
Concept explainers
a)
To construct: A product structure.
Introduction:
Product structure:
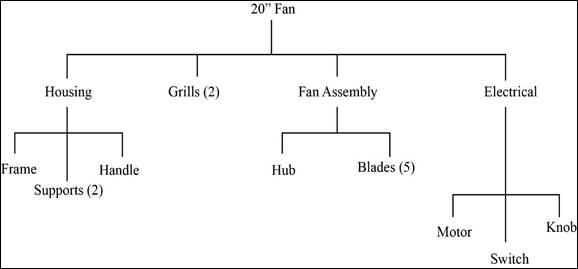
The product structure is a visual representation of the components needed for a product assembly and the sequence at which they must be developed. It will clearly depict the parents and children components at each level.
a)
Answer to Problem 13P
Product structure:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
- 1000 20” fans due in week 7.
- Each fan is made of a housing assembly, two grills, fan assembly and an electrical unit.
- Housing assembly is made of frame, two supports, and a handle.
- Fan assembly is made up of a hub and five blades.
- Electrical unit consists of a motor, switch and a knob.
| Component | Lead time | On-hand inventory | Lot size |
|
| 20" Fan | 1 | 100 | ||
| Housing | 1 | 100 | ||
| Frame | 2 | |||
| Supports (2) | 1 | 50 | 100 | |
| Handle | 1 | 400 | 500 | |
| Grills (2) | 2 | 200 | 500 | |
| Fan assembly | 3 | 150 | ||
| Hub | 1 | |||
| Blades (5) | 2 | 100 | ||
| Electrical unit | 1 | |||
| Motor | 1 | |||
| Switch | 1 | 20 | 12 | |
| Knob | 1 | 25 | 200 in week 2 |
Product structure:
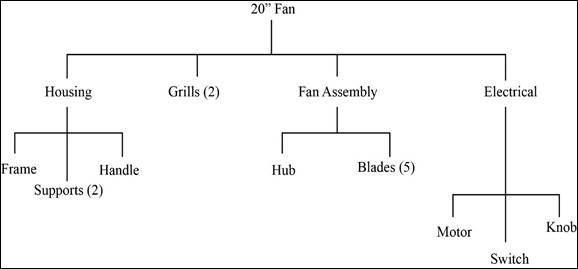
The product is a 20” fan. It is made of four components. Each fan is made of a housing assembly, two grills, fan assembly and an electrical unit. Housing assembly is made of frame, two supports, and a handle. Fan assembly is made up of a hub and five blades. Electrical unit consists of a motor, switch and a knob.
b)
To construct: A time-phased product structure.
Introduction:
Time-phased product structure:
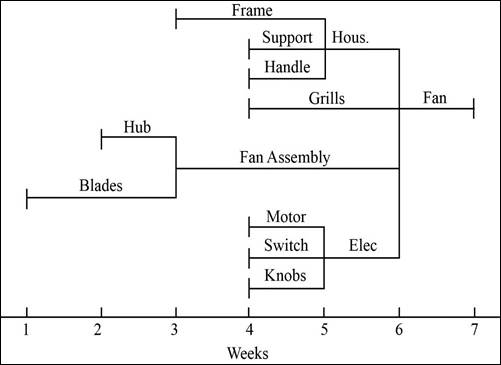
The time-phased product structure will represent the product visually with the details of when each component must begin production. It should be done to ensure that all the components are on time.
b)
Answer to Problem 13P
Time-phased product structure:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
- 1000 20” fans due in week 7.
- Each fan is made of a housing assembly, two grills, fan assembly and an electrical unit.
- Housing assembly is made of frame, two supports, and a handle.
- Fan assembly is made up of a hub and five blades.
- Electrical unit consists of a motor, switch and a knob.
| Component | Lead time | On-hand inventory | Lot size | Scheduled receipt |
| 20" Fan | 1 | 100 | ||
| Housing | 1 | 100 | ||
| Frame | 2 | |||
| Supports (2) | 1 | 50 | 100 | |
| Handle | 1 | 400 | 500 | |
| Grills (2) | 2 | 200 | 500 | |
| Fan assembly | 3 | 150 | ||
| Hub | 1 | |||
| Blades (5) | 2 | 100 | ||
| Electrical unit | 1 | |||
| Motor | 1 | |||
| Switch | 1 | 20 | 12 | |
| Knob | 1 | 25 | 200 in week 2 |
Time-phased product structure:

The end product is the fan which must be ready at week 7. All the other components must be completed on week 6. The components at the lower level must be completed first before proceeding to the higher levels. Each component at each level is begun depending on the lead time of the product.
The products are started in advance so that they are developed and ready on time so that the dependent parent will be ready to develop its product. The process is repeated until all the subassemblies are ready to make the final product.
c)
To develop: A net requirements plan.
Introduction:
Net requirements plan:
The net requirements plan is the plan which is established on the gross requirements plan formed by deducting the stock on and the scheduled receipts. If the total requirement is below the safety stock levels, a planned order is made based on the given lot sizing technique.
c)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
- 1000 20” fans due in week 7.
- Each fan is made of a housing assembly, two grills, fan assembly and an electrical unit.
- Housing assembly is made of frame, two supports, and a handle.
- Fan assembly is made up of a hub and five blades.
- Electrical unit consists of a motor, switch and a knob.
| Component | Lead time | On-hand inventory | Lot size | Scheduled receipt |
| 20" Fan | 1 | 100 | ||
| Housing | 1 | 100 | ||
| Frame | 2 | |||
| Supports (2) | 1 | 50 | 100 | |
| Handle | 1 | 400 | 500 | |
| Grills (2) | 2 | 200 | 500 | |
| Fan assembly | 3 | 150 | ||
| Hub | 1 | |||
| Blades (5) | 2 | 100 | ||
| Electrical unit | 1 | |||
| Motor | 1 | |||
| Switch | 1 | 20 | 12 | |
| Knob | 1 | 25 | 200 in week 2 |
Net requirements plan:
20’’ Fan:
| Week | ||||||||||||
| 20" Fan | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 1,000 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||||||
| On hand (100) | 100 | |||||||||||
| Net requirement | 900 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 900 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 900 | |||||||||||
Week 7:
The gross requirement is 1,000 (1 assembly). The on hand inventory is 100. Hence, the net requirement is 900. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 900 in week 6 which will be the planned order receipt in week 7.
Housing:
| Week | ||||||||||||
| Housing | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 900 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||||||
| On hand (100) | 100 | |||||||||||
| Net requirement | 800 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 800 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 800 | |||||||||||
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 900 (1 assembly) derived from the planned order release of 20” fan. The on hand inventory is 100. Hence, the net requirement is 800. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 800 in week 5 which will be the planned order receipt in week 6.
Grills:
| Week | ||||||||||||
| Grills | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 1,800 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||||||
| On hand (200) | 200 | 400 | ||||||||||
| Net requirement | 1,600 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 2,000 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 2,000 | |||||||||||
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 1,800 (2 assembly) derived from the planned order release of 20” fan. The on hand inventory is 200. Hence, the net requirement is 1,600. The lead time is 2 weeks. Therefore, the planned order release will be 2,000 (Lot Size = 500) in week 4 which will be the planned order receipt in week 6. The excess inventory will be available at week 7.
Fan assembly:
| Week | ||||||||||||
| Fan assembly | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 900 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||||||
| On hand (150) | 150 | |||||||||||
| Net requirement | 750 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 750 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 750 | |||||||||||
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 900 (1 assembly) derived from the planned order release of 20” fan. The on hand inventory is 150. Hence, the net requirement is 750. The lead time is 2 weeks. Therefore, the planned order release will be 750 in week 4 which will be the planned order receipt in week 6.
