
Concept explainers
Grace Greenberg, production planner for Science and Technology Labs, in New Jersey, has the master production plan shown below:
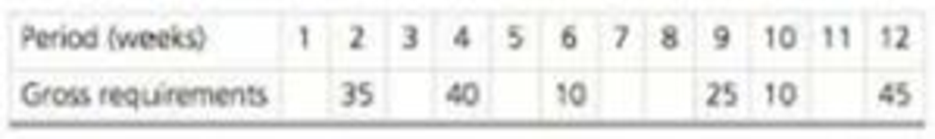
Lead time = 1 period; setup cost = $200; holding cost = $10 per week; stockout cost = $10 per week. Develop an ordering plan and costs for Grace, using these techniques:
a) Lot-for-lot.
b) EOQ.
c) POQ.
d) Which plan has the lowest cost?
a)
To determine: The ordering plan and cost for Lot for lot.
Introduction:
Lot for Lot:
The lot for lot method of requirements plan is the process where the planned order release will be equal to the net requirement of the period.
Net requirements plan:
The net requirements plan is the plan which is established on the gross requirements plan formed by deducting the stock on and the scheduled receipts. If the total requirement is below the safety stock levels, a planned order is made based on the given lot sizing technique.
Answer to Problem 27P
The cost for Lot for lot is $1,200.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Period (weeks) | |||||||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Gross requirements | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | 165 | ||||||
Holding cost = $10 / week
Setup cost = $200
Lead time = 1 period
Stockout cost = $10 / week
Lot for lot:
Net requirements plan:
| Period (weeks) | |||||||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Gross requirements | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | 165 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | |||||||||||||
| On hand (0) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| Ending inventory | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| Net requirement | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | |||||||
| Planned order receipt | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | |||||||
| Planned order release | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | |||||||
Week 2:
The gross requirement is 35 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 35. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 35 in week 1 which will be the planned order receipt in week 2.
Week 4:
The gross requirement is 40 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 40. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 40 in week 3 which will be the planned order receipt in week 4.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 10. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 10 in week 5 which will be the planned order receipt in week 6.
Week 9:
The gross requirement is 25 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 25. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 25 in week 8 which will be the planned order receipt in week 9. There is no ending inventory.
Week 10:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 10. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 10 in week 9 which will be the planned order receipt in week 10.
Week 12:
The gross requirement is 45 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 45. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 45 in week 11 which will be the planned order receipt in week 12. There is no ending inventory.
Number of planned orders = 6
Inventory holding units= 0
Formula to calculate total cost of the plan:
Calculation of total cost:
The total cost is calculated by adding the product of number of planned order and setup cost with the product of inventory holding period and holding cost.
Hence, the cost for Lot for lot is $1,200.
b)
To determine: The ordering plan and cost for EOQ.
Introduction:
Economic order quantity (EOQ):
The economic order quantity is the number of units a firm must add to their stock while making each order. The notion of EOQ is to reduce the total cost of inventory of the firm.
Net requirements plan:
The net requirements plan is the plan which is established on the gross requirements plan formed by deducting the stock on and the scheduled receipts. If the total requirement is below the safety stock levels, a planned order is made based on the given lot sizing technique.
Answer to Problem 27P
The cost for EOQ is $2,370.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Period (weeks) | |||||||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Gross requirements | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | 165 | ||||||
Holding cost = $10 / week
Setup cost = $200
Lead time = 1 period
Stockout cost = $10 / week
Formula to calculate EOQ:
Calculation of EOQ:
The EOQ can be rounded off to 23 units.
Net requirements plan:
| Period (weeks) | |||||||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Gross requirements | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | 165 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | |||||||||||||
| On hand (0) | 0 | 11 | 11 | 17 | 17 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 18 | 18 | ||
| Ending inventory | 11 | 11 | 17 | 17 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 18 | 18 | 19 | 137 | |
| Net requirement | 35 | 29 | 0 | 18 | 5 | 27 | |||||||
| Planned order receipt | 46 | 46 | 0 | 23 | 23 | 46 | |||||||
| Planned order release | 46 | 46 | 23 | 23 | 46 | ||||||||
Week 2:
The gross requirement is 35 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 35. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 46 (1 Lot = 23) in week 1 which will be the planned order receipt in week 2. The ending inventory is 11 which will be available at week 3.
Week 3:
The on hand inventory is 11. Since there is no requirement, the ending inventory at week 3 is 11 which will be available at week 4.
Week 4:
The gross requirement is 40 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 11. Hence, the net requirement is 29. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 46 (1 Lot = 23) in week 3 which will be the planned order receipt in week 4. The ending inventory is 17 which will be available at week 5.
Week 5:
The on hand inventory is 17. Since there is no requirement, the ending inventory at week 5 is 17 which will be available at week 6.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 17. Hence, the net requirement is 0. Therefore there will be no planned order assembly. The ending inventory is 7 which will be available at week 7.
Week 7:
The on hand inventory is 7. Since there is no requirement, the ending inventory at week 7 is 7 which will be available at week 8.
Week 8:
The on hand inventory is 7. Since there is no requirement, the ending inventory at week 8 is 7 which will be available at week 9.
Week 9:
The gross requirement is 25 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 7. Hence, the net requirement is 18. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 23 (1 Lot = 23) in week 8 which will be the planned order receipt in week 9. The ending inventory is 5 which will be available at week 10.
Week 10:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 5. Hence, the net requirement is 5. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 23 (1 Lot = 23) in week 9 which will be the planned order receipt in week 10. The ending inventory is 18 which will be available at week 11.
Week 11:
The on hand inventory is 18. Since there is no requirement, the ending inventory at week 11 is 18 which will be available at week 12.
Week 12:
The gross requirement is 45 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 18. Hence, the net requirement is 27. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 46 (1 Lot = 23) in week 11 which will be the planned order receipt in week 12. The ending inventory is 19 which will be available in the next week.
Number of planned order releases = 5
Total Ending inventory = 137
Calculation of total setup cost:
Calculation of total holding cost:
Calculation of total cost:
The total cost is calculated by summing the total setup cost and total holding cost.
Hence, the total cost for EOQ is $2,370
c)
To determine: The ordering plan and cost for POQ.
Introduction:
Periodic order quantity (POQ):
The POQ is the standard quantity of units that will be ordered over a fixed period of time. This method is followed when the usage of raw materials is consistent and is predictable.
Net requirements plan:
The net requirements plan is the plan which is established on the gross requirements plan formed by deducting the stock on and the scheduled receipts. If the total requirement is below the safety stock levels, a planned order is made based on the given lot sizing technique.
Answer to Problem 27P
The cost for POQ is $1,100.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Period (weeks) | |||||||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Gross requirements | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | 165 | ||||||
Holding cost = $10 / week
Setup cost = $200
Lead time = 1 period
Stockout cost = $10 / week
Net requirements plan:
The planned ordered release in the POQ plan is planned in a way such that the demand for next two periods is satisfied.
Net requirements plan:
| Period (weeks) | |||||||||||||
| Item A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Gross requirements | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 45 | 165 | ||||||
| Scheduled receipt | |||||||||||||
| On hand (0) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Ending inventory | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | |
| Net requirement | 35 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 45 | ||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 35 | 40 | 10 | 35 | 45 | ||||||||
| Planned order release | 35 | 40 | 10 | 35 | 45 | ||||||||
Week 2:
The gross requirement is 35 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 35. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 35 in week 1 which will be the planned order receipt in week 2. There is no ending inventory.
Week 4:
The gross requirement is 40 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 40. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 40 in week 3 which will be the planned order receipt in week 4. There is no ending inventory.
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 10. Therefore, the planned order release will be 10 in week 5 which will be the planned order receipt in week 6. There is no ending inventory.
Week 9:
The gross requirement is 25 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 25. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 35 in week 8 which will be the planned order receipt in week 9. The ending inventory is 10 which will be available at week 10.
Week 10:
The gross requirement is 10 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 10. Hence, the net requirement is 0. Therefore there will be no planned order inventory.
Week 12:
The gross requirement is 45 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 45. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 45 in week 11 which will be the planned order receipt in week 12. There is no ending inventory.
Number of planned orders = 5
Inventory holding units= 10
Formula to calculate total cost of the plan:
Calculation of total cost:
The total cost is calculated by adding the product of number of planned order and setup cost with the product of inventory holding period and holding cost.
Hence, the cost for POQ is $1,100.
d)
To determine: The plan which has the lowest cost.
Answer to Problem 27P
The plan which has the lowest cost is POQ.
Explanation of Solution
The total cost for Lot for lot is $1,200. The total cost for EOQ is $2,370. The total cost for POQ is $1,100. The total cost is less for POQ when compared with EOQ and Lot for lot. ($1,100 < $2,370, $1,200)
Hence, the plan which has the lowest cost is POQ.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Principles Of Operations Management
- In what ways does self-leadership affect the world around us?arrow_forward6:35 nvas.liberty.edu < 72% i You must post before seeing replies. Edit history will be available to instructors. ☑ Due Feb 13 33 Replies (33) 50 points Discussion Thread: How to Look at the Bible After reading the assigned chapters in Everyday Bible Study (Chapters 1-5), create a learning log that lists 10 quotes from the assigned reading that highlight either a concept that resonated with you or a concept that represents new learning for you. Following each of these quotes, you must provide a 3-5 sentence explanation of how the selected quote represents either what resonated with you or this new learning. For an example of this type of thread, please see the provided example. Pleas ◄ Previous cussion Assignment instructions ✓ and the ||| Next ▸arrow_forwardDo a report to promote an innovative product/service within an organization of your choice. In your assignment, you need to focus on the below: 1. Give a brief introduction of the innovative product/service you are thinking about within an organization of your choice. 2. Analyze how you are going to promote your idea internally to your colleagues (e.g. meetings, presenting and disseminating the information). 3. Explain how you are going to convince them that this product/service is applicable and that it will create a competitive advantage in the market. 4. Refer to a similar product/service that your competitors have and analyze how the competitors’ product can be considered as a threat to your new product/service. 5. Estimate how much will the whole procedure cost to the business. 6. In your conclusions, describe how the new product/service will influence the whole organization’s environment. 3000 words and include and introducion, conclusion and references.arrow_forward
- For my learning and not a assignment question: Tesla, the U.S. electric vehicle manufacturer, has recently proposed to join Indonesia’s initiative to develop an EV battery supply chain within the country. This information was shared by a senior Indonesian government official, who noted that the government received Tesla's proposal on Thursday. Indonesia, known for its rich nickel reserves, is already in discussions with companies like China's Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL) and South Korea's LG Chem to establish a comprehensive EV battery supply chain that covers everything from raw materials to the final product. Sepian Hari Seto, the deputy for investment and mining at the Coordinating Ministry of Maritime Affairs and Investment, expressed enthusiasm for Tesla's advanced lithium battery technology. He conveyed that the collaboration with Tesla, along with CATL and LG, presents a valuable opportunity for technology transfer and learning. Furthermore, Seto mentioned the…arrow_forwardYour company is considering investing in a Human Resource Information System (HRIS).Briefly explain the strategies for justifying HRIS investments.arrow_forwardPresent the criteria you would utilize to determine if a right should be extended to an employee or if it would unnecessarily impact a manager’s ability to manage. Additionally, assess how you would balance the need for management rights against the need for employee rights, and how greater employee rights positively and negatively affect the future of the organization.arrow_forward
- provide schoarly research and references as to how internal and exteral audit is a risk management strategy to mitigate risk in a financial institutionarrow_forwardLearning Activity 4: Strategic Sales Management How has the advent and rapid evolution of digital technology transformed traditional sales management strategies, and what do you think are the most significant challenges and opportunities this transformation brings? In addition, please select and describe an example of company that has embraced change and implemented a unique and effective sales strategy.arrow_forward1) View the two video excerpts (Ctrl+Click on the two links), Preview 1 to the Goal Movie (Goldratt) (11.17 minutes), https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2RVMgV37O_k and Preview 2 to the Goal Movie – How to Version (Goldratt) (9.40 minutes) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t_oM9LvK0rU and answer the following questions: a) What problems is UniCo facing and how are they tackling these problems currently? b) What advice did Jonah give to Rogo, and what lessons did Rogo learn from “Herbie’s Hike”? c) How do you think Rogo can leverage Jonah’s advice (as well as the lessons learnt from “Herbie’s Hike”) to solve UniCo’s problems? 2) A business program has the facilities and faculty to handle an enrollment of 2,000 new students per semester. However, in an effort to limit class sizes to a “reasonable” level the business dean, placed a ceiling on enrollment of 1,500 new students. Although there was ample demand for business courses last semester, conflicting schedules allowed only 1,450 new…arrow_forward
- The global marketplace has undergone a dramatic transformation, demanding that businesses adapt their supply chain management and implement new strategies to ensure the reliable sourcing of materials and goods. Please choose an organisation that you are currently working for or you are familiar with where its procurement operations has been greatly affected. You may pick a commercial or public institution as a choice for your study. You will need to briefly describe the institution and explain its category management structure which support the strategic procurement. You are required to provide an overview and discuss how spend are identified along with the types of categories purchased Briefly describe the organisation that you have chosen. Analyse the criticality of both the category management and strategic sourcing that will impact the business needs of the institution that you have chosen. Laing oxemples from the institution you have selected appraise and recommend COarrow_forwardThe Ideal Spot in the Segment Circles So, where should you try to position your product in the segment circles? As a basic rule, the 'Ideal Spot' will help guide you. The ideal spot represents the position with the highest point of demand for each consumer base – or segment. The ideal spot is made up by the product’s performance (speed) and size. As the perceptual map drifts down and to the right each year, the ideal spot will change as customers demand sensors with decreased size (smaller) and increased performance (faster). Although it would seem that the Ideal Spot would be in the center of the segment circle, the positioning actually varies due to the customer focus of each segment. For example, in the High End segment, the Ideal Spot is at the leading edge of the segment because those customers want the best possible product. Each segment’s ideal spot is represented by the pink dots on the Perceptual Map. Ideal Spots offset from segment center Calculating the Ideal Spot To…arrow_forwardIn Ecuador, cut roses are one of the country’s leading exports. Prior to advancements in the air transportation industry, this would have been impossible as roses must be sold within three to five days once cut. Today Ecuador is one of the world’s top producers of roses.arrow_forward
- MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning  Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning





