
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The following conversion should be explained.
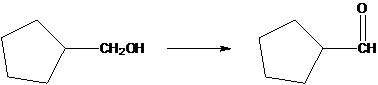
Concept Introduction:
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an
(b)
Interpretation:
The following conversion should be explained.

Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction is the procedure to transform the chemical substance in the new substance. During this procedure sometimes, acid is involved which is the substance which could either accept electron pairs or donate protons in the reactions.
A catalyst is the molecule which is used to speed up the chemical reaction, not being consumed within the procedure. Acids are used as catalysts are needed for an acid catalyzed hydration.
A dehydration reaction is aeration when any organic substance loses the water molecule to form an alkene.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- The following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 340.0 262.7 QUESTION: For both groups of data provide answers to the calculations attached in the imagearrow_forward7. Concentration and uncertainty in the estimate of concentration (class data) Class mean for sample (Regular) |[Cl-] (mmol/L) class mean Sn za/2 95% Confidence Interval (mmol/L) [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 95% Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardThe following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 223.4 148.7 353.7 278.2 334.6 268.7 305.6 234.4 340.0 262.7 304.3 283.2 244.7 143.6 QUESTION: For both groups of data calculate the answers attached in the image.arrow_forward
- Give reason(s) for six from the followings [using equations if possible] a. Addition of sodium carbonate to sulfanilic acid in the Methyl Orange preparation. b. What happened if the diazotization reaction gets warmed up by mistake. c. Addition of sodium nitrite in acidified solution in MO preparation through the diazotization d. Using sodium dithionite dihydrate in the second step for Luminol preparation. e. In nitroaniline preparation, addition of the acid mixture (nitric acid and sulfuric acid) to the product of step I. f. What is the main reason of the acylation step in nitroaniline preparation g. Heating under reflux. h. Fusion of an organic compound with sodium. HAND WRITTEN PLEASEarrow_forwardedict the major products of the following organic reaction: u A + ? CN Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te LMUNDARYarrow_forwardSketch the intermediates for A,B,C & D.arrow_forward
- Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? O ? A . If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. . If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ㅇ 80 F5 F6 A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cente FIGarrow_forwardIn methyl orange preparation, if the reaction started with 0.5 mole of sulfanilic acid to form the diazonium salt of this compound and then it converted to methyl orange [0.2 mole]. If the efficiency of the second step was 50%, Calculate: A. Equation(s) of Methyl Orange synthesis: Diazotization and coupling reactions. B. How much diazonium salt was formed in this reaction? C. The efficiency percentage of the diazotization reaction D. Efficiency percentage of the whole reaction.arrow_forwardHand written equations pleasearrow_forward
- Hand written equations pleasearrow_forward> each pair of substrates below, choose the one that will react faster in a substitution reaction, assuming that: 1. the rate of substitution doesn't depend on nucleophile concentration and 2. the products are a roughly 50/50 mixture of enantiomers. Substrate A Substrate B Faster Rate X Ś CI (Choose one) (Choose one) CI Br Explanation Check Br (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Farrow_forwardNMR spectrum of ethyl acetate has signals whose chemical shifts are indicated below. Which hydrogen or set of hydrogens corresponds to the signal at 4.1 ppm? Select the single best answer. The H O HỌC—C—0—CH, CH, 2 A ethyl acetate H NMR: 1.3 ppm, 2.0 ppm, 4.1 ppm Check OA B OC ch B C Save For Later Submit Ass © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center |arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