Electrical unit:
| Electrical Unit | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 900 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||||||
| On hand (0) | 0 | |||||||||||
| Net requirement | 900 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 900 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 900 |
Week 6:
The gross requirement is 900 (1 assembly) derived from the planned order release of 20” fan. The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 900. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 900 in week 5 which will be the planned order receipt in week 6.
Frame:
| Frame | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 800 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||||||
| On hand (0) | 0 | |||||||||||
| Net requirement | 800 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 800 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 800 |
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 800 (1 assembly) derived from the planned order release of Housing. The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 800. The lead time is 2 weeks. Therefore, the planned order release will be 800 in week 3 which will be the planned order receipt in week 5.
Supports:
| Week | ||||||||||||
| Supports | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 1,600 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||||||
| On hand (50) | 50 | |||||||||||
| Net requirement | 1,550 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 1,600 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 1,600 | |||||||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 1,600 (2 assembly) derived from the planned order release of Housing. The on hand inventory is 50. Hence, the net requirement is 1,550. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 1,600 (Lot size = 100) in week 4 which will be the planned order receipt in week 5. The excess inventory is available at week 6.
Handle:
| Week | ||||||||||||
| Handle | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 800 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||||||
| On hand (400) | 400 | 100 | ||||||||||
| Net requirement | 400 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 500 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 500 | |||||||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 800 (1 assembly) derived from the planned order release of Housing. The on hand inventory is 400. Hence, the net requirement is 400. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 500 (Lot size = 500) in week 4 which will be the planned order receipt in week 5. The excess inventory is available at week 6.
Hub:
| Week | ||||||||||||
| Hub | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 750 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||||||
| On hand (0) | 0 | |||||||||||
| Net requirement | 750 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 750 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 750 | |||||||||||
Week 3:
The gross requirement is 750 (1 assembly) derived from the planned order release of fan assembly. The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 750. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 750 in week 2 which will be the planned order receipt in week 3.
Blades:
| Week | ||||||||||||
| Blades | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 3,750 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||||||
| On hand (0) | 0 | 50 | ||||||||||
| Net requirement | 3,750 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 3,800 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 3,800 | |||||||||||
Week 3:
The gross requirement is 3,750 (5 assembly) derived from the planned order release of fan assembly. The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 3,750. The lead time is 2 weeks. Therefore, the planned order release will be 3,800 (Lot size = 100) in week 1 which will be the planned order receipt in week 3. The excess inventory will be available at week 4.
Motor:
| Week | ||||||||||||
| Motor | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 900 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||||||
| On hand (0) | 0 | |||||||||||
| Net requirement | 900 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 900 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 900 | |||||||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 900 (1 assembly) derived from the planned order release of Electrical unit. The on hand inventory is 0. Hence, the net requirement is 900. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 900 in week 4 which will be the planned order receipt in week 5.
Switch:
| Week | ||||||||||||
| Switch | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 900 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | ||||||||||||
| On hand (20) | 20 | 8 | ||||||||||
| Net requirement | 880 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 888 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 888 | |||||||||||
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 900 (1 assembly) derived from the planned order release of Electrical unit. The on hand inventory is 20. Hence, the net requirement is 880. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 888 (Lot Size = 12) in week 4 which will be the planned order receipt in week 5. The excess inventory will be available at week 6.
Knob:
| Week | ||||||||||||
| Knob | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Gross requirements | 900 | |||||||||||
| Scheduled receipt | 200 | |||||||||||
| On hand (0) | 200 | 200 | 200 | |||||||||
| Net requirement | 700 | |||||||||||
| Planned order receipt | 700 | |||||||||||
| Planned order release | 700 | |||||||||||
Week 2:
There is a scheduled receipt of 200 which can be used as inventory.
Week 5:
The gross requirement is 900 (1 assembly) derived from the planned order release of Electrical unit. The on hand inventory is 0. But, there is a scheduled receipt of 200. Hence, the net requirement is 7000. The lead time is 1 week. Therefore, the planned order release will be 700 in week 4 which will be the planned order receipt in week 5.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Principles Of Operations Management
- A small furniture manufacturer produces tables and chairs. Each product must go through three stages of the manufacturing process – assembly, finishing, and inspection. Each table requires 3 hours of assembly, 2 hours of finishing, and 1 hour of inspection. The profit per table is $120 while the profit per chair is $80. Currently, each week there are 200 hours of assembly time available, 180 hours of finishing time, and 40 hours of inspection time. Linear programming is to be used to develop a production schedule. Define the variables as follows: T = number of tables produced each week C= number of chairs produced each week According to the above information, what would the objective function be? (a) Maximize T+C (b) Maximize 120T + 80C (c) Maximize 200T+200C (d) Minimize 6T+5C (e) none of the above According to the information provided in Question 17, which of the following would be a necessary constraint in the problem? (a) T+C ≤ 40 (b) T+C ≤ 200 (c) T+C ≤ 180 (d) 120T+80C ≥ 1000…arrow_forwardAs much detail as possible. Dietary Management- Nursing Home Don't add any fill-in-the-blanksarrow_forwardMenu Planning Instructions Use the following questions and points as a guide to completing this assignment. The report should be typed. Give a copy to the facility preceptor. Submit a copy in your Foodservice System Management weekly submission. 1. Are there any federal regulations and state statutes or rules with which they must comply? Ask preceptor about regulations that could prescribe a certain amount of food that must be kept on hand for emergencies, etc. Is the facility accredited by any agency such as Joint Commission? 2. Describe the kind of menu the facility uses (may include standard select menu, menu specific to station, non-select, select, room service, etc.) 3. What type of foodservice does the facility have? This could be various stations to choose from, self-serve, 4. conventional, cook-chill, assembly-serve, etc. Are there things about the facility or system that place a constraint on the menu to be served? Consider how patients/guests are served (e.g. do they serve…arrow_forward
- Work with the chef and/or production manager to identify a menu item (or potential menu item) for which a standardized recipe is needed. Record the recipe with which you started and expand it to meet the number of servings required by the facility. Develop an evaluation rubric. Conduct an evaluation of the product. There should be three or more people evaluating the product for quality. Write a brief report of this activity • Product chosen and the reason why it was selected When and where the facility could use the product The standardized recipe sheet or card 。 o Use the facility's format or Design one of your own using a form of your choice; be sure to include the required elements • • Recipe title Yield and portion size Cooking time and temperature Ingredients and quantities Specify AP or EP Procedures (direction)arrow_forwardASSIGNMENT: Inventory, Answer the following questions 1. How does the facility survey inventory? 2. Is there a perpetual system in place? 3. How often do they do a physical inventory? 4. Participate in taking inventory. 5. Which type of stock system does the facility use? A. Minimum stock- includes a safety factor for replenishing stock B. Maximum stock- equal to a safety stock plus estimated usage (past usage and forecasts) C. Mini-max-stock allowed to deplete to a safety level before a new order is submitted to bring up inventory up to max again D. Par stock-stock brought up to the par level each time an order is placed regardless of the amount on hand at the time of order E. Other-(describe) Choose an appropriate product and determine how much of an item should be ordered. Remember the formula is: Demand during lead time + safety stock = amount to order Cost out an inventory according to data supplied. Remember that to do this, you will need to take an inventory, and will need to…arrow_forwardHuman Relations, Systems, and Organization Assignments ORGANIZATION: Review the organization chart for the facility • Draw an organization chart for the department. • . Identify and explain the relationships of different units in the organization and their importance to maintain the food service department's mission. Include a copy in your weekly submission. There is a feature in PowerPoint for doing this should you want to use it. JOB ORGANIZATION: ⚫ A job description is a broad, general, and written statement for a specific job, based on the findings of a job analysis. It generally includes duties, purpose, responsibilities, scope, and working conditions of a job along with the job's title, and the name or designation of the person to whom the employee reports. Job description usually forms the basis of job specification. • Work with your preceptor or supervisor to identify a position for which you will write a job description. Include a copy of the job description you write in your…arrow_forward
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,- MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing




