Ch. 14.3 - Select the proper value of k so that the maximum...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the speed of the brick just before it...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the speed of block A after it moves 5 ft...Ch. 14.3 - If the kinetic coefficient of friction between the...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the angle at which the box leaves the...Ch. 14.3 - If the cord is subjected to a constant force of F=...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the maximum distance A will fall before...Ch. 14.3 - If the cord is subjected to a constant force of F=...Ch. 14.3 - The barrier stopping force is measured versus the...Ch. 14.3 - The coefficient of kinetic friction between both...Ch. 14.3 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 14.3 - The 8-Kg block is moving with an initial speed of...Ch. 14.3 - At a given instant the 10-lb block A is moving...Ch. 14.3 - The 5-lb cylinder is falling from A with a speed...Ch. 14.3 - The propelling action is obtained by drawing the...Ch. 14.3 - By design the car cannot fall off the track,...Ch. 14.3 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction along AB is...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 29PCh. 14.3 - If the can is prevented from moving, determine the...Ch. 14.3 - Determine the placement R of the can from the end...Ch. 14.3 - If it starts from rest when the attached spring is...Ch. 14.3 - Neglect the size of the block.Ch. 14.3 - As shown, the spring is confined by the plate P...Ch. 14.3 - Determine his speed when he reaches point B on the...Ch. 14.3 - As shown, it is confined by the plate and wall...Ch. 14.3 - If the track is to be designed so that the...Ch. 14.3 - Neglect friction.Ch. 14.3 - Neglect friction and the size of the pulley.Ch. 14.3 - Neglect friction and the size of the pulley.Ch. 14.3 - An elastic cord having a stiffness k = 2 lb/ft is...Ch. 14.4 - In initially, the block is at rest.Ch. 14.4 - When s = 0, the 20-kg block is moving at v = 1...Ch. 14.4 - The load weighs 100 lb and the efficiency of the...Ch. 14.4 - If the block is traveling up the inclined plane...Ch. 14.4 - determine the power input to the motor, which...Ch. 14.4 - which is increasing at a rate of aP = 6 m/s2....Ch. 14.4 - Assuming the wheels do not slip on the ground,...Ch. 14.4 - Determine the power Input for a motor necessary to...Ch. 14.4 - If mechanical friction and wind resistance are...Ch. 14.4 - manufactures a turbojet engine that is placed in a...Ch. 14.4 - If the car is brought to a stop, determine how...Ch. 14.4 - If the steps are 125 mm high and 250 mm in length,...Ch. 14.4 - Determine the power generated. How long would a...Ch. 14.4 - Determine the maximum power that must be supplied...Ch. 14.4 - The cable is tied to the top of the oil rig, wraps...Ch. 14.4 - The motor has an efficiency of = 0.65.Ch. 14.4 - The 50-lb crate is given a speed of 10ft/s in t =...Ch. 14.4 - The engine has a running efficiency = 0.68.Ch. 14.4 - If the drag resistance on the car due to the wind...Ch. 14.4 - Hoisting is provided by the motor M and the 60-kg...Ch. 14.4 - If the rod is smooth, determine the power...Ch. 14.4 - Determine the power developed by the power...Ch. 14.4 - A force F = (40 + s2) lb, where sis in ft, acts on...Ch. 14.4 - If the steps are 125 mm high and 250 mm in length,...Ch. 14.4 - If the escalator in Prob.14-46 is not moving,...Ch. 14.4 - Neglect drag and rolling resistance, and the loss...Ch. 14.4 - Also, the velocity of the athletes arm acting in...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 63PCh. 14.4 - If the motor draws in the cable at a constant rate...Ch. 14.5 - If a force F = (60t2) N, where t is in seconds, is...Ch. 14.5 - Determine the potential energy of the block that...Ch. 14.5 - Determine the potential energy in the spring that...Ch. 14.5 - The 2-kg pendulum bob is released from rest when...Ch. 14.5 - The 2-kg package leaves the conveyor belt at A...Ch. 14.5 - The 2-kg collar is given a downward velocity of 4...Ch. 14.5 - Determine the speed of the collar when it strikes...Ch. 14.5 - Determine the compression of each spring when the...Ch. 14.5 - If the guide rod is smooth, determine the speed of...Ch. 14.5 - If she is swinging to a maximum height defined by ...Ch. 14.5 - If it is then released, determine the maximum...Ch. 14.5 - Determine the speed of the collar when it reaches...Ch. 14.5 - Determine its speed when its center reaches point...Ch. 14.5 - If it is released from rest when = 0, determine...Ch. 14.5 - If the car is released from rest, determine its...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 72PCh. 14.5 - If it is released from rest at the top of the hill...Ch. 14.5 - Determine the speed of each block when B descends...Ch. 14.5 - Determine the distance B must descend in order for...Ch. 14.5 - The spring has a stiffness k =50 N/m and an...Ch. 14.5 - Neglect friction.Ch. 14.5 - If it is attached to the 3-kg smooth collar and...