
Concept explainers
14-8 Answer true or false.
- The
functional group of an alcohol is the —OH (hydroxyl) group.
(h, The solubility of alcohols in water increases with increasing molecular weight.
(a)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: The functional group of an alcohol is the −OH (hydroxyl) group, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The functional group of an alcohol is the −OH (hydroxyl) group. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The functional group of any alcohol is the —OH group. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(b)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: The parent name of an alcohol is the name of the longest carbon chain that contains the −OH group, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The parent name of an alcohol is the name of the longest carbon chain that contains the −OH group.Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
According to IUPAC nomenclature, the parent name of an alcohol is the name of the longest.
carbon chain that contains the —OH group. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: A primary alcohol contains one −OH group, and a tertiary alcohol contains three-OH groups, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
A primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohol contains only one -OH groups but the connectivity of carbon atoms bearing −OH group is different. Thus, the statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Primary alcohol is alcohol in which the -OH group is linked to carbon that is connected to only one carbon atom. It has like -CH2 OH group in molecule. Secondary alcohol is alcohol in which the -OH group is linked to carbon that is connected to two other carbon atoms. Tertiary alcohol is alcohol in which the -OH group is linked to carbon that is connected to three other carbon atoms. Primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols have only one -OH group in their molecule but the connectivity of carbon atom bearing -OH group is different. Therefore, the given statement is false.
(d)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: In the IUPAC system, the presence of three −OH groups is shown by the ending −triol, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
In the IUPAC system, the presence of three −OH groups is shown by the ending −triol. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
In IUPAC nomenclature, the presence of three -OH groups is shown by the ending triol Therefore, the given statement is true.
(e)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: A glycol is a compound that contains two-OH groups. The simplest glycol is ethylene glycol,
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
A glycol is a compound that contains two-OH groups. The simplest glycol is ethylene glycol,
Explanation of Solution
Glycol is a compound that has two -OH groups attached to carbon atoms. Ethyl glycol is the simplest form of glycol. Its structural formula is:
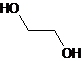
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(f)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: Because of the presence of an-OH group, all alcohols are polar compounds, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
Because of the presence of an -OH group, all alcohols are polar compounds. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Polar molecules have polar covalent bonds connected between the atoms. Methanol is an example of alcohol. Here, the O-C bond and O-H bond are polar covalent bonds. In methanol, there is a difference in electronegativity between the O-C bond (3.5-2.5 = 1.0) and O-H bond (3.5-2.1 = 1.4) Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself. Due to the presence of the O-H bond, all alcohols are polar molecules.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(g)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: The boiling point of alcohols increases with increasing molecular weight, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The boiling point of alcohols increases with increasing molecular weight. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The temperature at which the atmospheric pressure is equal to the vapor pressure is known as boiling point. As the molecular weight increases, more atoms are involved in the non-covalent interaction. Due to this tact, more energy (more temperature) is required to break this non-covalent interactions.Therefore, the given statement is true.
(h)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: The solubility of alcohols in water increases with increasing molecular weight, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are those organic compounds wherein a hydrogen atom of the aliphatic carbon molecule is substituted by a hydroxyl group. Hence an alcohol molecule has two parts, one comprising the alkyl group and the other carrying hydroxyl group.
The boiling point of alcohols is significantly higher than those of alkanes having similar molecular weights. The solubility of alcohol is inversely proportional to the size of the alkyl group. Alcohols reacts with active metals like sodium, potassium and many more to form the corresponding alkoxide.
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The solubility of alcohols in water decreases with increasing molecular weight. Thus, the statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Alcohols are more soluble in water than hydrocarbons. This is due to the presence of the O-H group in alcohol. The O-H group undergoes hydrogen bonding with a hydrogen atom in the water molecule.
As the molecular weight increases, simultaneously the hydrocarbon chain in alcohol will also increase. Now the alcohol stars behaving more like hydrocarbons. Therefore, the solubility decreases with the increase in molecular weight.
Therefore, the given statement is false.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Propose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forwardSelect the stronger base from each pair of compounds. (a) H₂CNH₂ or EtzN (b) CI or NH2 NH2 (c) .Q or EtzN (d) or (e) N or (f) H or Harrow_forward4. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for each of the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a. 2. 1. LDA 3. H3O+ HOarrow_forward
- b. H3C CH3 H3O+ ✓ H OHarrow_forward2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. CH3arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forward
- Identify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forwardInstructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardе. Д CH3 D*, D20arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning