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 79PCh. 14.5 - If the arm is pulled back such that s = 100 mm and...Ch. 14.5 - If the arm is pulled back such that s = 100 mm and...Ch. 14.5 - For the calculation, locate the datum at r . Also,...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 83PCh. 14.5 - The spring has an unstretched length of 1 m.Ch. 14.5 - A 60-kg satellite travels in free flight along an...Ch. 14.5 - If friction and air resistance can be neglected,...Ch. 14.5 - If the mass of the bumpers A and B can be...Ch. 14.5 - If the collar moves over the smooth rod, determine...Ch. 14.5 - When the 6-kg box reaches point A it has a speed...Ch. 14.5 - Determine the normal force the box exerts on the...Ch. 14.5 - Determine how high the box reaches up the surface...Ch. 14.5 - Determine the cars velocity and the normal force...Ch. 14.5 - The 10-kg sphere C is released from rest when =...Ch. 14.5 - If the chain is released from rest from the...Ch. 14.5 - Each spring has a stiffness k = 40 N/m and an...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 96PCh. 14.5 - Initially each spring has a tension of 50 NCh. 14.5 - Determine the approximate normal force it exerts...Ch. 14.5 - If a 150-lb crate is released from rest at A,...Ch. 14.5 - During the motion, the collar is acted upon by a...Ch. 14.5 - Determine the speed at which it slides off at B....Ch. 14.5 - If the block starts from rest when the attached...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 5RPCh. 14.5 - The motor has an efficiency of = 0.76.Ch. 14.5 - If the collar is released from rest at A and...Ch. 14.5 - respectively. They are connected together by a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 4 ft 200 Ib 1000 Ib.ft C 2 ft 350 Ib - за в 2.5 ft 150 Ib 250 Ib 375 300 Ib Replace the force system acting on the frame. shown in the figure by a resultant force (magnitude and direction), and specify where its line of action intersects member (AB), measured from point (A).arrow_forwardA continuous flow calorimeter was used to obtain the calorific value of a sample of fuel and the following data collected: Mass of fuel: 2.25 kgInlet water temperature: 11 ° COutlet water temperature 60 ° CQuantity of water: 360 Liters Calorimeter efficiency: 85%Calculate the calorific value of the sample ( kJ / kg ). ive submitted this question twice and have gotten two way different answers. looking for some help thanksarrow_forward15 kg of steel ball bearings at 100 ° C is immersed in 25 kg of water at 20 ° C . Assuming no loss of heat to or from the container, calculate the final temperature of the water after equilibrium has been attained.Specific heat of steel: 0.4857 kJ / kg / ° KSpecific heat of water: 4.187 kJ / kg / ° Karrow_forward
- Sketch and explain a PV Diagram and a Temperature Entropy Diagram for a 4 stroke diesel enginearrow_forwardA continuous flow calorimeter was used to obtain the calorific value of a sample of fuel and the following data collected: Mass of fuel: 2.25 kgInlet water temperature: 11 ° COutlet water temperature 60 ° CQuantity of water: 360 Liters Calorimeter efficiency: 85%Calculate the calorific value of the sample ( kJ / kg ).arrow_forwardChapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... Scoresarrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Scoresarrow_forwardanswer the fallowing Brake Specific Fuel Consumption - 0.3 kg/kwh, Mechanical Efficiency- 90% Calorific Value of Fuel -45 MJ/kg. Given these values, find the indicated power, indicated thermal efficiency and brake thermal efficiencyarrow_forwardProblem 6. The circular plate shown rotates about its vertical diameter. At the instant shown, the angular velocity ₁ of the plate is 10 rad/s and is decreasing at the rate of 25 rad/s². The disk lies in the XY plane and Point D of strap CD moves upward. The relative speed u of Point D of strap CD is 1.5 m/s and is decreasing at the rate of 3 m/s². Determine (a) the velocity of D, (b) the acceleration of D. Answers: =0.75 +1.299]-1.732k m/s a=-28.6 +3.03-10.67k m/s² 200 mm x Zarrow_forwardProblem 1. The flywheel A has an angular velocity o 5 rad/s. Link AB is connected via ball and socket joints to the flywheel at A and a slider at B. Find the angular velocity of link AB and the velocity of slider B at this instant. (Partial Answer: @ABN = -2î + 2.25; red Z -1.2 ft C -7 Y -1.5 ft- B 2.0 ftarrow_forwardNeed help pleasearrow_forwardPROBLEM 15.225 The bent rod shown rotates at the constant rate @₁ = 5 rad/s and collar C moves toward point B at a constant relative speed u = 39 in./s. Knowing that collar C is halfway between points B and D at the instant shown, determine its velocity and acceleration. Answers: v=-45 +36.6)-31.2 k in./s āc = -2911-270} in./s² 6 in 20.8 in. 14.4 in.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Introduction to Undamped Free Vibration of SDOF (1/2) - Structural Dynamics; Author: structurefree;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BkgzEdDlU78;License: Standard Youtube License